2 minute read
The basic structure of skin - (1 of 2)
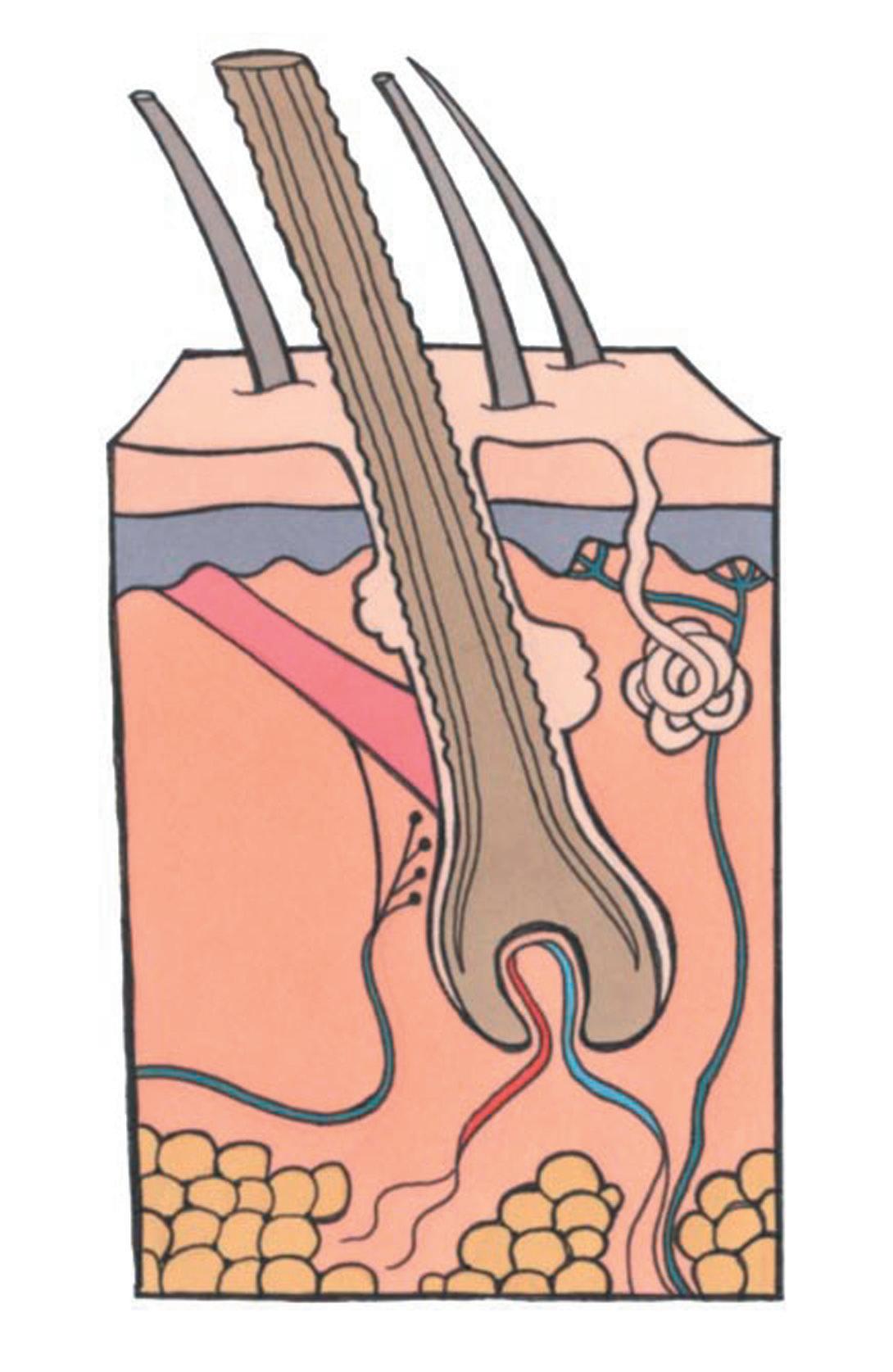
There are two main layers in the skin:
• the epidermis – this is the surface layer, the one that we can see and feel
• the dermis – this is the deep layer that has a blood and nerve supply and where the hair follicle lies.
The area beneath the dermis is called the subcutaneous layer and this is where the skin stores fat that gives us smooth curves rather than sharp angles.
As well as having a good blood and nerve supply, the skin has various appendages and most of these, although they lie in the dermis, are down growths of the epidermis. The main appendages are:
• the follicles – hairs grows through these
• the dermal papilla - all cell growth and cell division of hair occurs here
• the sebaceous glands – these secrete oil called sebum that protects us against bacteria because it is slightly acidic, it also lubricates and waterproofs the skin
• the sudoriferous (sweat) glands – these excrete waste in the form of sweat and when sweat evaporates this cools the body
• the arrector pili muscles – these are attached to the hair follicles and, when we are cold they contract, this pulls the hair upright, makes goose pimples and traps warm air around the body to help keep us warm
The skin is one of the biggest organs of the body and has four main functions:
• it protects us from strong sunlight and bacteria
• there are nerves in the skin that give us sensation – the sense of touch
• glands in the skin get rid of some waste and others make oil to waterproof us
• it helps to control body temperature by the evaporation of sweat to cool us and by trapping air around us to keep us warm
The natural pigment of the skin and hair is called melanin and is produced by cells called melanocytes.
The basic structure of skin - (2 of 2)
The characteristics of different hair types and textures
There are three hair types:
• African Caribbean
• Asian
• Caucasian (European)
African Caribbean hair is usually very tightly curled and often very dark in colour. It is easily damaged and all treatments, especially chemical treatments, must be done with care.
The shape of the hair, when looked at in cross-section, is almost kidney shaped.
The colour is usually dark to medium brown.
Asian hair tends to be straight and is sometimes quite lank. When a crosssection is examined the shape of the hair is round. This type of hair varies in colour from very dark to medium brown. It is often very thick and strong. If cut very short it sometimes stands straight out from the head.
Caucasian hair can be straight, wavy or curly. It varies in colour from very dark brown to very light blonde. It is oval in shape when inspected under a microscope.
Hair texture:
Hair can be described as fine, medium or coarse. This means that each hair is fine, medium or thick – the distance around the hair, its circumference, defines its texture.
If a hair has a large circumference measurement it is considered to be coarse. If it has a small circumference measurement it is fine textured.
Density:
The density of hair is how many hairs are on the one head, so a fine textured head may contain many more hairs than a coarse textured head.

