1 minute read
Pollution
pollution
The World Health Organization (WHO) defines pollution as the introduction of contaminants or harmful substances into the environment, resulting in adverse effects on the natural ecosystem, living organisms, and human health. Pollution can take various forms and can occur in different environments, including air, water, and soil.
Advertisement
(UNEP, 2022)
United nations Environment programme
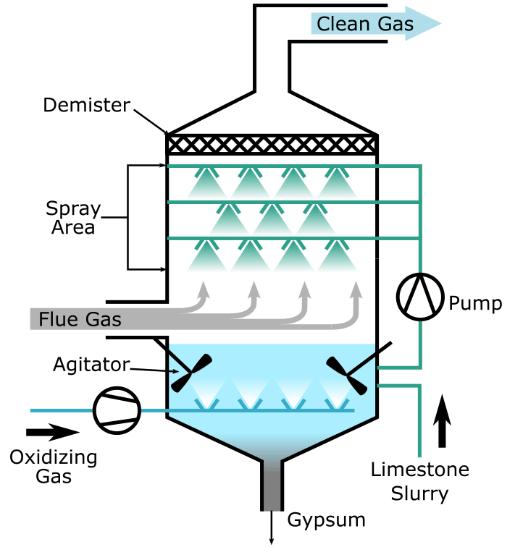
Contamination of the air by harmful substances, including gases, particulate matter, and pollutants, that can be harmful to human health and the environment.
Contamination of water bodies, including rivers, lakes, oceans, and groundwater, by the introduction of harmful substances, such as chemicals, toxins, pathogens, or pollutants, which can negatively impact water quality, aquatic life, and human well-being.
Contamination of the environment by radioactive substances, such as those released from nuclear accidents, nuclear waste, or nuclear weapons testing, which can pose health risks to living organisms and ecosystems.
Contamination of soil by pollutants, including chemicals, heavy metals, pesticides, or improper waste disposal, which can lead to soil degradation, reduced fertility, and potential harm to plants, animals, and humans.
The accumulation of plastic waste in the environment, particularly in oceans and waterways, which can harm marine life, damage ecosystems, and have potential implications for human health.