3 minute read
Diversity
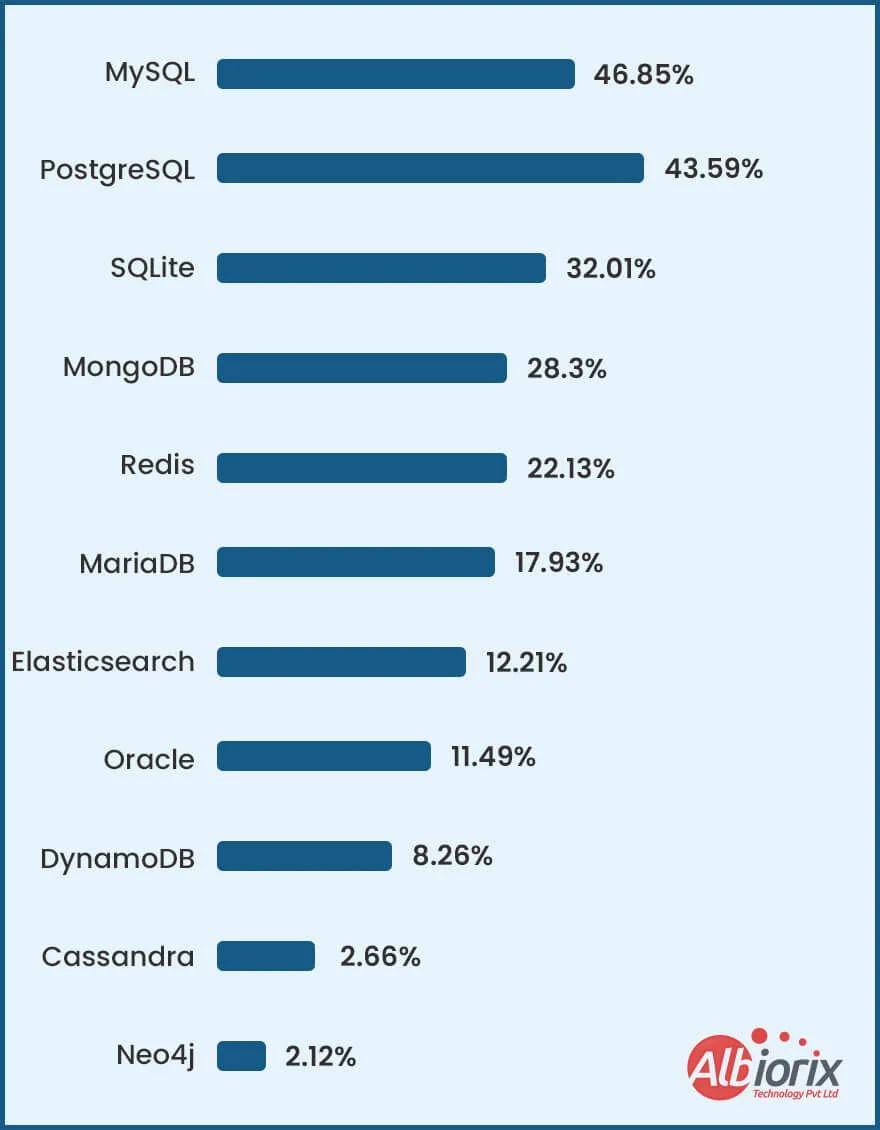
Your code is stored in databases like MySQL, PostgreSQL, or MongoDB. A tech stack's databases are an essential component. You need a location to store all your information, regardless of how straightforward or complex your application. MongoDB and MySQL are two common databases. In addition to storing and retrieving data, contemporary data platforms like MongoDB also offer cognitive querying, aggregation, and transformation capabilities. A computer software or physical device known as a server, such as Apache, Nginx, or IIS, distributes (or serves) your programmed content to users as a website or application. A web server receives HTTP requests from the client (such as a browser), sends them to the database, retrieves the needed data, and manages the answer. Depending on the project's styling requirements, a user interface to employ markups like HTML and CSS stylesheets, or frameworks like Bootstrap orTailwind.
Advertisement
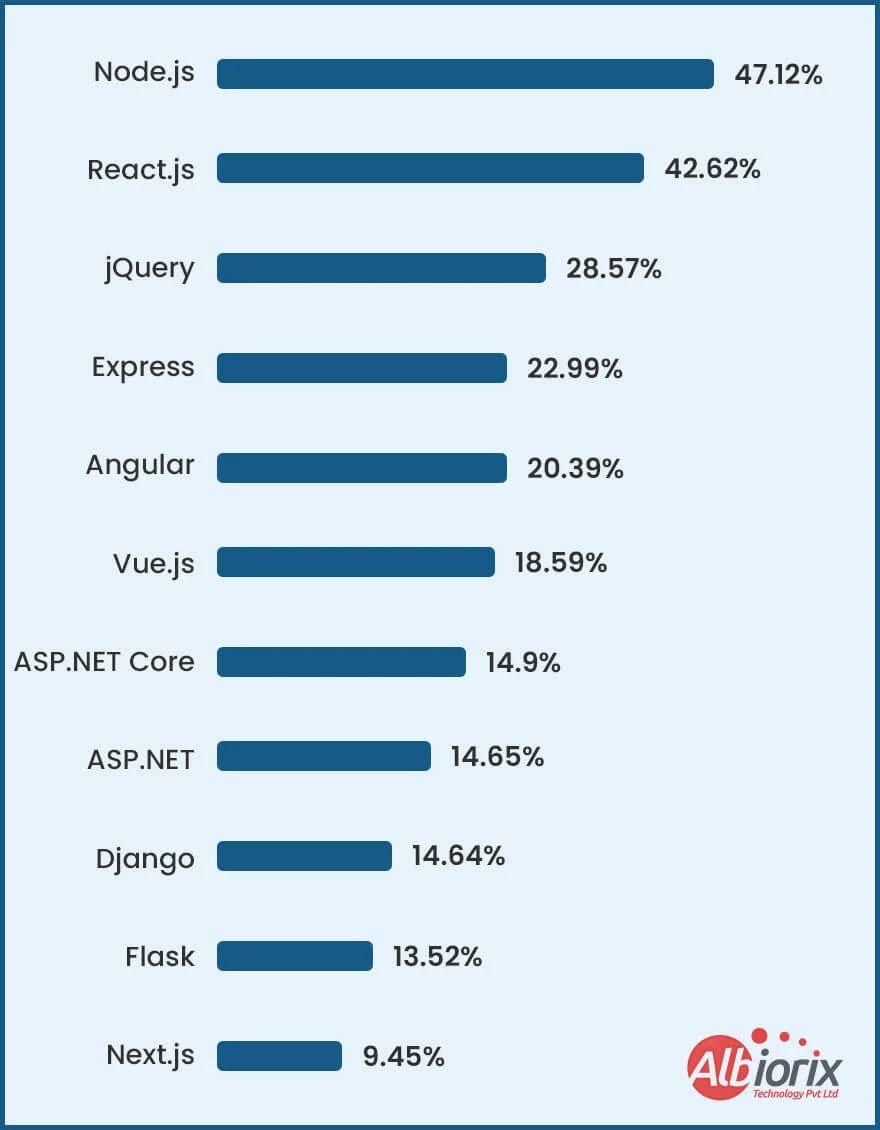
The runtime environment is the terminology by which an application is run. Runtime provides cross-platform compatibility. Java Runtime Environment (JRE), Node.js, and Common Language Runtime (CLR) are examples of runtime environments. Other elements, like as APIs, BI and analytics tools, cloud services, and microservices, can improve an application's capabilities.
What is a Tech Stack Used For?
The primary aim of creating a tech stack for your application is to
● Maximize the application efficiency
● Enhance the productivity of your application
● Improve the performance and security of the application
Selecting the perfect tech stack for your application is an essential factor that you need to consider for your entire website or app development process. Moreover, the selection of the right tech and tools makes it easy for you to build faster and more responsive apps.
Difference Between Web and MobileApp Tech Stack
After having a look at the basic concept of what is a tech stack, let’s focus on understanding the difference between web and mobile app stacks.
❖ MobileApp Tech Stacks
For developing a mobile application for your business, you need to take into account various user perspectives. In simple words, you need to make applications for different devices as day by day new devices are getting launched in the market. And if we talk about mobile app development, you need to be ready with various mobile apps platforms likeAndroid and iOS. Apart from Android and iOS app development, there exists an option where you can write the same code for both technologies and that’s what is called cross-platform technologies.
Let’s start by understanding theAndroid tech stack.
Java is the only primary language that is specifically used for developing Android applications.This language is fully-supported and has great scalability.
Android Studio is the official development platform for Google’sAndroid app.
Android UI comes up with pre-built templates that are handy for developers to build user interfaces quickly
Apart from Java, Kotlin is the most-preferred language for developing Android apps.The good part is that it is considered to be the second official Android development language by Google.
Built upon Jetbrain’s technology, it provides an intuitive interface for developers to buildAndroid apps.
Android UI make use of prebuilt Android UI components, like structured layout objects and UI controls, to build the graphical user interface for your applications.
Programming Language iOSApp Development Tools UI Framework
Objective-C is the original language used to build the iOS app. Nevertheless, building an app with Objective-C isn’t easy, and developers are prone to make mistakes with it.
Xcode –An official development tool byApple, and it’s your easy-to-use platform whether you’re using Swift or Objective-C. It comes up with all the features needed to build the native iOS mobile app, including a visual interface builder.
UIKit – UIKit is the basic framework for building graphical components in the iOS app. It contains templates defining the UI elements which form the building blocks of the app.
Swift is a relatively newer language and developers are favouring it over Objective-C. With its safer syntax, fewer mistakes are committed and apps are developed in much less time. It’s also easier to find developers adept in Swift as it’s easier to learn and master.
AppCode – Developed by a 3rd party,AppCode is an open-source alternative to XCode. While it enables iOS mobile app development, it lacks the features of XCode and to an extent, is still dependent on the latter.
SwiftUI – SwiftUI is a newer framework that offers a more efficient way of designing UI elements in iOS apps. However, it only works for iOS 13 and above, and there are limited resources as it was just launched in 2019.
The cross-platform tech stacks.
● React Native (JS)
● Flutter (Dart)
● Xamarin (C#)
❖ WebApp Tech Stack
Compared to the mobile app, desktop apps works differently. You don’t need to download a web app to your device to use it. Web app tech stacks use resources that are available in an internet browser. There are many internet browsers, and your tech stack should work with all of them. However, it’s wise to test your websites and online applications on all the most popular browsers to make sure it works the way you expect.


