
3 minute read
Powershift Transaxle Overview....................................................... 5 Section 2 Torque Converter......................................................................... 6 Converter Parts................................................................................. 6 How the Converter Multiplies Torque
This section is designed to acquaint you with the functioning's of a Powershift Transaxle and the safety precautions that should be taken when working on it. Other sections of this manual will cover these functions in greater detail.
Powershift Transaxle Overview
Clark lift trucks owe a large share of their excellent reputation to the Powershift Transaxle. The Powershift Transaxle is dependable and performs well in high-cycle, heavy-duty operations.
The Powershift Transaxle consists of four units:
•Torque Converter • Transmission •Transmission hydraulic system • Drive axle.
The fl torque converter (often referred to as "converter") takes energy from the engine's
ywheel and increases it as needed by multiplying torque. The converter transfers this energy to the transmission. Most Powershift Transaxles have two power-shifted packs: forward and reverse. A few transmissions will have an optional four-pack system: high and low in addition to forward and reverse. The drive axle transmits power to the wheels and differentiates the speed of the wheels. Both the converter and transmission are hydraulically operated (or fluid operated) systems that use transmission fluid (sometimes referred to as "oil") to increase transmission power as well as to cool and lubricate the Powershift Transaxle's mechanical parts. Throughout the years, Clark has produced numerous types of transmissions. The TA 12, TA18, and the TA 30 are examples of transmissions designed by Clark Material Handling Company. Because of the different types of transmissions and transaxles, how to troubleshoot, tear down, and rebuild specific transmissions and transaxles will be discussed in other classes. This class will focus on how a typical Powershift Transaxle works and how to troubleshoot it. This class will use the TA18 transmission as an example. Note Even though most transmissions will have the same parts, the names and locations of these parts may vary according to models. Always be sure you consult the appropriate manuals when you troubleshoot a transmission.
Section 2 Torque Converter
In this section you will learn what the torque converter is, how its parts operate tiply torque, and what problems might arise with the converter and its parts. to mulThe torque converter is a fluid operating device that takes the place of a conventional clutch and multiplies torque. The torque converter is driven by its driving disc which is bolted to the engine flywheel. The converter receives its power from the flywheel, increases it when needed, and transfers it to the transmission.
The torque converter has four advantages: • It absorbs shock to prolong the power train's life. • It permits the transmission to quickly change gears-even under heavy loads. • It multiplies torque and delivers smooth power which creates more driving force at the wheels. • It requires no periodic adjustments and does not use complicated components. Though the torque converter is not repairable, the converter plays such an important part in the functioning of the fork truck that we will cover its operation in detail.
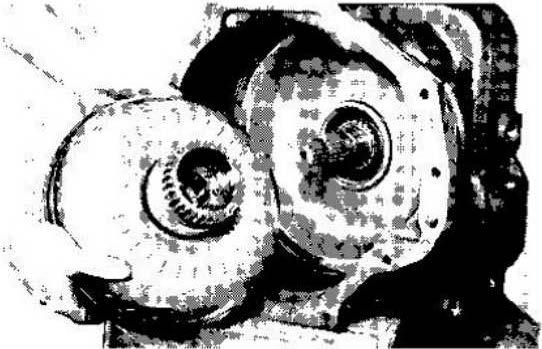

Torque Converter
Converter Parts
The torque converter consists of three parts: impeller, turbine, and stator. These three parts and the hydraulic fluid in them function as one unit to multiply torque from the engine. Impeller The impeller is driven by the engine in a clockwise direction (as viewed from the front of the engine). The impeller and the cover welded to it form the torque converter's outer housing. The housing, which is completely filled with transmission fluid, contains the stator and turbine. A properly functioning impeller turns whenever the engine is turning and acts like a hydraulic pump.



