
14 minute read
Projects presented at the Venice International Architecture Biennale in 2018 and 2021
Academic Journal on the Internet
Two documents on the Internet are linked here: They are published by the University of Trieste, Italy, concerning the projects made with
Advertisement
some architecture students of mine and presented at the Venice
International Architecture Biennale in 2018 and 2021. The journal of the University of Trieste is named: “QuaderniCIRD”, Journal of the Interdepartmental Center for Educational Research of the University of Trieste - ISSN: 2039-8646. Here the links to the two papers: 1. Biennale Architecture, Venice 2018 - DOI: 10.13137/20398646/32083
Here the abstract of the paper in English, Italian and Russian https://www.openstarts.units.it/handle/10077/32083
Here the paper, only in Italian https://www.openstarts.units.it/bitstream/10077/32083/3/Grossi.pdf 2. Biennale Architecture, Venice 2021 - DOI: 10.13137/20398646/32083
Here the abstract of the paper in English, Italian and Russian https://www.openstarts.units.it/handle/10077/33408
Here the paper, only in Italian https://www.openstarts.units.it/bitstream/10077/33408/3/Grossi_CIRD22.pdf
************************************************* Hybrid Education & Smart Learning, Innovative Teaching in the Post-Coronavirus Era
presented at the IV All-Russian Scientific and Practical conference "Digital transformation as a vector of sustainable development", held on December 9, 2021 in Kazan, Tatarstan, Russian Federation.
Prof. Franco Claudio Grossi
Abstract: The educational science has evolved over time, especially by virtue of the use of new ICT technologies for learning. Even the internal layout of the classrooms is undergoing a transformation in consideration of the fact that today we tend to work in a team and to bring out the intrinsic personality of each individual. To all this are added the provisions deriving from the pandemic, which imposed distance learning as a solution to the problem. Now, in the post-Covid era, we must capitalize on the experience acquired in order to generate new types of education, based both on pedagogical innovations and on those of new generations of technological systems for the acquisition and sharing of knowledge. To this end, it was decided to adopt a "hybrid" and "smart" educational system, capable of combining face-to-face and remote training and developing a teaching method to share and spread the culture of knowledge in a conceptually creative and socially oriented way. From a purely technological point of view, systems have been developed, so they will be able to help all the "actors" of the teaching chain
RICOSTRUIRE - YEAR XLIV - No. 3-2021 – Page 2
(student teachers, specialists, researchers, business executives, etc.) to interact in a totally flexible environment, equipped with laptops, large screens, virtual reality and augmented reality devices, up to and including chatbots with Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning. The implementation of this work plan was possible with the use of existing innovative technologies and, of course, could increase the strength of KIU in the field of education.
1. DESCRIPTION
The purpose of this work is to examine the situation of educational processes in the pre and post Covid-19 era, foreseeing innovations in teaching / learning methodologies, assisted by new ICT technologies and this also from the point of view of the interior design of the classrooms. In particular, we refer to the pragmatic educational proposals, enunciated by two pedagogues who lived between the nineteenth and twentieth centuries, Maria Montessori [1] and John Dewey. Dewey himself emphasized the "active" role of educational institutions. The method he suggested is aimed at making the student acquire an "operational intelligence" [2] and this in the context of specific groups and workshops aimed at developing skills in various sectors. Dewey proposed a "progressive educational activism", such as to allow the student to gradually overcome obstacles and difficulties and this by developing personal strategies. From a methodological point of view, in carrying out the design of this "theoretical-practical" training course, the methodologies of the ergonomics discipline were used [3]. In this regard, it should be noted that the field of investigation of applied ergonomics (User-Centered Design, Interaction Design, etc.) also deals with activities aimed at the practical realization of classrooms and it is that type of project that is preferable to apply in the design process, in order to make it more usable and enjoyable even by students of different backgrounds. The ergonomic principles, highlighted by precise ISO standards [4], require, in fact, both a design of the classrooms oriented to the needs of the students, and a systemic approach on the part of the teacher. Therefore, a student-centered teaching, which includes the interdisciplinary nature of the courses, the promotion of team work activities, the use of no more than a single classroom, but a network connection between teachers, students and with external influences (case histories, business leaders, etc.). This innovative technological proposal then provides for the use of new learning systems, capable of assisting each student and attracting his attention, through perceptual processes capable of involving his cognitive processes and this both in real and virtual mode. In particular, it was decided to develop a hybrid network technology, in order to make different "actors" interact in the educational process, both in presence and at a distance, until reaching an "intelligent" type of teaching, able to involve the students with virtual reality, with multiple screens and direct connections with companies and external laboratories.
2. TRADITIONAL TEACHING CLASSROOM.
The "old-fashioned" classrooms [5] (pre-Covid-19) were structured to carry out "one-to-many" lectures. Normally the teaching took place in a single environment, where the teacher interacted frontally with a multitude of students and with few opportunities for interaction. The teacher's task was to make students receive "content". Furthermore, the internal design of traditional training classrooms was not suitable for integration with modern teaching technologies. In short, a general design of the spaces was lacking, oriented towards a future vision, also because the IT and audiovisual tools have always remained technological bodies “external” to the interior design of the classrooms.
RICOSTRUIRE - YEAR XLIV - No. 3-2021 – Page 3
Figure 1. A Traditional/Old-Style Classroom.
3. THE HYBRID EDUCATION CONCEPT.
In this project, it is a question of structuring an "intelligent" classroom, which is networked with the other locations of the University, with students who learn at a distance and with external realities (experts, managers of institutions, sector managers, etc.). All this is made possible using a remote interactive network system, thus allowing the sharing of teaching resources between different study rooms, different academic campuses and different regional realities. So, not only the teacher will be able to interact with the students, but also the students among themselves, sharing screens. All students will be able to view the resources and materials of the courses, receive personalized feedback from the teacher, integrate the theoretical classrooms with classrooms / practical laboratories, in order to be able to use all the teaching methods in an integrated and shared way.
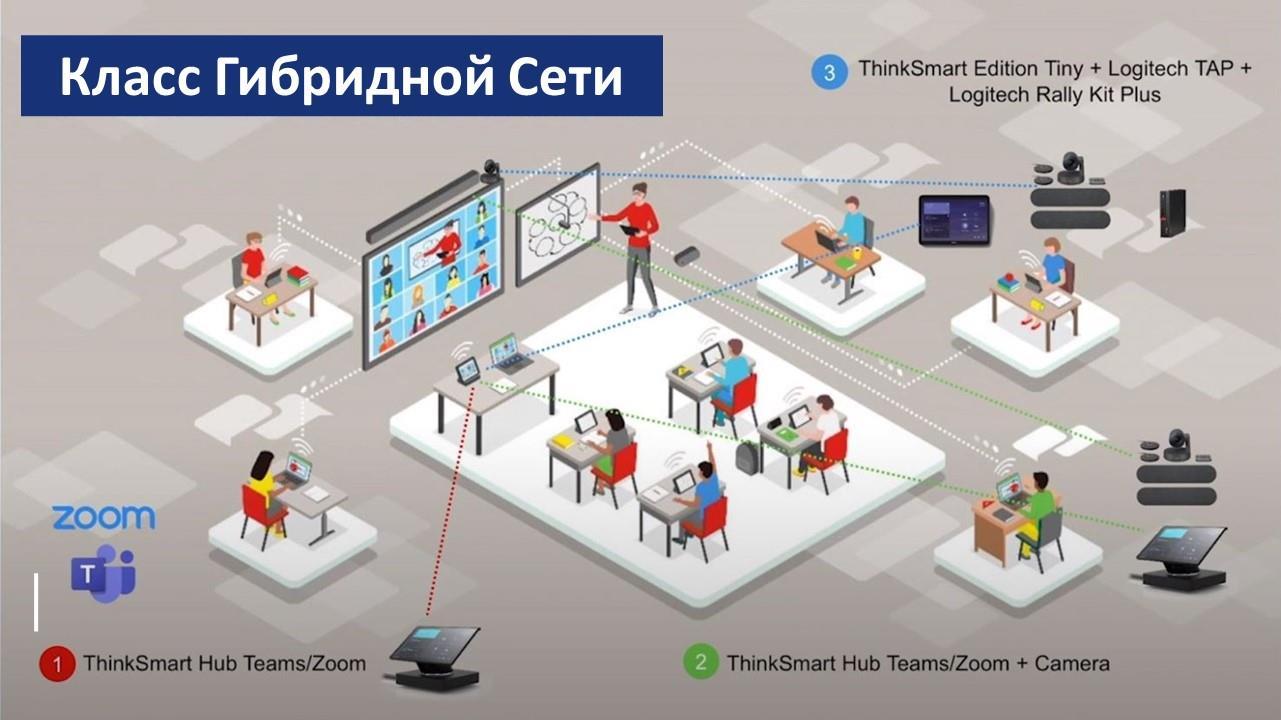
Figure 2. An example of a hybrid network classroom.
The goal is to design an "intelligent" type of teaching, capable of responding to those needs of effectiveness, efficiency and pleasure, which are also typical of ergonomic design and which will make teaching easier and more usable. The distribution of the didactic spaces is redefined by eliminating the traditional podium, placed at the back of the classroom, in order to allow the teacher to interact directly with the students, who will collaborate in group projects and with classroom discussions. The teacher will maintain his role as organizer and guide in the teaching process, assisted by a giant screen, "multiple touch all-in-one" laptop and tablet, interactive systems for the integration between mobile phones and tablets, able to fully satisfy the educational needs of group discussions and information sharing.
RICOSTRUIRE - YEAR XLIV - No. 3-2021 – Page 4

Figure 3. An example of a Smart Classroom.
In short, it is a question of developing a new training methodology of the "learning by doing" type [6], identifying, from time to time, a common denominator, which allows the study / work group to enhance what has been learned in the classroom and respect the peculiar aspects of different cultures and idioms in the context of social and working life, in order to achieve a shared result. It would be interesting, for example, to consider the thoughts of students attending foreign universities, giving everyone the opportunity to share their communication knowledge and experiences. So, everyone would be able to use this information, feeling an integral part of a group with common educational goals [7]. With this type of education, the traditional way of presenting multi-type educational content has been completely changed and the technological system is able to support this complex teaching process. For example, a multi-window presentation system will be implemented in the big screen, driven by a high-performance graphics workstation. This innovative educational typology is able to implement the visualization and comparison of a large variety of educational resources and contributions from multiple "actors", allowing the shared development of difficult and complex problems, optimizing the presentation of educational content and deepening the knowledge of students. Figure 4. A multi-window presentation system.

Continuing in the description of innovative teaching classrooms, always in the key of "smart education", we can represent an "intelligent" type, which aims to provide an interactive space for educational activities, through the combination of physical space and digital space, and combination of local and remote.


Figure 5. Smart Education, a Classroom.
RICOSTRUIRE - YEAR XLIV - No. 3-2021 – Page 5
In this case, a "contamination" is established between tangible physical space and immaterial digital space, proposing the representation of didactic contents through different intelligent devices, which help to facilitate learning and favor the sharing of contents and group interaction in the classroom. All this is implemented using large interactive touch screens and devices for virtual reality [8] and augmented reality [9]. With these devices it will be possible to present three-dimensional teaching material in distinction (for example, to compare organs before and after a disease), up to the presentation on the same screen of manipulation processes [10].


Figure 6. Virtual reality and augmented reality.
One final note concerns the use of chatbots. A Chatbot is a bot (Robot) designed to converse with humans [11]. In other words, Chatbots are computer programs created to simulate human conversations on a website, messaging app, or virtual assistant. In its simplest form, chatbots can be programmed to answer specific and frequently asked questions, providing an easy way to interact with students.
4. CONCLUSIONS
The development of an innovative "hybrid" and "smart" teaching methodology, both in terms of teaching and learning methods and in terms of new ICT technologies, involves today the entire "educational chain". In fact, it is a question of completely redesigning the classroom spaces, using new interior design provisions, in full compliance with the concept of ergonomic usability (ISO 9241: effectiveness, efficiency, pleasantness). All currently available devices (IoT, AI, VR, AR, Big Data, etc.) will be used on the basis of a "smart" technology and equipment, enhancing new teaching and research and promoting the updating of educational information. All of this could certainly make KIU the most innovative university in Tatarstan and one of the most innovative universities in the Russian Federation.
6. ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
First, I would like to express gratitude to the engineers from Lenovo, Beijing, who gave me the idea of writing this document. Also, I would like to thank all the researchers at Intel, Microsoft Teams, Google Meet and Zoom whose guidelines advised me how to proceed in this report.
7. REFERENCES
[1] Montessori M., To educate the human potential, Published May 1st 1989 by ABC-CLIO Ltd (first published 1947) Santa Barbara CA,
USA, ISBN 978-1851090945. [2] Dewey J., My Pedagogic Creed (1897), https://en.wikisource.org/wiki/My_Pedagogic_Creed [3] McCauley Bush P, Ergonomics, CRC Press, Boca Raton FL, USA,
ASIN: B00DHKPTEC, ISBN: 978-1439804452 [4] The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) takes due consideration the fundamental principles of ergonomics as basic guidelines for the design of work and educational systems, e.g.: ISO 6385, ISO 26800, ISO 9241 series, ISO 24500 series,
ISO 29241 series, ISO 7250 series, etc.
RICOSTRUIRE - YEAR XLIV - No. 3-2021 – Page 6
[5] Greene G., The Old School, Oxford University Press, August 1, 1984, originally published: London: Cape, 1934, ISBN 9780192814845 [6] Dewey J., Experience & Education, Simon & Schuster, New
York, NY, USA, 2008, ISBN: 978-0684838281 (first edition by
Kappa Delta Pi Indianapolis, IN, USA, 1938, ISBN 0-684-838281) [7] Grossi F.C., Practical projects within university training courses in
Applied Ergonomics / Практические проекты рамках университетских курсов по прикладной эргономике, in Journal of the Interdepartmental Center for Educational Research of the
University of Trieste, No. 21/2020, University of Trieste Press,
ISSN: 2039-8646, DOI: 10.13137/2039-8646/32083, Pages 73 –92. [8] https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Virtual_reality [9] https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Augmented_reality [10] https://www.autodesk.com/solutions/virtual-reality [11] https://www.merriam-webster.com/dictionary/chatbot
The Business Warfare School, Kazan, Russia
presented at the Congress " Future strategies in the context of digital transformation", held in Kazan, Russian Federation, on October, 22nd 2020, invited by the Innovative Marketing Dept. of the University of Innovation, Kazan, Russia.
Prof. Franco C. Grossi Figure 1. Tips for startups in Tatarstan.
RICOSTRUIRE - YEAR XLIV - No. 3-2021 – Page 7
This project was born in order to satisfy the need, now no longer postponable, as regards the creation of new SMEs in Tatarstan, taking into consideration the fact of having to operate today, in a global market, extremely liquid and fluctuating, but being placed at an advantage by the Internet.
Figure 2. Economy oil based
For too many years, in Russia, the extraction of raw materials (e.g. oil) has been favored, to be sold on international markets, in order to obtain the capital necessary to meet the needs of products for the population, which are however imported without promoting one's own business culture, aimed at enticing young people to become "entrepreneurs" and therefore produce at home. Furthermore, large Russian companies often make "non-exportable" products, as they do not meet the "Western" quality criteria. Figure 3. Factories must be innovated Then, "foreign" settlements were privileged, with the wording "invest", which, if on the one hand contribute to the creation of jobs, on the other hand, absolutely do not contribute to bringing entrepreneurial knowhow within the nation.
Figure 4. Indicators of the Russian economy 2020
RICOSTRUIRE - YEAR XLIV - No. 3-2021 – Page 8
After a growth of just 1.3% in 2019, the Russian economy is expected to contract by 6.3% in 2020, due to a double blow due to the social distancing measures resulting from the coronavirus, and the shock of the global oil price. Both falling oil prices and falling oil demand are hitting the Russian economy hard, as oil and gas exports account for 55% of total exports and about 40% of federal government revenues.
Figure 5. Loss of the ruble exchange rate
As a result, the value of the ruble is experiencing a sharp depreciation, which could however be contrasted with a net inflow of foreign exchange following an intense campaign for a mass starting of new companies capable of exporting their products. Figure 6. Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs
Today, the problems that grip young people willing to emerge, are essentially linked to the lack of a "School", which, through adequate training, motivates them to "set up a business", stimulating them to the personal success they could obtain in society and the consequent contribution of GDP and employment, which could lead to Tatarstan and to the Russian Federation. Therefore, this project is intended to encourage the birth of new SMEs and to foster their ability to internationalize their production and this, using suitable strategies and tactics of a "business warfare". The suitable tools will be identified to produce innovation especially as regards the enhancement of the corporate brand (communication, marketing, sales), in order to be able to identify those competitive advantages, which allow you to always settle in higher positions in the market.
RICOSTRUIRE - YEAR XLIV - No. 3-2021 – Page 9
Figure 7. Need for lifelong learning
Furthermore, young people will have to understand that the diploma (for example the always longed for "degree") is no longer an "end", but only the means (and only if "provided" with adequate skills) to access the "world of work ". In other words, we are witnessing the decline of school certifications as "qualifications" valid for life, to the advantage of the ability to implement "competent" behaviors ("real" skills) in real situations and this, through a "lifelong learning" program. As regards, then, the numerous attempts to launch "start-ups", which in the West have been almost 90% unsuccessful, it must be said that universities and university professors are unable to act as entrepreneurs, however, they are able to provide young people with guidelines for becoming one. The present initiative will include both a training course and a practical value and the work plan will focus not only on theoretical bases, but also and above all on specific practical projects, also concerning the diffusion of the brand "Made in Tatarstan" (or "Made in in Russia "), all for a concrete internationalization. Figure 8. The Business Warfare School
Figure 9. Mobile and Flexible workers



