2 minute read
Schools in High-density Cities
from WANG YUJING 23183282
by 1048139302
l:Territorial
Advertisement
Population density is an important aspect of the population problem. With urbanization, people enter the city, forming a high-density population gathering. However, in a high-density city, there is a lot of pressure on environmental capacity.
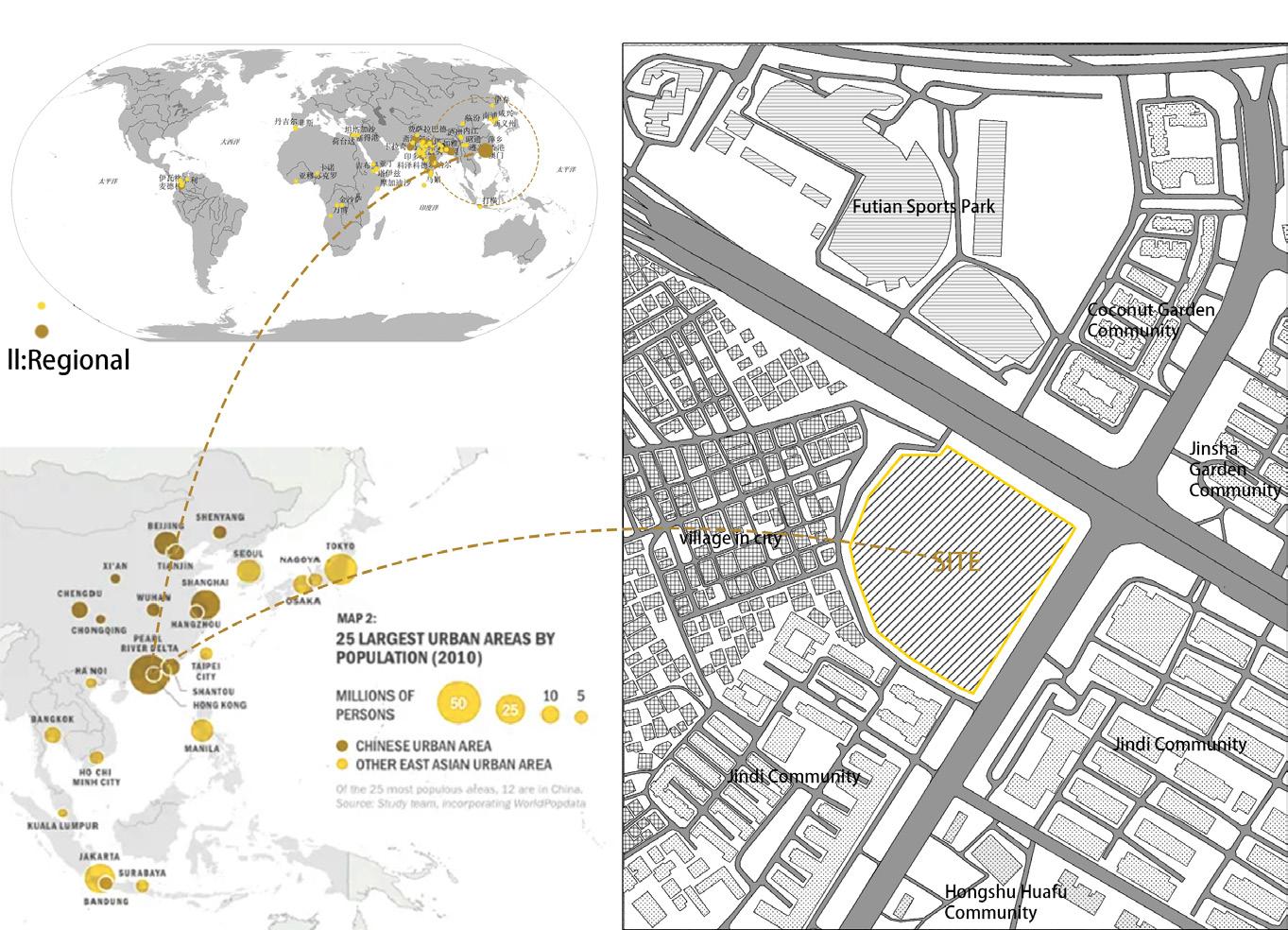
lll:Local
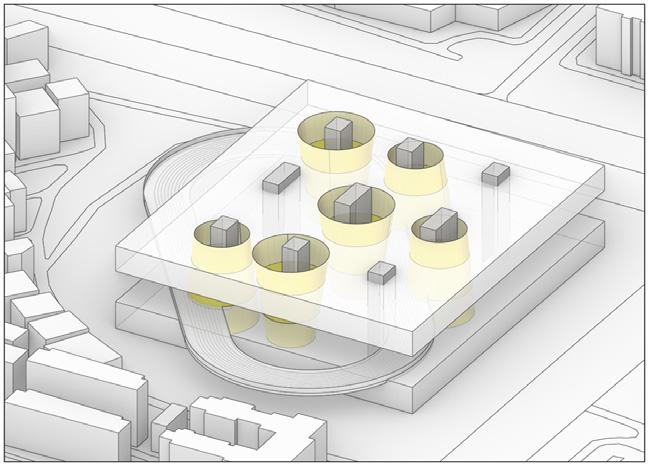
The plot is surrounded by densely populated residential areas, which need supporting primary schools of a certain scale. The west side is a crowded village in the city. The northeast side is close to the urban trunk road and should not be used as the main entrance of the campus, so the main entrance of the site is set up on the southeast side.
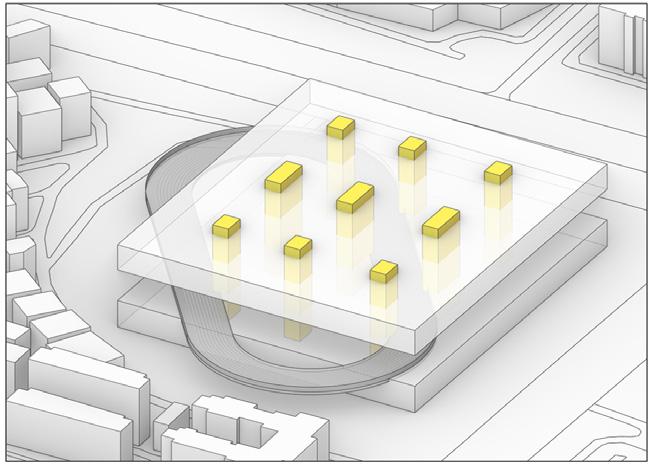
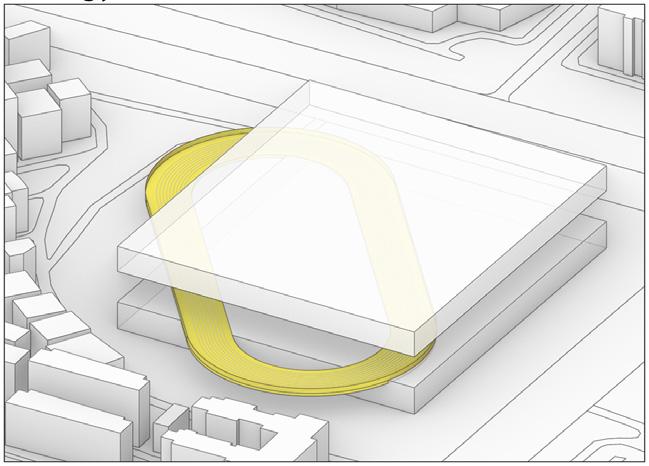
Concept
Population density (person/km2)
15000-25000
25001-44400
ll:Regional
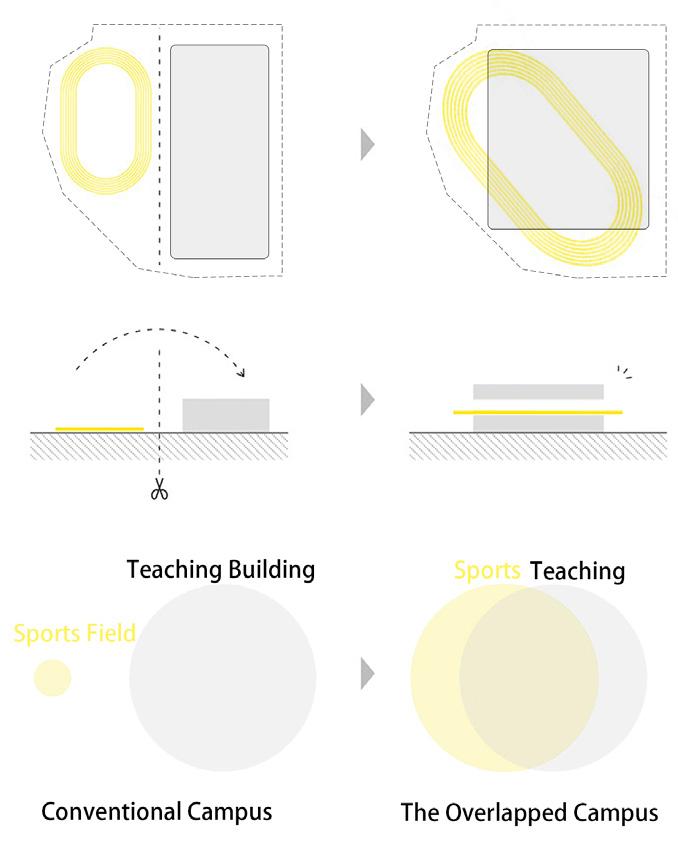
High density urban construction has always been a common feature of Asian cities. Increasing urban density has squeezed the quality of urban youth space.
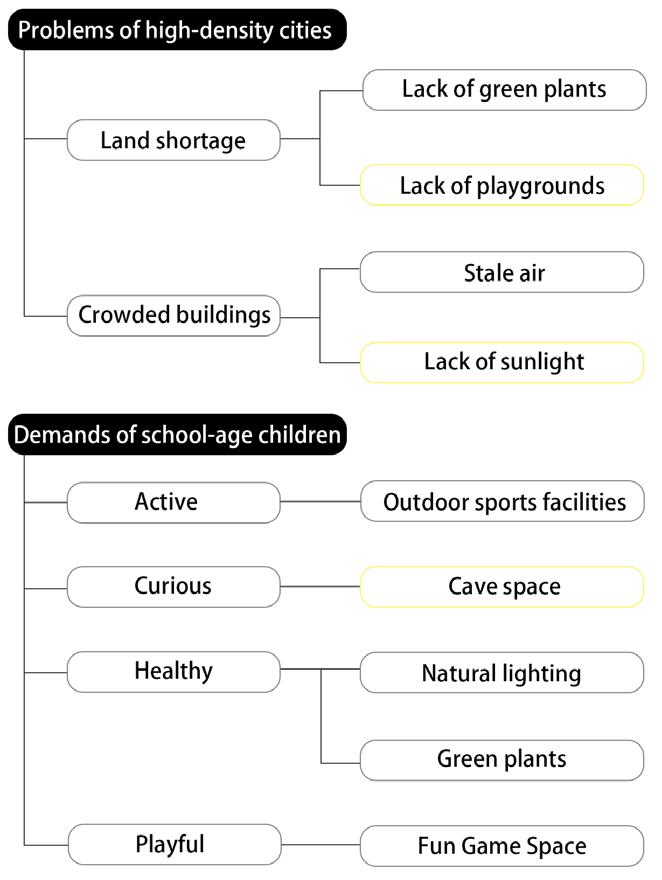
Strategy

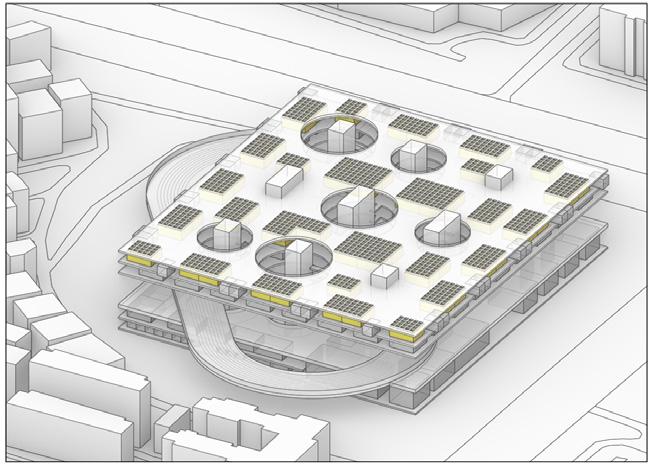
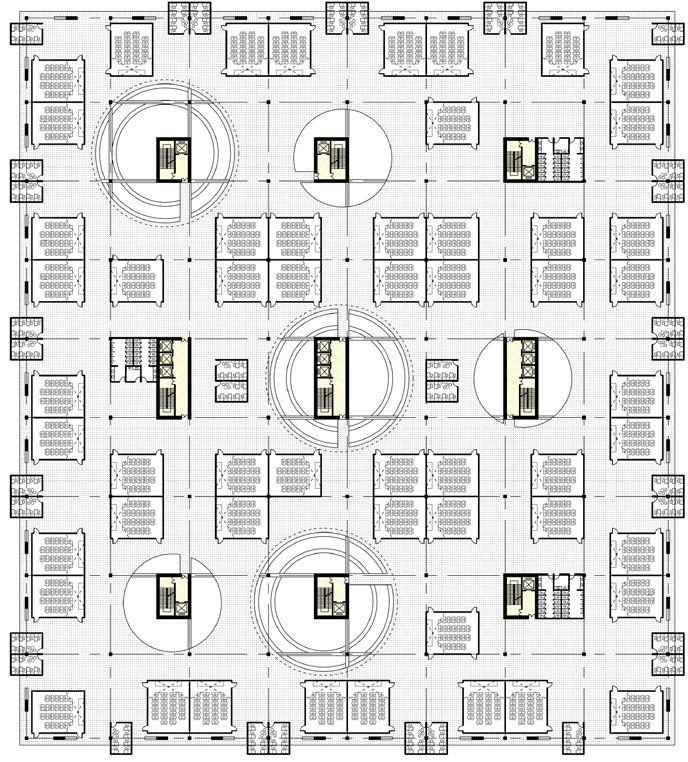
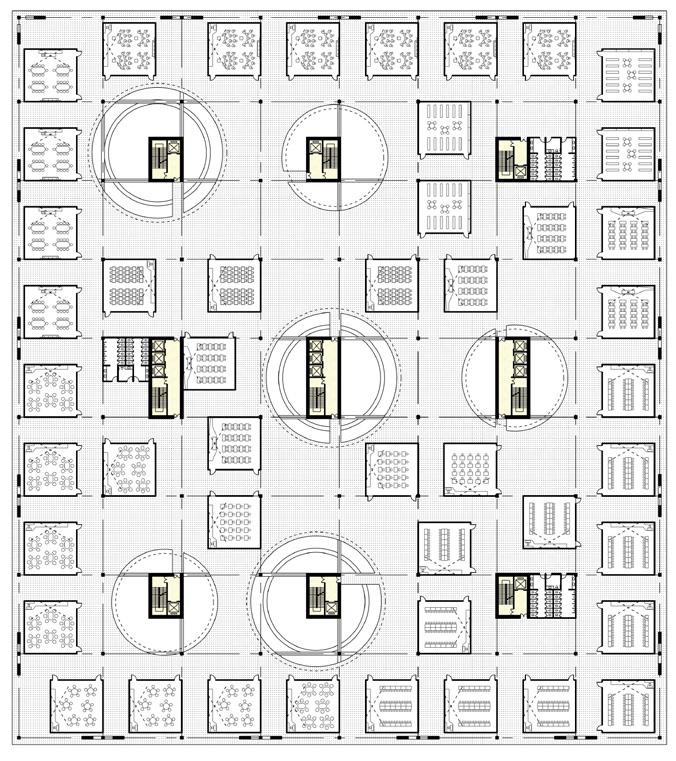
1.Mathematics Laboratory 2.Physics laboratory 3.Preparation Room (Science and Chemistry) 4.Instrument Room (Science and Chemistry) 5.Chemistry laboratory 6.Pharmacy Room (Chemical and Biological) 7.biology laboratory
8.culture room 9.Laboratory Room (Science and Chemistry) 10.Toilet
1.art classroom 2.art equipment room 3.history and geography classroom
4.Labor technology (science) classroom 5.Computer network classroom
6.Information Technology Laboratory 7.Special multimedia classroom
8.Intelligent Teaching classroom 9.School-based curriculum laboratory 10.Classroom teaching digital recording and broadcasting room 11.STEAM laboratory 12.Toilet
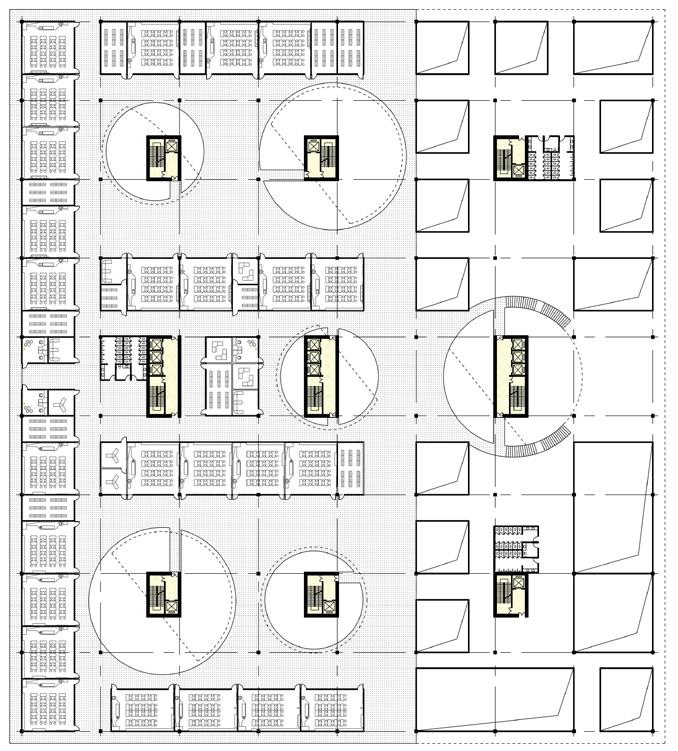
1.400m Circular track (including 100m straight)
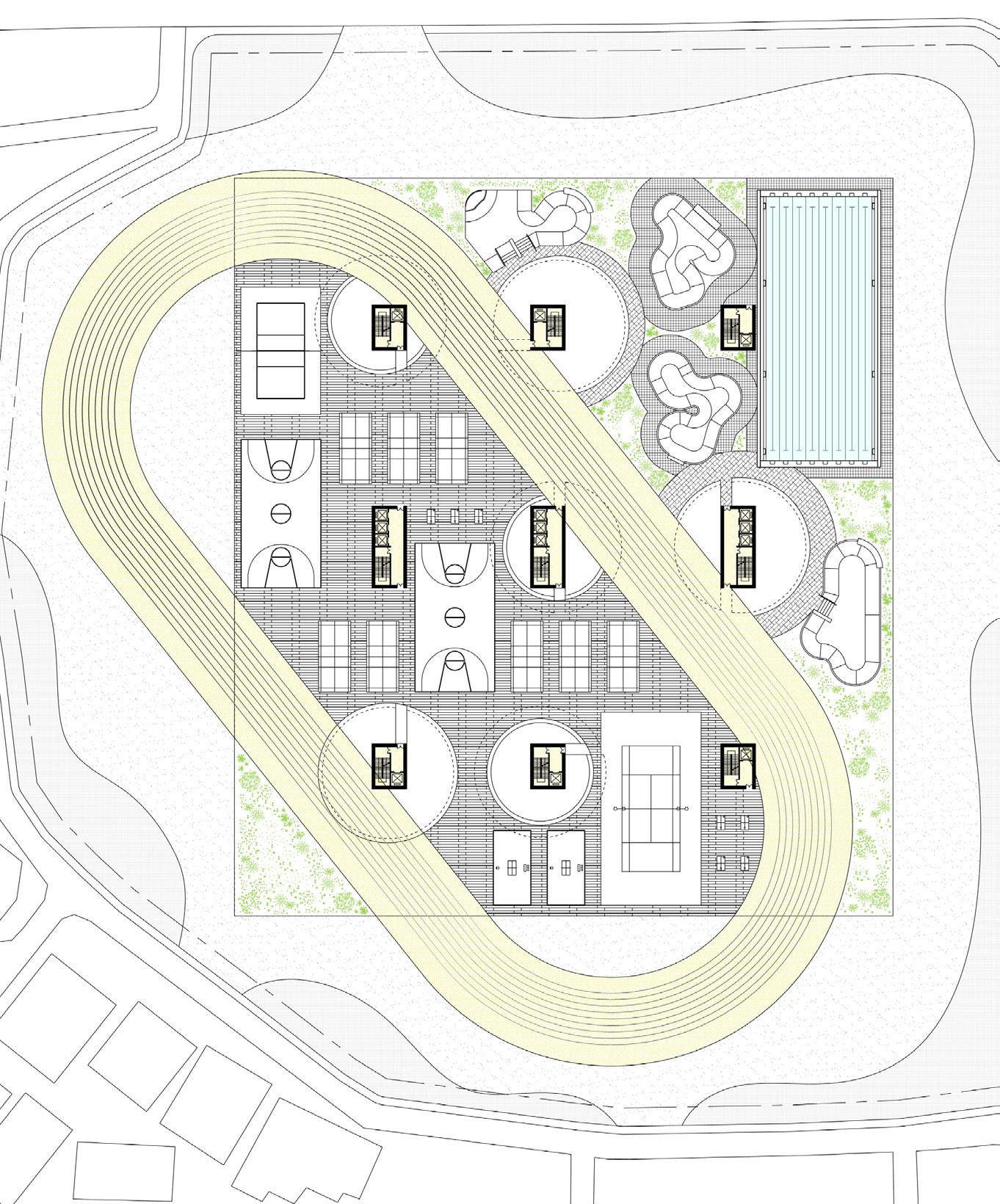
2.Standard tennis court
3.Standard basketball court
4.Standard volleyball court 5.Standard badminton court 6.Ping pong table 7.50m swimming pool 8.Skateboarding bowl pool 9.Garden green space
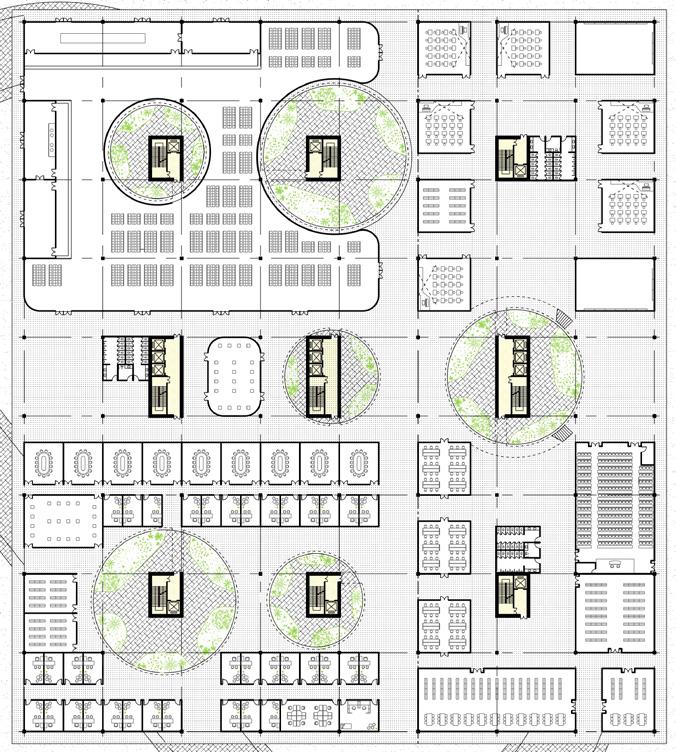
1.Faculty and Student dining halls 2.larder 3.refrigeration storage 4. kitchen 5.Office of Administration 6.Accounting office 7.Conference reception room
8.Broadcasting Societies Office 9.Moral Exhibition Room 10.Mental health counselling centres 15.Campus public address system control room 20.The archives 21.General warehouse 24.Communicate to the duty room 25.Student audio-visual Reading Room 26.Teacher's reading room 27.Student reading room 28.library 29.Multimedia Science Reporting Office 30.dance classroom 31.Music classroom 32.Music equipment room 33.Toilet
1.general classrooms 2.teacher's offices 3.Toilet
Daylighting test of Rooms from each floor
The dynamic lighting indicators, namely, the proportion of daylight valves (sDA) and annual light exposure (ASE), are used for daylighting evaluation.Spatial Daylight Autonomy (sDA) is the annual adequacy of daylight levels in space. The percentage of the analysis area (e.g. work plane) where the sDA test reaches the minimum illumination level (e.g. 300 lux) during the specified working hours of each year (e.g. 50% of the working hours of a year).Annual Sunlight Exposure (ASE) describes the possibility of visual discomfort in space every year. ASE is the percentage of the analysis work plane area that exceeds the specified illumination level and exceeds the specified number of hours.The model operation platform is a battery pack used in Grasshopper. The analysis platform is set at 0.7m above the ground. The sDA measurement parameters are set as 500lux, 1000lux and 1500lux.
Floor:fifth floor
Test room:general classroom
Illumination: Adequate Dazzle:No glare
Section A-A
Floor:fourth floor
Test room:Labor technology (science) classroom
Illumination: Adequate Dazzle:No glare
Floor:ground floor (Full height of two floors)
Test room:Multimedia Science Reporting Office
Illumination: Adequate Dazzle:A little glare
Floor:ground floor
Test room:office of administration
Illumination: slightly low Dazzle:No glare


