
2 minute read
Types of Escalators
from Mechanical Systems
by Fazil Ali
Assignment-5
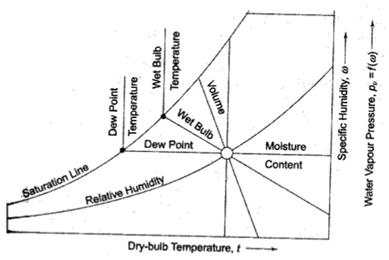
1. Locate on psychrometric chart a) dew point b) wet bulb temperature c) specific volume d) relative humidity
Advertisement
2. What is dry bulb temperature ? Ans: The dry bulb temperature is the temperature measured by a thermometer freely exposed to the air, but shielded from radiation and moisture.
3. What is wet bulb temperature ? Ans: Wet bulb temperature is a temperature of air with humidity. It is therefore measured by wrapping a wet cotton around th bulb of a thermometer and the measured temperature.
4. What is specific volume ? Ans: Specific volume is a property of materials defined as the number of cubic meters occupied by one kilogram of a particular substance. The standard unit is the meter cubed per kilogram.
5. What is humidity ratio? Ans: Humidity ratio is ratio of weight of moisture to the weight of dry air in air vapour mixture
6. What is dew point temperature ? Ans: Dew point temperature is defined as the temperature to which the air would have to cool in order to reach saturation.
7. What is sensible heating or cooling ? Ans: ) A psychrometric process that involves the increase or decrease in the temperature of air without changing its humidity ratio.
8. What is Heating and Humidifying ? Ans: A psychrometric process that involves the simultaneous increase in both the dry bulb temperature and humidity ratio of the air.
9. What is Cooling and Dehumidifying? Ans: A psychrometric process that involves the removal of water from the air as the air temperature falls below the dew point temperature.
10. What is Adiabatic or Evaporative Cooling ? Ans: A psychrometric process that involves the cooling of air without heat loss or gain. Sensible heat lost by the air is converted to latent heat in the added water vapor.
11. What is the use of Bio-climatic chart Ans: Bio-climatic charts are used in assessing the effectiveness and selection of the passive cooling. These charts are based on the typical dry bulb temperature and humidity extracted from the typical meteorological years (TMY) at a given location.
12. What is cooling load? Ans: It is the thermal energy that must be removed from the space in order to maintain the desired comfort conditions.
13. Why are HVAC systems used? Ans: HVAC systems are used to maintain thermal conditions in comfort range.
14. List down the purposes of load estimate Ans: Load profile over a day Peak load Operation energy analysis HVAC construction cost.
15. List down the principles of cooling load estimate Ans: Enclosure heat transfer characteristics Design condition Heat gains Thermal capacity
16. What are the different types of heat transfer Ans: conduction, convection, radiation
17. Define space heat gain Ans: The instantaneous rate at which heat enters into , out of, or generated within a space.
18. Define space cooling load. Ans: The rate at which heat must be removed from a space to maintain air temperature and humidity at the design values.
19. What is space heat extraction rate? Ans: The actual heat removal rate by the cooling equipment from the space. The heat extraction rate is equal to cooling load when the space conditions are constant which is rarely true.
20. What is cooling coil load? Ans: the rate at which energy is removed at the cooling coil.
21. What are different types of external loads? Ans: heat gain from walls and roof Solar gains through fenestrations Outdoor air


