
1 minute read
Different Forms of International Trade Finance
International Trade Financing
For businesses looking to launch new products while taking advantage of favorable exchange rates and cheap manufacturing costs, import finance provides the way for hassle-free importing of goods and services from international suppliers. Various documents, including bills of exchange, promissory notes, bills of lading, letters of credit, and the like, typically secure it.
Advertisement
Offering financial support for pre-and postshipment activities is a part of export financing. Excellent export financing can offer financial support at every stage of the production process, from manufacturing to delivery to the customer. Even before the importer's payments start to come in, it makes sure that every operation is carried out exactly as it should.
When we examine the classification of global trade finance using different financial instruments, it becomes more complex. The primary categories of tools used to facilitate international trade finance are as follows:
1. Letter of Credit:
A bank issues a letter of credit on the buyers' behalf. It ensures that the seller will be compensated for the goods and services provided to the customers. If the buyers are unable to make the payment due to unavoidable circumstances, the bank or financial institution will step in. In accordance with the letter of credit's terms and conditions, it will pay the seller.

2. Bank Guarantee:
In keeping with its name, a bank also issues this guarantee. If the importer or exporter fails to make the payments as required by the contract, the bank steps in as a third-party guarantee.


3. Forfaiting:
4. Factoring:
Contracts containing payment terms that do not mandate the customer to pay for the goods for several months are frequently used to export goods overseas.
It is not ideal for suppliers who have to pay invoices on a monthly basis to have to wait 6+ months for payment. It is at this point that Indian factoring businesses can help. They stand for an additional post-export financing kind. The supplier's receivables are, in this case, discounted by a financial institution. When the invoice is prepared, the purchaser must pay the factor rather than the vendor.
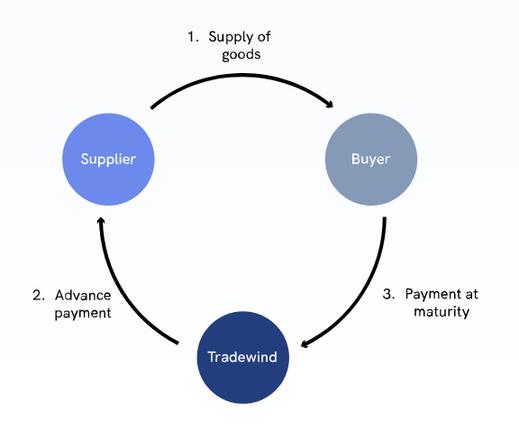
5. Payment in Advance:

Pre-export trade finance of this kind entails the buyer paying the supplier in full or in advance of the delivery of the products, whichever comes first. In terms of keeping a steady cash flow, this allows suppliers more flexibility. However, in the event of a missed or delayed delivery, it may be harmful for the customers.



