2 minute read
The 4 technical requirements for automated driving
by saam.swiss
Vehicles travelling on the road without a person at the wheel are no longer an idea. The technology has developed considerably in recent years. This article explains what we mean by self-driving and autonomous vehicles.
For a car to be self-driving or automated, it must be equipped with advanced controls and systems based on artificial intelligence (AI). Sensors, LiDAR (a type of laser scanning), radar and cameras allow the vehicle to immediately recognise its surroundings and steer without human intervention. The car detects possible routes, traffic signs and obstacles and navigates independently.
As a result, automated vehicles travel more smoothly than with human steering. The idea is that such cars can perform all driving functions under all conceivable conditions and in a variety of environments. Requirements that hardly any human driver can cope with in reality.
The degree of automation (see the next section) can vary and ranges from partial assistance to full self-driving capability where a person is no longer required. n
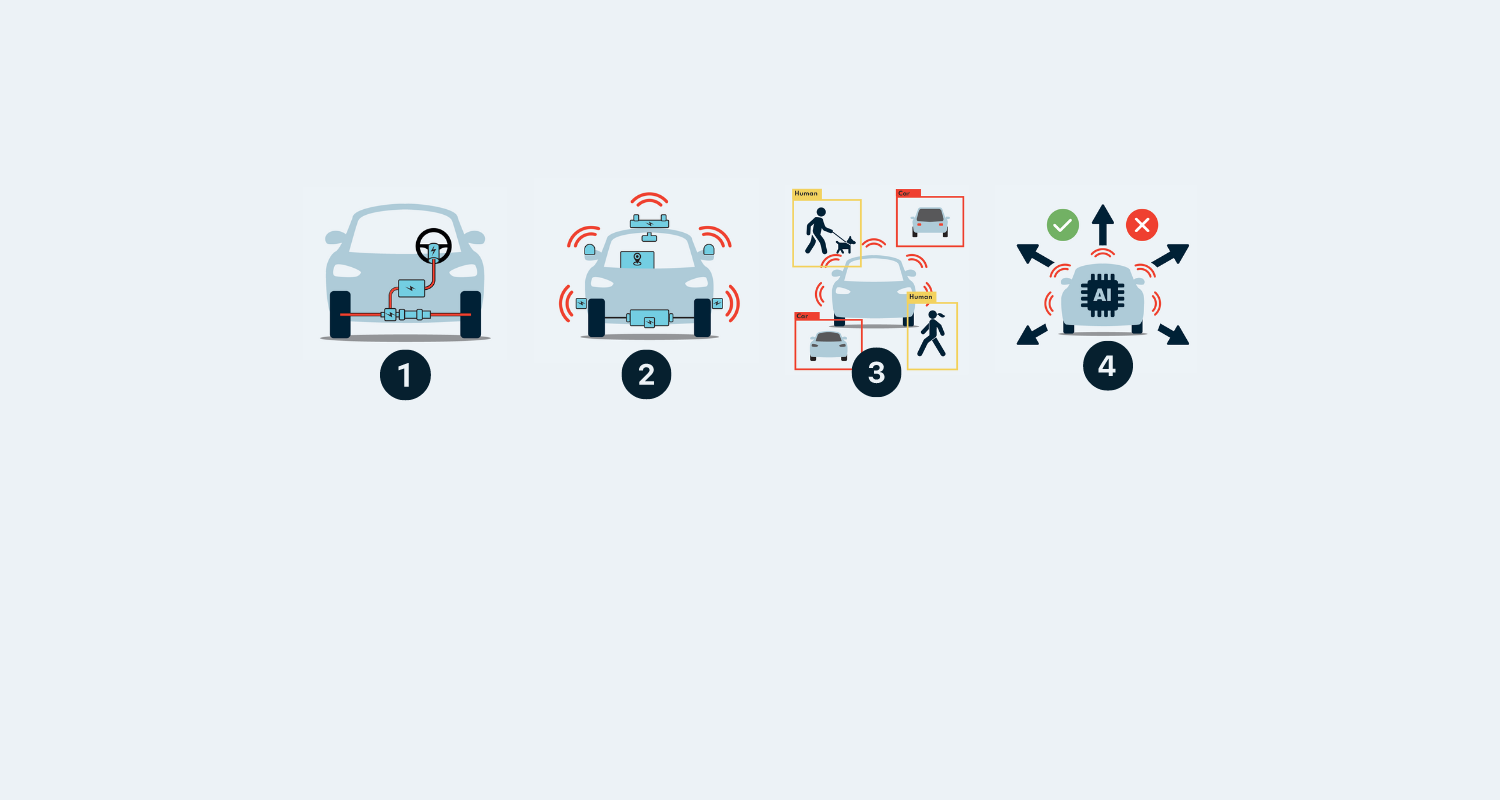
Drive-by-wire vehicle
Drive-by-wire (DbW) is crucial for automated driving, as it enables direct electronic control of all vehicle functions. This simplifies the integration of advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS) and autonomous driving functions, as commands can be transmitted electronically efficiently and precisely.
By eliminating mechanical connections, DbW also increases the reliability, safety and efficiency of the vehicle, which is essential for the complex requirements of automated driving.
Vehicle body with technical components
To effectively navigate its environment, an autonomous vehicle utilises a sophisticated array of sensors, including cameras, radars and LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging).
These technologies work together to ensure comprehensive position detection for the vehicle in all weather conditions, even when visibility is limited.
Situational awareness
This is the vehicle's ability to perceive, understand and localise itself in its environment in real time.
It requires data from different sensors to be merged and processed.
Decision-making and manoeuvring
The vehicle makes decisions based on data from its sensors and the situational awareness.
Earlier automated driving systems were heavily dependent on existing map material. This has changed. Advances in sensor technology, artificial intelligence and machine learning mean that modern automated vehicles are increasingly driving "map-free"










