2.2 How detailed should the needs analysis be? The answer to this question has to be ‘How long is a piece of string?’ However, for a teacher new to ESP the advice would be: as detailed as possible (time and resources permitting). The more experience you have, the better you’ll be able to make decisions about the length and the amount of detail a needs analysis requires. Certainly there are many good models or templates of needs analysis in ESP literature, and novices to the profession are advised to refer to, for example (see also opposite page): 4 From profiles to course activities: mechanical engineers 89
•
Dudley-Evans & St John. Developments in English for Specific Purposes, Cambridge, Cambridge University Press, 1998, pp. 140–144
•
Huhta, Vogt, Johnson, Tulkki, David R. Hall (Editor). Needs Analysis for Language • express views • ask rhetorical questions Course Design: A holistic approach to ESP, Cambridge: Cambridge University Press 2013
•
Hutchinson & Waters. English on forwhat Specifi c Purposes, Cambridge, Cambridge • comment others have said and make additional points. University Press, 1987, p. 59 The distribution of the following type of needs analysis questionnaire will already be
•
familiar toJack. experienced ESP teachers. However, the in the profiNew le givesYork, the teachRichards, Curriculum development in information language teaching, Cambridge er a benchmark against which the information collected from the learners can be assessed. University Press, 2001 – Appendix 3 Needs analysis questionnaire for non-English For example, if the learner group consists of pre-service professionals, it may be interesting background students to compare which areas they expect to be confident in against what the profile shows profes-
• interrupt a speaker
• ask for more detailed information
sionals already working in the industry regard as the most demanding situations (Part E). And if (as often happens in our experience) the results of the questionnaire show that the majority of the learner group want further development of their spoken English, then the profile again provides guidance for the most relevant contexts of spoken interaction. These contexts will be exemplified in simulation activities on the course.
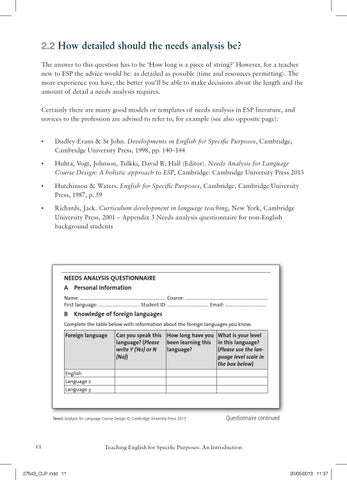
NEEDS ANALYSIS QUESTIONNAIRE A
Personal information
Name: ………………………………………………………………… Course: ……………………………………………………………… First language: ……………………………… Student ID: ……………………………… Email: ………………………………
B
Knowledge of foreign languages
Complete the table below with information about the foreign languages you know.
Foreign language
Can you speak this How long have you language? (Please been learning this write Y (Yes) or N language? (No))
What is your level in this language? (Please use the language level scale in the box below)
English
Language 2 Language 3
Language level scale Pre-intermediate (A2): I know some vocabulary words Questionnaire Needs Analysis for Language Course Design © Cambridge University Pressand 2013I can understand some
continued
and phrases in conversation and lectures. I do not use this language much, because it takes time.
11
27543_CUP.indd 11
Intermediate (B1): I understand some texts on familiar topics and parts of clear conversations and lectures; I can deal with many ordinary daily situations with help.
Teaching English for Specific Purposes: An Introduction
Upper intermediate (B2): I understand texts, conversations and lectures; given time I can manage daily situations without help, and can be an active participant in interaction for limited periods of time.
20/05/2013 11:37