3 minute read
What is Middleware?
It first came into existence in the 1960s, when mainframe computers were the dominant computing platform. These mainframes were expensive and complex, requiring a lot of specialised knowledge to operate. Middleware was developed to make it easier for developers to build applications that could run on these mainframes.
In the 1980s, it became more popular as the use of personal computers and distributed systems grew. Middleware was used to connect these different systems and applications together, providing common services such as security and data management.
Advertisement
Today, middleware is an essential part of any modern IT infrastructure. It’s used to connect a wide variety of applications and systems, providing a wide range of services, some of the most common types of middleware include:
Message brokers are used to send and receive messages between applications.
Transaction processing monitors are used to manage transactions between applications.
Enterprise application integration (EAI) is used to integrate different applications and systems together.
Web services are used to expose application functionality over the internet.
API management is used to control access to application programming interfaces (APIs).
Why Is Middleware Essential?
Middleware is a complex and everevolving field. However, it is essential for the development and operation of modern IT systems with benefits such as:
Increased Flexibility - Make applications more flexible and adaptable to change.
Improved Performance - Improve the performance of applications by providing common services and optimising communication between applications.
Reduced Costs - Reduce the costs of developing and maintaining applications by providing reusable components and services.
Improved Security - Improve the security of applications by providing features such as authentication and authorisation.
Increased Scalability - Increase the scalability of applications by providing features such as load balancing and clustering.
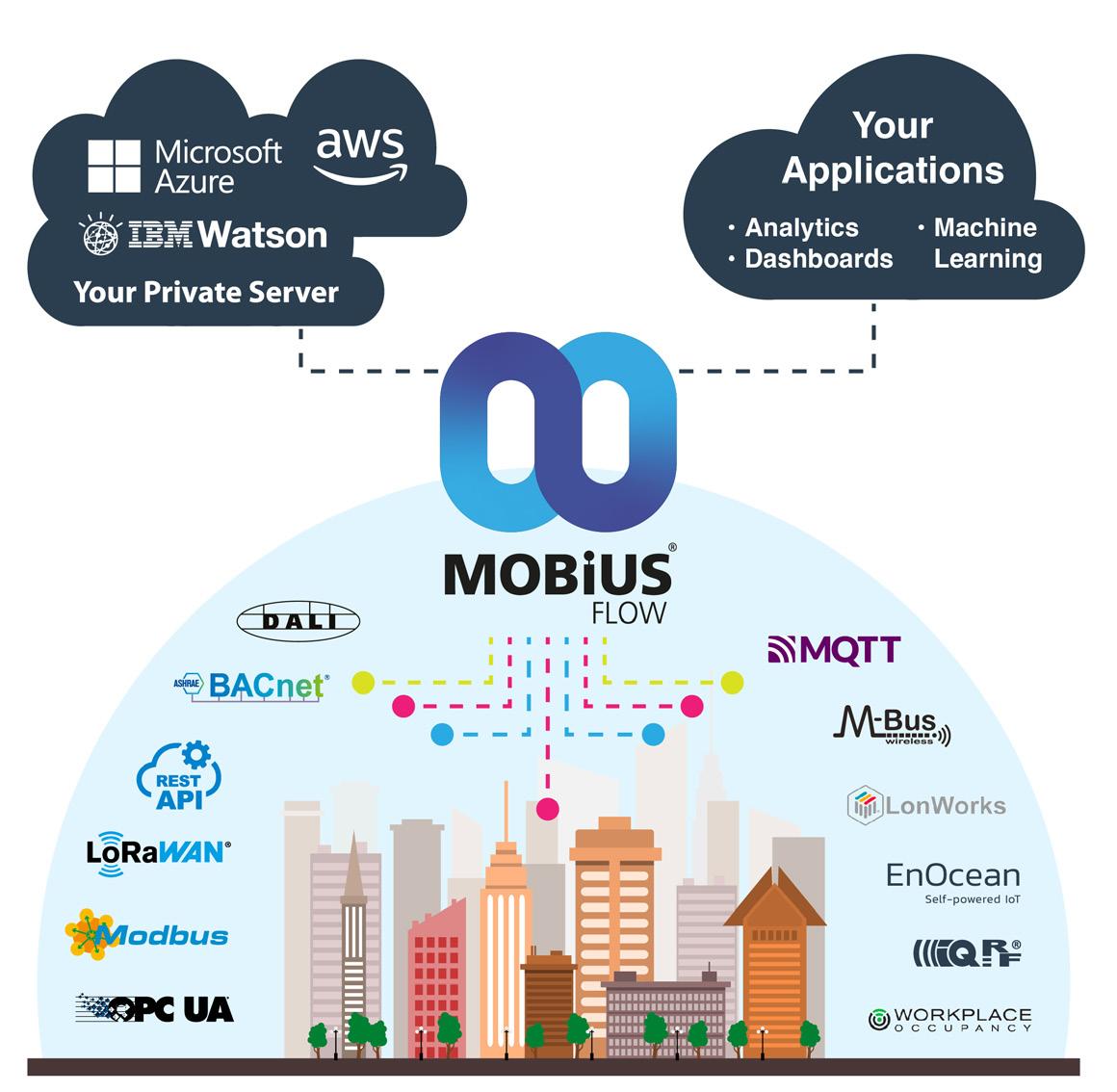
So what is MobiusFlow?
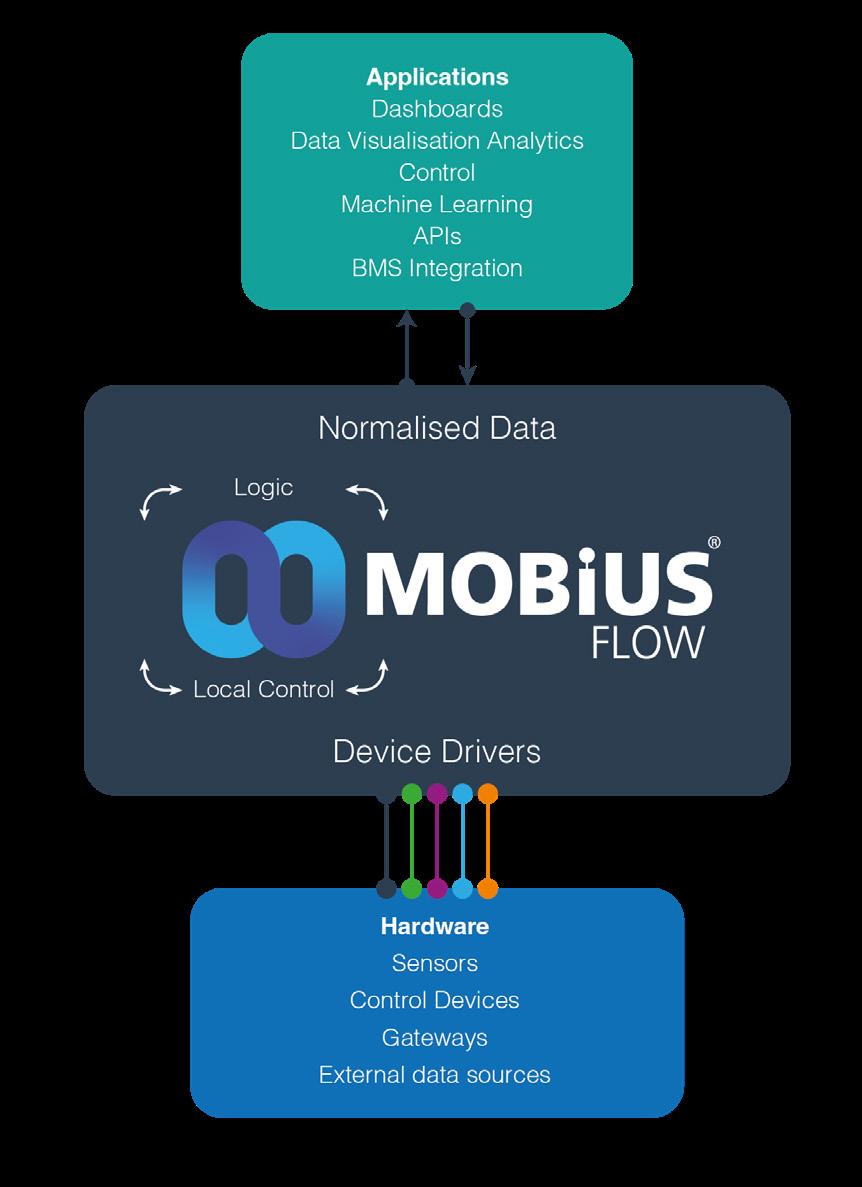
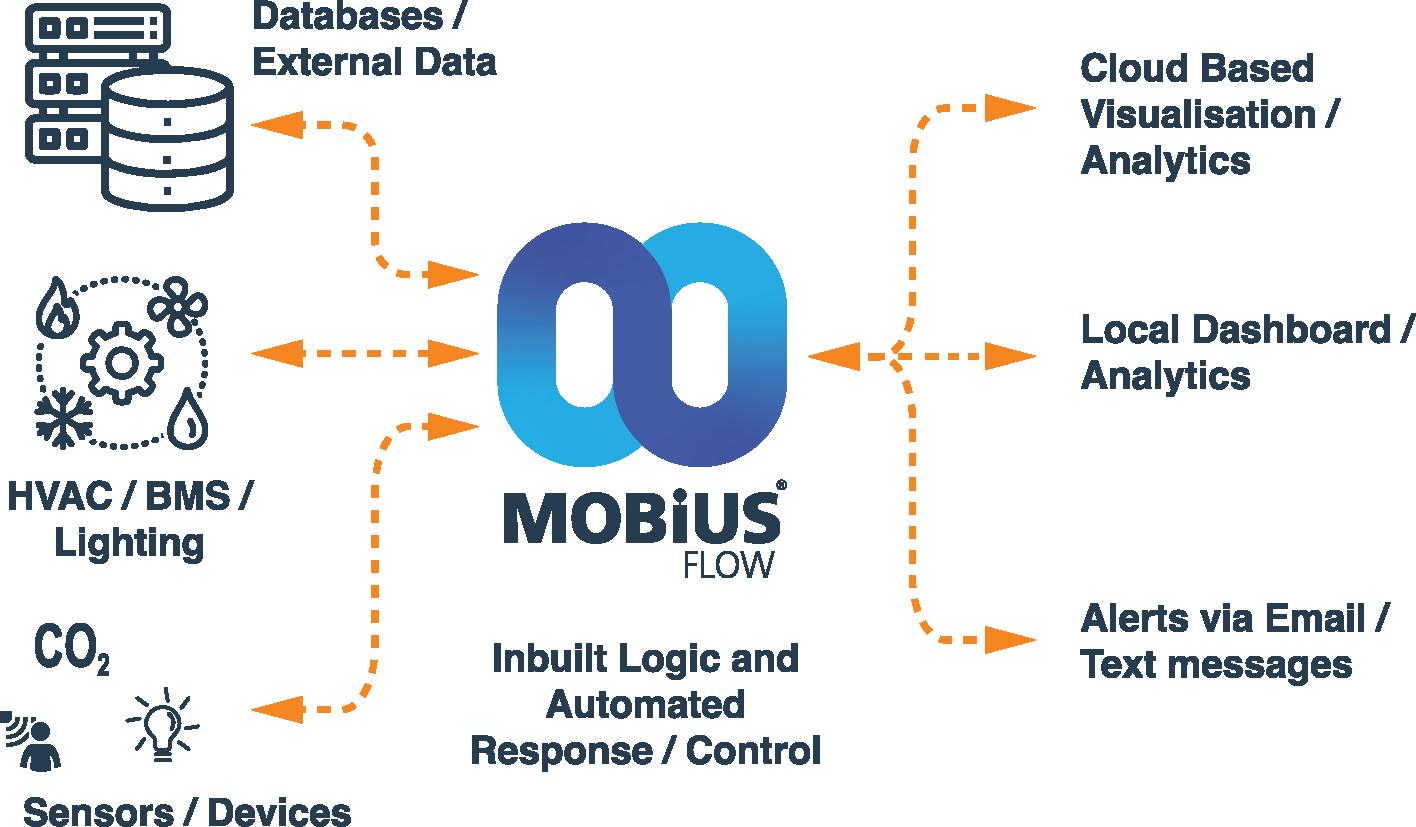
MobiusFlow is an advanced middleware solution that can be used to connect, control, monitor, and communicate with Internet of Things (IoT) devices, like sensors, it provides a variety of features, including:
Device Connectivity - Connect to a wide variety of IoT devices, including sensors, actuators, and gateways.
Data Collection and ProcessingCollect data from devices and process it in real time.
Device Control - Control IoT devices, such as turning on and off lights or opening and closing doors.
Device Monitoring - Monitor for problems, such as low battery or sensor failure.
Data Visualisation - Collect, collate and push data to visualisation tools such as Microsoft Azure, Thingsboard and Amazon Web Services as well as local servers and systems or just a simple email or text message notification for alerts.
MobiusFlow can also be used to integrate IoT devices with other systems, such as enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems or manufacturing execution systems (MES). This can help to improve the efficiency and productivity of businesses.
A Bable fish? A Universal Translator? Middleware? A Broker? What is it?
A bit of everything. A key feature of MobiusFlow is its ability to integrate with multiple protocols at the same time. For any advanced middleware solution, being protocol agnostic is crucial.
Being protocol agnostic refers to the ability of a system or device to work seamlessly with multiple communication protocols, regardless of the underlying technology or infrastructure. In the context of the internet of things (IoT), this means that devices can communicate and exchange data with each other (WiFi, LoRaWAN, EnOcean, Bluetooth, Power over Ethernet (PoE), MQTT etc), regardless of the specific protocols they use.
Flexibility
This flexibility allows businesses to choose the best devices for their specific needs, without being limited by compatibility issues. This also future-proofs businesses’ IoT investments by ensuring that their devices can adapt and work with new protocols as they emerge.
This also promotes interoperability, allowing devices from different manufacturers and suppliers to work together seamlessly. This is crucial for creating a unified and efficient IoT ecosystem, where devices can communicate and share data effortlessly.
For example you may wish to use LoRaWAN for long range estate management for daily updates on water quality or silo levels but use EnOcean in your offices to monitor desk occupancy and air quality on a minute by minute basis.
Both are excellent systems but one is long distance, low power and the other is high frequency short range, so by combining these with MobiusFlow you end up with a very powerful, data accurate, reliable and robust solution all running through one system, enabling actionable insights, automated responses and a view of your assets all in one place.
Scalable
IoT solutions often start small, with a proof of concept (PoC) or a pilot project. However, as businesses grow and expand, their IoT needs may evolve and require a largerscale implementation. Being protocol agnostic allows businesses to scale their IoT solutions seamlessly, from a single device to thousands, without major compatibility issues.
This scalability and flexibility ensure that businesses can adapt and grow their IoT infrastructure as needed, without being constrained by specific protocols.
Introducing MobiusFlow to your portfolio enables you to offer new sensors and devices to your existing user base as well as expanding your reach to new customers and offering additional solutions.
As a big data, visualisation or analytics company MobiusFlow can connect and collate the right data, to the right place, in the right format for your end users.
Future-Proofing and Interoperability
Technology is constantly evolving, and new communication protocols are regularly introduced. Being protocol agnostic future-proofs businesses’ IoT investments by ensuring that their devices can adapt and work with new protocols as they emerge.
This also promotes interoperability, allowing devices from different manufacturers and suppliers to work together seamlessly.
This is crucial for creating a unified and efficient IoT ecosystem, where devices can communicate and share data effortlessly █




