Jobs and social cohesion
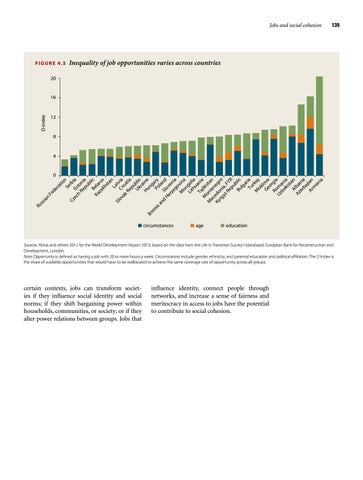
FIGURE 4.5
139
Inequality of job opportunities varies across countries
20
D-index
16
12
8
4
Ru
ss
ia
n
Fe
de
ra
tio Se n rb Cz ec Es ia h to Re ni pu a b Be lic Ka la za ru kh s st an La tv Sl ov C ia ak roa Re tia pu Uk blic ra Hu ine Bo ng sn Po ary ia an la d Sl nd He ov rz en eg ia o M vin on a Lit gol hu ia Ta ani M jiki a M ont sta ac en n Ky edo eg rg ni ro yz a, Re FY pu R b Bu lic lg ar Tu ia r M key ol do Ge va o Ro rgia m Uz a be ni kis a t A an Az lba er nia ba Ar jian m en ia
0
circumstances
age
education
Sources: Abras and others 2012 for the World Development Report 2013; based on the data from the Life in Transition Survey I (database); European Bank for Reconstruction and Development, London. Note: Opportunity is defined as having a job with 20 or more hours a week. Circumstances include gender, ethnicity, and parental education and political affiliation. The D Index is the share of available opportunities that would have to be reallocated to achieve the same coverage rate of opportunity across all groups.
certain contexts, jobs can transform societies if they influence social identity and social norms; if they shift bargaining power within households, communities, or society; or if they alter power relations between groups. Jobs that
influence identity, connect people through networks, and increase a sense of fairness and meritocracy in access to jobs have the potential to contribute to social cohesion.