1 minute read
Key Takeaways
KEY TAKEAWAYS
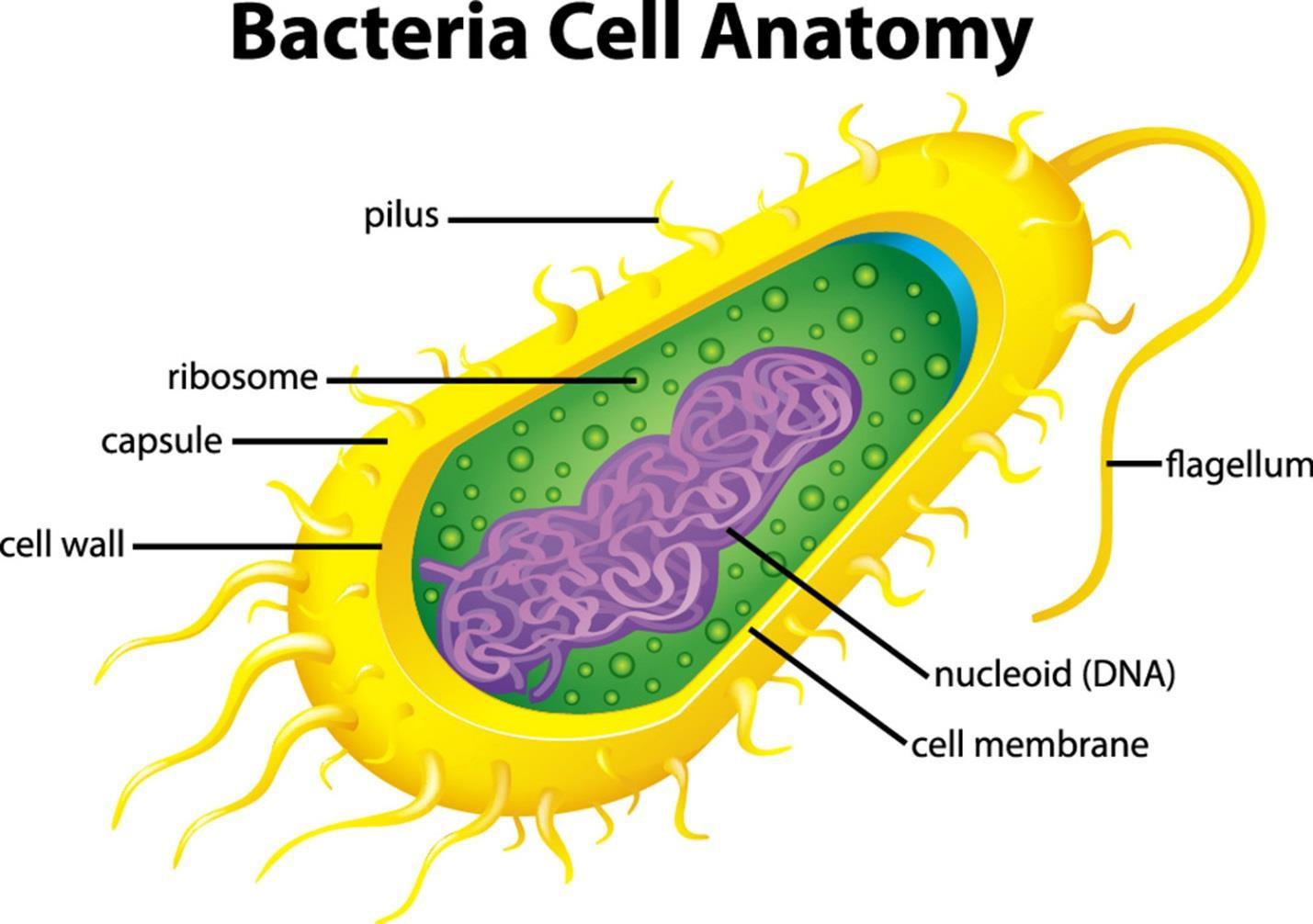
• The study of genetics in some form has existed since ancient times, when philosophers thought about dominant and recessive traits, and speculated on how these might get passed to one’s offspring. • The first uses of genetics happened when individuals worked with plants to create plant hybrids. • Mendel’s work on pea plants was done without his knowing about the existence of genes. • There are many branches of genetics, including classical, molecular, and population genetics. • The basic unit of genetics is the gene. Genes are arranged on chromosomes. The chromosomes are circular in prokaryotes and linear in eukaryotes. • Chromosomes must pack themselves into small spaces. This happens through supercoiling in prokaryotes and through the use of histone proteins in eukaryotes. • The molecular expression of genes starts with transcription, proceeds with translation, and ends with post-translational modification of proteins. • The genetic code is based on codons that themselves are made from triplets of nucleotides that together determine what amino acid gets made from a specific segment of DNA or RNA. • There are some traits based on single genes, while most traits in complex organisms depend on the interaction of several genes at once.
Advertisement