4 minute read
A Dietary and Botanical Approach to the Treatment of Sibo: A Case Report
Kara J. Cucinotta College of Health & Wellness, Providence Ou Han-Wen, M.D., Redox Clinic Dana Elia, Fusion Integrative Health & Wellness, LLC
application: A DIETARY AND BOTANICAL APPROACH TO THE TREATMENT OF SIBO: A CASE REPORT
Advertisement
Small intestinal bacterial overgrowth (SIBO) is an incompletely understood acquired condition which causes multiple gastrointestinal complaints. There is no accepted treatment “gold standard” and therapeutic options range from broad spectrum antibiotics to dietary interventions and botanical supplements. Since SIBO and irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) have overlapping symptoms, a low fermentable oligo- di- mono- and polyol diet (FODMAP) is commonly used to manage the condition. This case reports on the use of a low FODMAP diet and botanical supplementation in a patient with a positive lactulose hydrogen breath test (LHBT), a non-invasive tool used to diagnose SIBO.
DESCRIPTION OF SCHOLARLY INQUIRY
As there is no “gold standard” for treatment of SIBO, this case study sought to examine the efficacy of a combination of a
low FODMAP diet and botanical supplement regimen in eradicating SIBO. The essential question guiding inquiry was:
what is an appropriate treatment of SIBO that does not require the use of antibiotics?
This patient is a 31-year-old female presenting with intermittent eczema, constipation, abdominal bloating, and suspected
food allergy. During her first visit to the functional medicine physician, a hydrogen breath test was positive for SIBO —
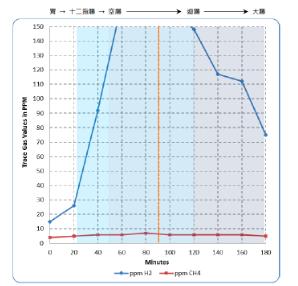
hydrogen (H2) levels were 162 ppm by the sample at 100 minutes. The patient was prescribed a treatment plan consisting
of a low FODMAP diet, dietary and botanical supplements including digestive enzymes, berberine, thyme, cinnamon,
neem, uva ursi, and oregano.
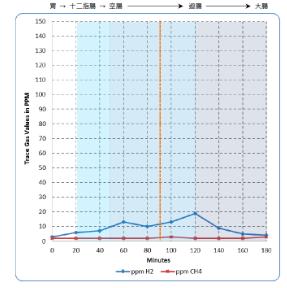
After 8 weeks of dietary modifications and botanical supplement regimen, a repeat hydrogen breath test revealed H2
levels within normal limits, and the patient reported improvement in her abdominal bloating and eczema.
After 12 weeks of continued treatment, the patient reported complete resolution of her eczema and abdominal bloating.
OUTCOME
This case report highlights the usefulness of the lactulose hydrogen breath test in accurately diagnosing small intestinal
bacterial overgrowth in a young adult female with multiple gastrointestinal complaints. In addition, antimicrobial
botanicals--including berberine, oregano, cinnamon, neem, and uva ursi—were associated with elimination of the
infection without the use of antibiotics. In this case, S. boulardii, a probiotic was used to prevent diarrhea and colitis.
Future research may include large, experimental trials investigating the efficacy of a combination therapy of a low
FODMAP diet along with the aforementioned botanicals. Future research may also compare intervention with antibiotic
SIGNIFICANCE OF OUTCOME
In this present case, SIBO was suspected due to the patient’s complaints of intermittent eczema, constipation, abdominal
bloating and belching after meals. Breath testing is a useful, inexpensive, simple, and safe diagnostic tool in gastroenterology
and is important for the diagnosis of carbohydrate maldigestion syndromes and SIBO and was used for diagnosis of SIBO
The treatment of SIBO is a complex, step-by-step process aiming to eliminate the bacteria in the small intestine, repair
the intestinal barrier and reintroduce the bacteria into gut lumen. In antibiotic therapy, metronidazole and rifaximin are
commonly prescribed. Herbal therapies, such as oregano oil and berberine, have been shown to be equivalent in efficacy
Dietary intervention is important during SIBO treatment to help alleviate symptoms, influence the microbiome and heal the mucosal lining. While dietary adherence can be challenging for patients, the low-FODMAP diet shows symptomatic
improvement.
This case report may serve as a catalyst to future research to investigate and develop best practices for management of
SIBO.
v
PMH: allergic rhinitis; abdominal bloating, constipation, intermittent eczema and suspected food allergy for months.
SIBO Breath Test #1
Nov 2017

SIBO Breath Test #2


SIBO Breath Test #3 Dec 2017
Jan 2018 SIBO Diagnosis



FUNCTIONAL MEDICINE VISIT #1
Dietary Intervention: Low FODMAP Diet



Nutritional Supplements: Weeks 1-4 : Microcidin AF, GI Detox, GI Digest, Ultrazyme, Betaine Plus Weeks 2-4 : GI Restore Weeks 3-4 : S. boulardii
FUNCTIONAL MEDICINE VISIT #2
Dietary Intervention: Continue Low FODMAP Diet



Nutritional Supplements: Weeks 1-4 : Microcidin AF, GI Detox, GI Digest, Ultrazyme, Betaine Plus, Berberine HCl Weeks 2-4 : GI Restore Weeks 3-4 : S. boulardii
Feb 2018

Mar 2018 Pt D/C’d Low FODMAP Diet



FUNCTIONAL MEDICINE VISIT #3
Dietary Intervention: Regular Diet



Nutritional Supplements: S. boulardii GI Restore






