5 minute read
1 Performance Analysis
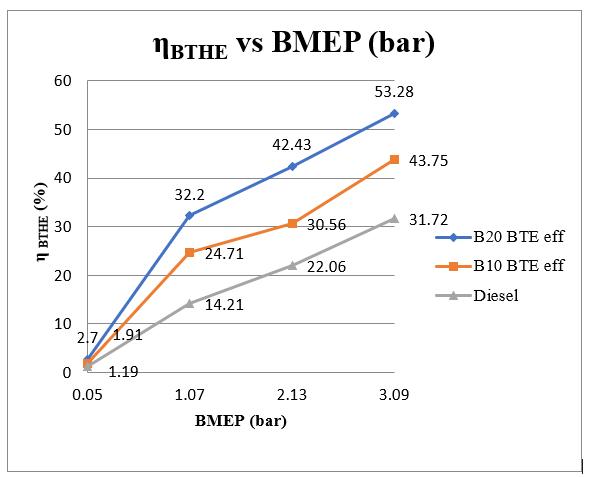
Figure 4.1: BTE vs BMEP
The Brake Mean Effective Pressure is considered as independent variable and the dependent variable of Brake Thermal Efficiency in percentage is constructed.
Advertisement
4.1 Indicated Thermal Efficiency
The variation of indicated thermal efficiency with brake mean pressure for the biodiesel blends and diesel is shown in figure 5.3.Indicated thermal efficiency is slightly lower at part, but at full pressure, they are comparable with the diesel.
Table 4.2: BMEP vs ITE


Figure 4.2: Indicated Thermal Efficiency vs BMEP
4.3 Mechanical Efficiency
Table 4.3: Mechanical Efficiency vs BMEP
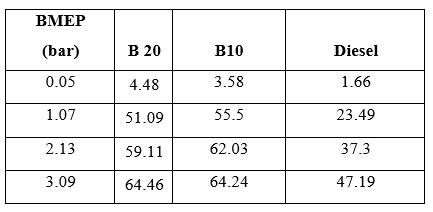
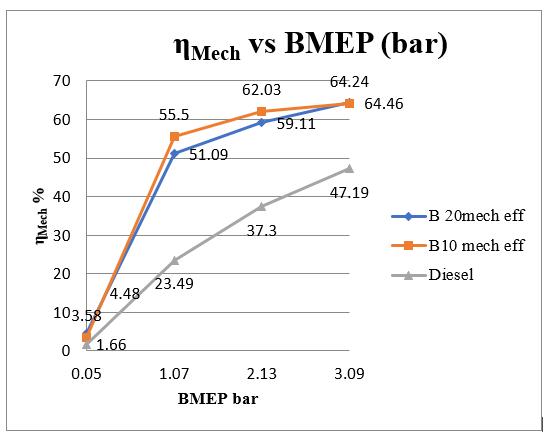
Figure 4.3: Mechanical Efficiency vs BMEP
4.4 Volumetric Efficiency
The variation of volumetric efficiency with brake mean pressure for the Neem biodiesel blends and diesel is shown in figure 5.4. The volumetric efficiency is slightly higher at part, but at full pressure, they are comparable with the diesel.
Table 4.4: Volumetric Efficiency vs BMEP
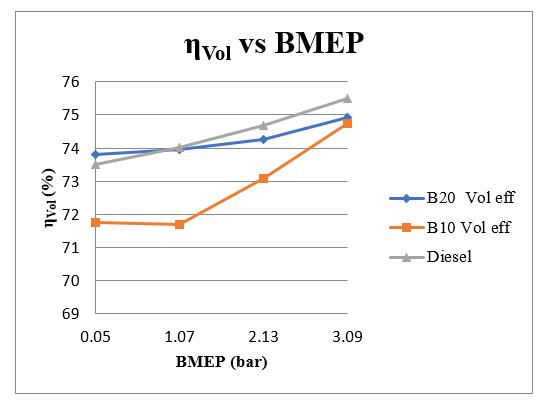
Figure 4.4: Volumetric Efficiency vs BMEP
4.5 Specific Fuel Consumption
The variation of specific fuel consumption with brake mean pressure for the Neem biodiesel blends and diesel is shown in Figure 5.5 The specific fuel consumption is slightly higher at part, but at full pressure, they are comparable with the diesel.
Table 4.5: SFC vs BMEP

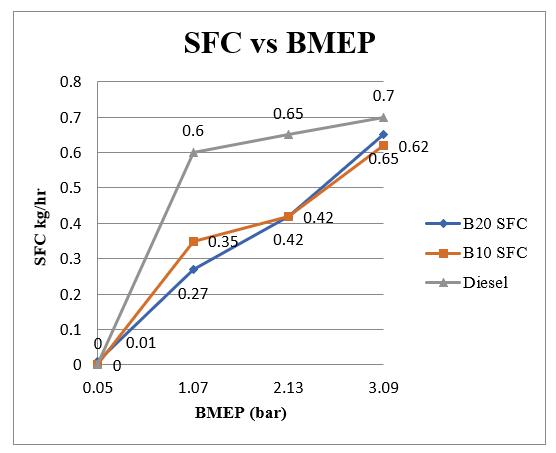
Figure 4.5: SFC vs BMEP.
4.6 Exhaust Gas Temperature
The variation of exhaust gas temperature with brake mean pressure for the Neem biodiesel blends with diesel is shown in
figure 4.6. The exhaust gas temperature is slightly higher at part, but at full pressure, they are comparable with the diesel.
Table 4.6: Exhaust Gas Temperature vs BMEP
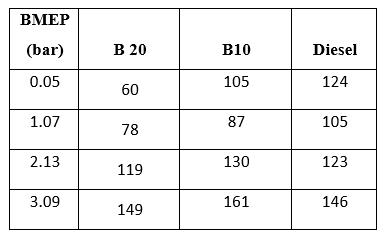

Figure 4.6: Exhaust Gas Temperature vs BMEP.
5. CONCLUSIONS
A single cylinder water cooled compression ignition engine was operated successfully using Neem oil biodiesel, methanol, with and without nickel oxide and diesel blends.
Neem oil biodiesel, methanol, with and without nickel oxide and diesel blends results in a slight increase of 40 % brake thermal efficiency, as compared to diesel.
Neem oil biodiesel, methanol, with and without nickel oxide and diesel blends results in a slight decrease of 13 % indicated thermal efficiency, as compared to diesel.
Neem oil biodiesel, methanol, with and without nickel oxide and diesel blends results in a slight increase of 17 % mechanical efficiency as compared to the diesel.
Neem oil biodiesel, methanol, with and without nickel oxide and diesel blends results in a slight decrease of 0.1 % specific fuel consumption as compared to diesel.
Neem oil biodiesel, methanol, with and without nickel oxide and diesel blends B10 results in a slight increase of
15OC exhaust gas temperature, as compared to diesel.
Combustion parameters for Neem oil, methanol, with and without nickel oxide and diesel blends such as ignition delay and peak pressure were nearly close to those observed for diesel oil combustion at the same load, speed and nozzle diameter.
Neem oil biodiesel, methanol, with and without nickel oxide and diesel blends results in a slight decrease of 2 %
CO emission, as compared to the diesel. Neem oil biodiesel, methanol, with and without nickel oxide and diesel blends results in a slight decrease of 2.16 % NOx emission, as compared to diesel.
Neem oil biodiesel, methanol, with and without nickel oxide and diesel blends results in a slight increase of 0.12 % HC emission as compared to diesel.
Neem oil biodiesel, methanol, with and without nickel oxide and diesel blends results in a slight decrease of 0.4 %
CO2 emission, as compared to diesel.
Neem oil biodiesel, methanol, with and without nickel oxide and diesel blends results in an increase with 3.56 %
O2 emission, as compared to diesel.
Filter smoke number for the Neem oil methanol, with and without nickel oxide and diesel blends was lower than the diesel.
On the whole, it is concluded that the Neem oil methanol, with and without nickel oxide and diesel blends and diesel blend will be good alternative fuel for the diesel engine.
Efficiency and Emission of to B20 blends is equal and lesser when compared to Diesel.
Performance and emission test on compression ignition engine using Neem oil methanol, with and without nickel oxide and diesel blends is done.
The mechanical efficiency of the butane and diesel blend is more.
REFERENCES
1. Ajay Kumar Kaviti, Jayashri N Nair, “Analysis of performance and emission on compression ignition engine fuelled with blends of Neem biodiesel”, Egyptian journal, Sep 2016. 2. D. Srikanth, M. V. S. Murali Krishna, P.Ushasri& P. V. Krishna Murthy, “Performance, Exhaust Emissions and Combustion
Characteristics of Cotton Seed Oil Based Biodieselin Ceramic Coated Diesel Engine”, International Journal of
MechanicalEngineering (IJME), Vol. 2, Issue 5, pp. 67-82 3. Ammar Asmaa M and Mansour, “Performance Evaluation of Environmentally Friendly Insulating Oil under Accelerated
Aging Tests”, IEEE, 2016. 4. P. Senthilkumar& G. Sankaranarayanan, “Production of Waste Polyethylene Bags in to Oil and Studies Performance,
Emission and Combustion Characteristics in Di Diesel Engine”, BEST: International Journal of Humanities, Arts, Medicine and Sciences (BEST: IJHAMS), Vol. 3, Issue 10, pp. 149-158 5. Bhojawani.V and Madiwale.S, “An Overview on Production, Properties, Performance and Emission Analysis of blends of
Biodiesel”, Science direct 2016. 6. M.V.S. Murali Krishna & K. Vamsi Krishna, “Studies on Exhaust Emissions of Di Diesel Engine with Low Grade LHR
Combustion Chamber Fuelled with Linseed Biodiesel “, International Journal of Mechanical Engineering (IJME), Vol. 3,
Issue 6, pp. 63-72 7. D. Hymavathi, G. Prabhakar & B. Sarath Babu, “Biodiesel Production from Vegetable Oils: An Optimization Process”,
International Journal of Chemical & Petrochemical Technology (IJCPT), Vol. 4, Issue 2, pp. 19-28 8. Bijan Kumar Mandal, "Performance and Emission Test on I.C. Engine using Bio-Diesel Extracted from Jatropha Oil",ISSN, 2017.
9. Chao Mu-Rong, “Performance and Emission Characteristics of Cotton Seed Oil Methyl Ester Using VCR Diesel Engine”,
ISSN No: 0974-2115, 2015. 10. Gowari, M.Kannan, A.MurugesanG.Vijay “Investigation of Neem Ethyl Ester for Electrification”, IEEE, 2011.

