
9 minute read
5 Things a Hug Can Cure
Think that a hug is just a nice way to greet someone you haven’t seen in a long time? Think again.
There’s a reason why hugs feel so good, there’s healing power in them. Seriously!
Advertisement
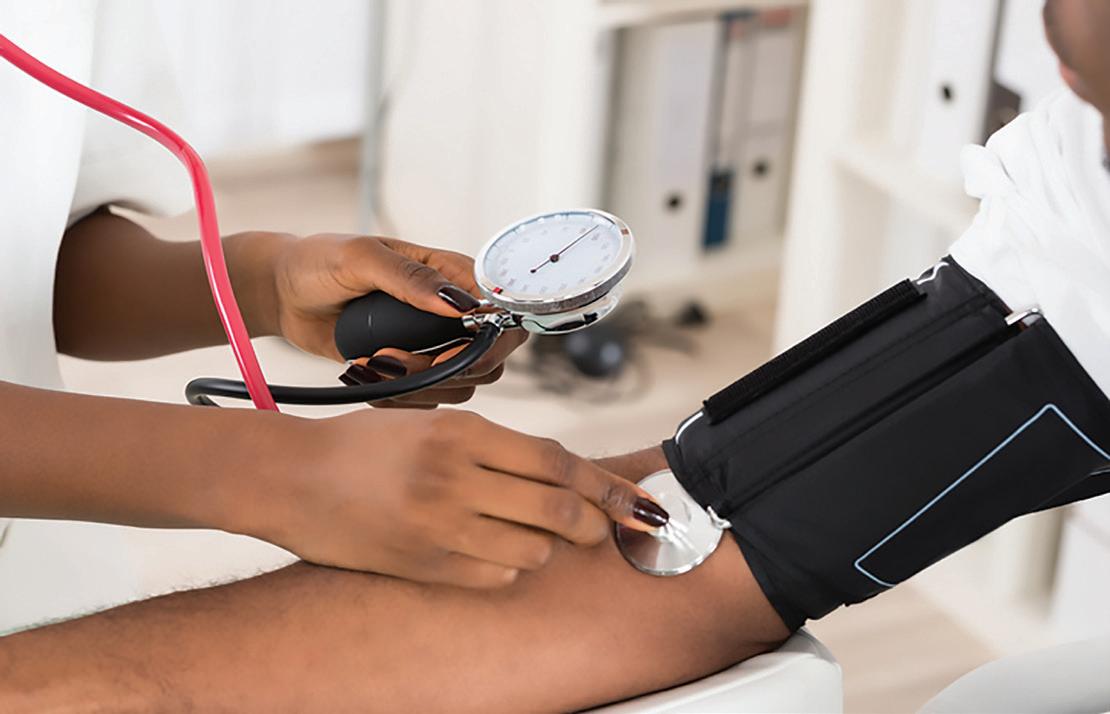
Studies show that a 20-second hug, along with 10 minutes of hand-holding, also reduces the harmful physical effects of stress, including its impact on your blood pressure and heart rate. This makes sense, since hugging is known to lower levels of stress hormones like cortisol.
Yet, many people are touchdeprived. One study found that one-third of people receive no hugs on a daily basis while 75 percent said they wanted more hugs.
Check out the five reasons why you should stop and give someone a hug today:
5. Hugs Lower Blood Pressure
The hormones that are released in the body after a hug aren’t just good for happy feelings — they can also help your physical health. When someone touches you, the sensation on your skin activates pressure receptors called Pacinian corpuscles, which then send signals to the vagus nerve, an area of the brain that is responsible for (among many things) lowering blood pressure, NPR reported.
4. Hugs Heal Your Heart (Literally)
Embracing someone may warm your heart, but according to one study a hug can be
4 Essential Heart Tests For A Longer Life
good medicine for it too: In an experiment at the University of North Carolina, Chapel Hill , participants who didn’t have any contact with their partners developed a quickened heart rate of 10 beats per minute compared to the five beats per minute among those who got to hug their partners during the experiment.
3. Hugs Get More Powerful With Age
Studies have shown that loneliness, particularly with age,
Cost: $19
Duration: 5 minutes
Why It’s Heart Smart: Sizing up your particles gives a clearer picture of heart risk than the conventional test: Having a lot of large particles cuts risk, while small ones raise it. The more Lp(a) you have, the worse it is, too–it makes LDL particles extra sticky, so they cling to the lining of blood vessels, causing plaque and clots.
Get It If: You have a family history of heart disease.
What Happens To Your Body When You Eat Too Much Seafood...continued

body at unnecessary risk.
– issues with hand-eye coordination can also increase stress and have adverse health effects. Because of that, researchers at Ohio State University concluded that hugging becomes increasingly important as you age since the need for physical touch grows. It’s your body’s way of coping with
2. Hugs Reduce Stress
When we embrace, we immediately reduce the amount of the stress hormone cortisol produced in our bodies. Hugs also make our bodies release tension and send calming messages to the brain.
1. Hugs Strengthen Your Immune System
When you hug someone, you exert pressure on the sternum (breastbone) and an emotional charge is created. This activated the solar plexus chakras which in turn stimulates the thymus gland. This gland regulates the production of WBCs (white blood cells) in the body, thereby, keeping you healthy.
Mercury may affect the nervous system, leading to neurological symptoms such as:
– nervousness or anxiety
– irritability or mood changes
– numbness
– memory problems
– depression – physical tremors
As the levels of mercury in the body rise, more symptoms will appear. These symptoms may vary depending on a person’s age and exposure levels. Adults with mercury poisoning may experience symptoms such as:
– muscle weakness
– metallic taste in the mouth
– nausea and vomiting
– lack of motor skills or feeling uncoordinated
– inability to feel in the hands, face, or other areas
– changes in vision, hearing, or speech
– difficulty breathing
– difficulty walking or standing straight
How Seafood Affects Children
Too Mercury can also affect a child’s… early development.
Children with mercury poisoning may show symptoms such as:
– being physically unaware of their surroundings
Mercury poisoning tends to develop slowly over time if a person comes into frequent contact with mercury. However, in some cases, mercury poisoning comes on quickly and is associated with a specific incident.
Anyone who experiences a sudden onset of mercury poisoning symptoms should call a doctor or poison control.
Exposure to high levels of mercury may also put a person at risk for long-term complications, including neurological damage: side effects of eating too much seafood
– Mercury poisoning may cause slow reflexes, damaged motor skills, and intelligence disorders.
A study in the Journal of Preventive Medicine and Public Health noted that many incidents of mercury poisoning have led to long-term nerve damage, which can cause:
– intelligence disorders and low IQ
– slow reflexes
For decades, doctors had nothing more sophisticated than a stress test to identify potential heart problems. Not anymore. Cardiologists now use advanced imaging and blood tests that give a much more accurate assessment of heart attack risk. These tests are the best ways to tell who is in danger, because they can catch cardiovascular disease 20 to 30 years before it gets severe enough to cause a heart attack or stroke. They are available at most major medical centers and hospitals. If your doctor doesn’t request them for you, demand the ones that are recommended for your age group and risk category.
1) Carotid Intimal Medial Thickness Test
How It Works: This “ultrasound of the neck” takes a picture of the left and right carotid arteries, which supply blood to your head and brain. After putting a gel on your neck, a technician glides an ultrasound transducer over your carotids to measure the thickness of the arteries’ lining.
Duration: 15 minutes
Why It’s Heart Smart: Studies show a link between the abnormal thickness of the carotid lining and coronary artery disease. This test can detect even the earliest stages before blood flow is blocked. Because it’s not an x-ray, it’s also helpful for women who are or may be pregnant.
What the Results Mean: You’ll get two numbers: the thickness of your carotid lining (normal is less than 1.06 mm) and your “arterial age,” an estimate of how that thickness compares to others in your age group. If your arteries are more than 8 years “older” than you are, your doctor can tailor a treatment to reduce your risk.
2) High-Sensitivity C-Reactive Protein Test
How It Works: A blood test measures CRP, a protein in your blood that’s a strong indicator of inflammation throughout your body.
Cost: $8
Duration: 5 minutes
Why It’s Heart Smart: Cholesterol plaque injures blood vessels, triggering inflammation and raising CRP levels in your blood. That’s dangerous because people with high levels of CRP may be up to 4 times more likely to suffer a heart attack or stroke. A high CRP is most dangerous if you also have another risk factor: a waist circumference of more than 35 inches, indicating the presence of belly fat.
What the Results Mean: If your score is under 1.0 mg per liter, your risk of developing heart disease is low. A score between 1.0 and 3.0 mg/l equals average risk. Above 3.0 mg/l, you’re at high risk. It’s possible to have high CRP without heart disease, though, because infections and injuries can also trigger a spike in levels.
3) Advanced Lipid Profile and Lipoprotein(a) Test
How It Works: Unlike the traditional cholesterol blood test, which measures total cholesterol, HDL, LDL, and triglycerides, the advanced test also looks at particle size. This is important because some particles are big and fluffy, so they tend to bounce off artery walls as they travel through the body. Others are small and dense, meaning they can penetrate the artery lining and form clumps of plaque. (Think beach balls versus bullets.) The Lp(a) blood test analyzes a specific type of cholesterol that can triple heart risk.
What the Results Mean: You do not want more than 15% of your particles to be the small, dense type. For Lp(a), levels above 30 mg/dl put you at increased risk.
4) A1C Blood Glucose Test How It Works: A blood test indicates your average level of blood sugar over the prior 3 months. Unlike other glucose tests that require fasting or drinking a sugary beverage, this test requires neither.
Cost: $50
Duration: 5 minutes
Why It’s Heart Smart: This is the simplest way to detect your future risk of diabetes. This disease puts you at a 5 times higher risk of developing heart disease–yet 5.7 million Americans have undiagnosed diabetes (on top of the 17.9 million who are diagnosed) because they haven’t had their blood sugar checked.
Get It if: You’re 45 or older–or earlier if you’re overweight and have one or more diabetes risk factors, such as family history, high triglycerides, or low HDL.
What the Results Mean: An A1C level between 4.5 and 6% is normal, between 6 and 6.4% indicates prediabetes, and 6.5% or higher on two separate tests means you have diabetes.
What Happens To Your Body When You Eat Too Much Seafood
are then eaten by other fish. These fish will now have more methylmercury in their bodies than the original shrimp.
– impaired motor skills
– problems thinking or problem-solving
– difficulties learning to speak or understanding language
– damaged motor skills – paralysis
– numbness
– problems with memory and concentration
– symptoms of ADHD
After a Pandemic Pause, the State Will Restart Checking Medi-Cal Eligibility...continued from page 6
Medi-Cal renewal process will be taking place at a time when California is preparing for some key expansions and changes.
Starting in 2024, more people will qualify for full-scope MediCal benefits as the state opens enrollment to income-eligible undocumented people ages 26 to 49, the last remaining age group. About 700,000 people are expected to gain benefits through that expansion. At the same time, the state will also commence new Medi-Cal contracts with insurers, which could result in health plan changes for some enrollees. That’s a separate process, Huang at the state department said, and will not require any action from enrollees.
But these different moving parts happening at the same time will create more traffic in county social services offices, Baackes said.
“It’s just unfathomable to me,” he said, “that the state thinks that this is all going to happen without huge confusion on the part of the people we’re trying to serve.”
Unpacking Biden’s Budget — The President Wants Guns and Butter

By Peter White
President Biden's recently announced budget proposal promises to maintain entitlement programs while dramatically increasing defense spending.
When trying to cut back on red meat, many people often turn to their deep-sea favorites. Tilapia, catfish, crab legs, lobster, or some great scallops are delicious. But many articles are showcasing the nation is being overrun by seafood with high levels of mercury. Should you be concerned? Continue reading this article to know what happens to your body when you will be eating too much seafood and fish.
Eating seafood that has been tainted with mercury is one of the most common ways humans accumulate mercury in their bodies. The mercury in seafood is a highly poisonous form of the metal called methylmercury, which forms when mercury dissolves into the water.
Methylmercury can be absorbed from the water by all sea creatures, but it also continues through the food chain.
Small sea creatures, such as shrimp and crawfish, often ingest methylmercury and
This process continues all the way up the food chain, so that a large fish may contain much more mercury than the fish it has eaten. This does not necessarily make it better to eat smaller fish, however. It is always essential for a person to check the source of their seafood to avoid contaminated fish and shellfish.
People worried about their exposure to mercury may want to limit their seafood intake, particularly of fish that are high on the food chain, such as swordfish, shark, white tuna, pike, walleye, and bass.
Pregnant or breastfeeding women may want to avoid or restrict their intake of fish and shellfish, as any mercury they contain can pass to the fetus or infant through the umbilical cord or breast milk.
Consuming food that contains mercury is the most common cause of mercury poisoning.
Mercury poisoning can cause severe symptoms and put the
When President Biden formally unveiled his budget last week in Philadelphia, he took direct aim at the political football that is entitlement reform. “I guarantee you I will protect Social Security and Medicare without any change,” the president said.
But analysts say looming shortfalls will put those commitments to the test.
“They’re really two choices, very straightforward. You can increase revenues going in, or you can reduce benefits being paid out,” said Andrew Eschtruth, associate director for external relations at the Center for Retirement Research at Boston College.
“The president’s budget did not go into any detail other than to say that it was absolutely not going to propose any benefit reductions and would fight any benefit reductions that were proposed by the Congress,” Eschtruth added.
He was among a panel of speakers during an Ethnic Media Press briefing last week examining the president’s proposed budget.
Biden wants high-income workers to pay more taxes to ensure the nation’s popular Social Security program will have stable financial footing in the future. Social Security is the backbone of the retirement and disability income systems in this country, providing inflationadjusted benefits to more than 65 million people.
According to Eschtruth, based on incoming payroll taxes the program could continue to pay





