expert zone
Clinical topic
30
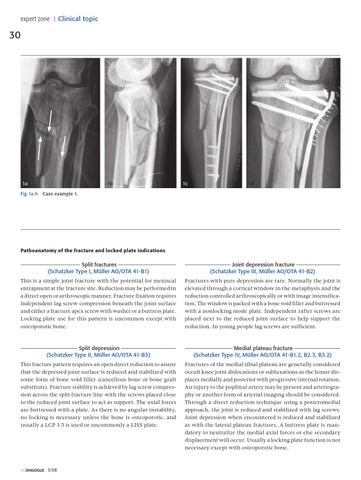
1a Fig 1a-h
1b
1c
1d
Case example 1.
3 Pathoanatomy of the fracture and locked plate indications
Split fractures (Schatzker Type I, M端ller AO/OTA 41-B1)
Joint depression fracture (Schatzker Type III, M端ller AO/OTA 41-B2)
This is a simple joint fracture with the potential for meniscal entrapment at the fracture site. Reduction may be performed in a direct open or arthroscopic manner. Fracture fixation requires independent lag screw compression beneath the joint surface and either a fracture apex screw with washer or a buttress plate. Locking plate use for this pattern is uncommon except with osteoporotic bone.
Fractures with pure depression are rare. Normally the joint is elevated through a cortical window in the metaphysis and the reduction controlled arthroscopically or with image intensification. The window is packed with a bone void filler and buttressed with a nonlocking mode plate. Independent rafter screws are placed next to the reduced joint surface to help support the reduction. In young people lag screws are sufficient.
Split depression (Schatzker Type II, M端ller AO/OTA 41-B3)
Medial plateau fracture (Schatzker Type IV, M端ller AO/OTA 41-B1.2, B2.3, B3.2)
This fracture pattern requires an open direct reduction to assure that the depressed joint surface is reduced and stabilized with some form of bone void filler (cancellous bone or bone graft substitute). Fracture stability is achieved by lag screw compression across the split fracture line with the screws placed close to the reduced joint surface to act as support. The axial forces are buttressed with a plate. As there is no angular instability, no locking is necessary unless the bone is osteoporotic, and usually a LCP 3.5 is used or uncommonly a LISS plate.
Fractures of the medial tibial plateau are generally considered occult knee joint dislocations or subluxations as the femur displaces medially and posterior with progressive internal rotation. An injury to the popliteal artery may be present and arteriography or another form of arterial imaging should be considered. Through a direct reduction technique using a posteromedial approach, the joint is reduced and stabilized with lag screws. Joint depression when encountered is reduced and stabilized as with the lateral plateau fractures. A buttress plate is mandatory to neutralize the medial axial forces or else secondary displacement will occur. Usually a locking plate function is not necessary except with osteoporotic bone.
3 | 08