3 minute read
CENEBA BIOPROCESS
Rapid quantification and identification of product impurities (nitrosamines)
The recent product impurity crisis has firmly put the spotlight on genotoxic impurities (GTI’s). Nitrosamines, or more correctly N-nitrosamines, refer to any molecule containing the nitroso functional group. These molecules are of concern because nitrosamine impurities are probable human carcinogens, signifying that long-term exposure above certain levels may increase the risk of cancer development. Although they are also present in some foods and drinking water supplies, their presence in medicines is nonetheless considered unacceptable.
Advertisement
The regulatory agencies, including the US FDA and the European Medicines Agency (EMA), have issued guidelines on the allowable limits of genotoxic impurities in pharmaceutical products. These limits are to ensure product safety, not just for the ones frequently highlighted because of nitrosamines, but for all potentially contaminated drugs and processes in a company’s portfolio of active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs).

The CHMP and CMDh extended the deadline for submitting variation applications for chemical medicines from 26 September 2022 to 1 October 2023 in July 2022.
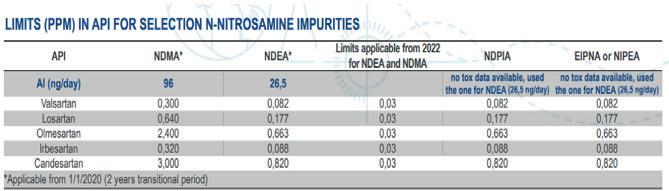
Hardly a day goes by without mention of a newly emerging active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) nitrosamine, eg, nitrosamine propranolol. This has led to a great deal of pre-competitive data sharing. Many companies have initiated a Nitrites in Excipients database to facilitate risk assessment of drug products.
The database categorises excipients thus: 1) excipients show varying nitrite contents with pronounced batch-to-batch variance, 2) the nitrite impact is dependent on the amount of excipient in a product, 3) these excipients show low nitrite levels and low variability, resulting in an average value of 1 μg/g nitrite, and 4) different excipient vendors show pronounced differences in nitrite levels. A recent open-access publication discusses the generation of acceptable intakes for unknown API nitrosamines.
The authors catalogued these complex nitrosamines based on common structural features, identifying 13 groups in total. Carcinogenicity data was then reviewed for structurally relevant nitrosamines and group-acceptable intakes were derived based on the most potent compound within each group. The authors indicated that the acceptable intakes of several of these API nitrosamine groups were found to be much higher than the corresponding simple nitrosamines, which results in a commensurately higher analytical LoQ.

In CENEBA BIOPROCESS a mexican analytical lab located in Jalisco, we have a validated method to Highly selective and sensitive method for quantitation of nitrosamines in pharmaceutical products, in compliant with FDA regulation limits and EMA, and recently stablish by FEUM 13va Ed. also in Mexico.

A rapid method for quantifying nitrosamine compounds with confirmation to the Analysis of genotoxic nitrosamines in active pharmaceutical ingredients, by HPLC-MS/MS.