End of topic questions Note: The marks awarded for these questions indicate the level of detail required in the answers. In the examination, the number of marks awarded to questions like these may be different.
1. a) How was crude oil (petroleum) formed?
(2 marks)
b) Why is crude oil called a ‘non-renewable’ fuel?
(1 mark)
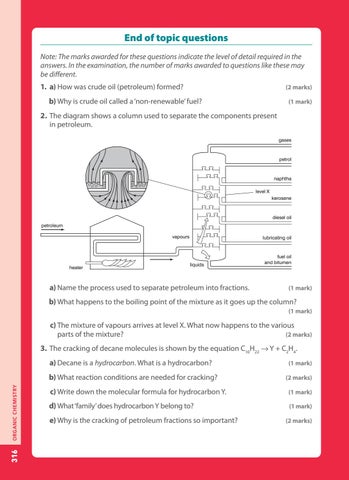
2. The diagram shows a column used to separate the components present in petroleum. gases
petrol
naphtha level X kerosene
diesel oil petroleum vapours
heater
lubricating oil
liquids
a) Name the process used to separate petroleum into fractions.
fuel oil and bitumen
(1 mark)
b) What happens to the boiling point of the mixture as it goes up the column? (1 mark) c) The mixture of vapours arrives at level X. What now happens to the various (2 marks) parts of the mixture? 3. The cracking of decane molecules is shown by the equation C10H22 → Y + C2H4. a) Decane is a hydrocarbon. What is a hydrocarbon?
(2 marks)
c) Write down the molecular formula for hydrocarbon Y.
(1 mark)
d) What ‘family’ does hydrocarbon Y belong to?
(1 mark)
e) Why is the cracking of petroleum fractions so important?
(2 marks)
316
Organic chemistry
b) What reaction conditions are needed for cracking?
(1 mark)
92654_P306_364.indd 316
19/06/14 7:10 PM