TIMES
















Indices play a crucial role in gauging the performance of the Indian stock market. They offer investors a concise representation of how a specific segment or the overall market is behaving.
Major Stock Exchanges:
• Bombay Stock Exchange (BSE): Established in 1875, the oldest stock exchange in Asia. Its flagship index is the BSE Sensex.
• NationalStockExchange(NSE): Founded in 1992, the leading stock exchange in India. Its benchmark index is the Nifty 50.
Popular Indices:
• BSE Sensex: Tracks the performance of the top 30 blue-chip companies listed on the BSE. Represents approximately 70% of the market capitalization of the BSE.
• Nifty50: Represents the top 50 companies by market capitalization and liquidity on the NSE. Covers around 65% of the market capitalization of the NSE.
• Nifty Next 50: Tracks the next 50 companies after the Nifty 50 in terms of market capitalization and liquidity on the NSE.


• Nifty 200: Covers the top 200 companies by market capitalization and liquidity on the NSE.
• S&P BSE All-Cap: A broader index encompassing over 2000 companies across the BSE's large, mid, and small-cap segments.
Types of Indices:
• Market Capitalization-based: Indices like Sensex and Nifty are based on the market capitalization of the included companies.
• Sectoral Indices: Focus on sectors like banking, IT, and infrastructure.
• Thematic Indices: Track companies based on themes like sustainability or clean energy.
Importance of Indices:
• Benchmarking Performance: Investors compare their portfolio returns against index performance to evaluate their investment strategies.
• Market Trend Assessment: Indices provide insights into the overall market sentiment and direction.
• Diversification Tool: Sectoral and thematic indices help investors diversify their holdings within specific sectors or themes.
In the last five years, the Indian stock market has outperformed many major markets around the world. The following is a breakdown of its performance:
Market as a Whole:
• Nifty 50: Over the last five years (as of December 26, 2023), the benchmark index, which represents the top 50 companies by market capitalization, has delivered an annualized return of 18.8%. This is significantly higher than major developed market returns such as the S&P 500 (6.9%) and the Nikkei 225 (12.1%).
• BSE Sensex: The Bombay Stock Exchange's flagship index also delivered strong returns, with an annualised gain of 17.5% over the last five years. This highlights the Indian market's overall positive performance.
Sectoral Performance:
IT Sector: The IT sector has been a key driver of the market's growth, with the Nifty IT index delivering an annualized return of 27.8% in the last five years. This is due to factors like India's strong IT talent pool, growing domestic demand, and the increasing adoption of technology globally.
Pharma Sector: The pharma sector has also been a bright spot, with the Nifty Pharma index delivering an annualized return of 21.6% in the last five years. This due to factors like India's growing healthcare market, increasing government spending on healthcare, and the rising demand for generic drugs.

Key
• Strong Economic Growth: India has been one of the fastestgrowing major economies in the world, with GDP growth exceeding 7% in recent years. This strong economic growth has fuelled corporate earnings and boosted investor sentiment.
• Government Reforms: The Indian government has implemented various reforms aimed at improving the business environment and attracting foreign investment. These reforms have helped to make the Indian market more attractive to investors.

• Rising Disposable Income: Rising disposable income in the hands of Indian consumers has led to increased demand for goods and services, which has benefited companies across various sectors.
• In 2023, the Indian stock market displayed dynamic fluctuations influenced by both domestic and international factors. The year began with a bullish rally but encountered a corrective phase in October, creating a challenging period for blue-chip stocks. November saw remarkable milestones, with BSE Sensex and NSE Nifty reaching unprecedented highs.

• The market's year-on-year return for 2021 stood at an impressive 21.5%, outperforming the global average. Strong corporate earnings, economic recovery, and supportive policies contributed to this robust performance. However, challenges included elevated inflation, rising interest rates, geopolitical tensions, and valuation concerns.
• As the year concluded, experts expressed caution for 2024, citing potential headwinds like slowing growth, regulatory uncertainties, and increased competition from emerging markets. The Indian market exhibited resilience, paralleling global trends and surpassing Hong Kong to become the seventh-largest in the world.
• The events that are to be noted included the Nifty 50 index reaching a historic high and a significant market valuation milestone. By the end of November, the Nifty 50 index showed a remarkable year-to-date performance, surging by 16%.
• Despite a gradual economic slowdown, market experts predicted a 9% rise in India's stock market by the end of 2023. The Reserve Bank of India's (RBI) decision to maintain the repo rate at 4% and adopt an accommodative stance on December 8, 2023, was pivotal.
• The accommodative stance signals the RBI's commitment to supporting economic growth by boosting liquidity and encouraging borrowing. Maintaining the repo rate at 4% suggests a pause in the current rate cycle, influencing borrowing costs and economic activity. This stance is expected to stimulate investment and consumption, fostering a positive market sentiment.
India has emerged as the fifth-largest equity market globally, showcasing relative resilience compared to the impact of the Covid pandemic and the Ukraine war on globalequities in 2022. The country's share in global market capitalization has reached an all-time high of 3.5%, rebounding from a low of 2.05% in 2020 after the pandemicinduced market collapse. This outperformance is attributed to India's robust economic growth, leading to increased attractiveness for investors. Despite short-term decoupling from global markets, the absolute performance of the Indian market has been nearly flat. However, high valuations pose a risk, especially in the face of adverse events, with potential vulnerabilities including elevated US interest rates and a strong US dollar. Foreign institutional investments (FIIs) have played a significant role, driving Indian markets since August, and the MSCI India index has outperformed the MSCI Emerging Market index by 27%.
India has rebounded from the COVID-19 pandemic shock to become the fifth-largest economy, with a strong 7.8% GDP growth in the first quarter of FY23. The services sector, driven by pent-up demand and vaccination coverage, is anticipated to be a key growth driver in 2022–2023. In April-September 2023, India's service exports reached US$ 164.89 billion, while overall exports (services and merchandise) stood at US$ 376.29 billion. The government's future capital spending is expected to be supported by factors like tax buoyancy, low tax rates, and digitization. Increased investment in infrastructure and assetbuilding projects, along with a revival in agriculture, is set to boost growth. India's status as the fastest-growing major economy is reinforced by its robust democracy and global partnerships, making it an attractive investment destination amid global unpredictability.
While the Indian stock market has performed well in the last five years, some challenges could impact future performance. These include rising global interest rates, geopolitical tensions, and potential domestic economic slowdown. However, India's long-term growth prospects remain strong, and the stock market is expected to continue to deliver attractive returns for investors over the long term. Investors are keenly watching for future rate cuts, contingent on economic conditions and inflation trends remaining within the central bank's comfort zone. Global factors, including the U.S. Federal Reserve's decisions and global economic conditions, also impact India's monetary policy.
The Indian derivative market is a vital component of the financial landscape as it allows investors and traders to manage risk, speculate on prices, and develop various investment strategies. The Indian derivatives market has expanded rapidly in recent years, with a yearly

increase of more than 20% on average. The Indian derivatives market is young relative to established markets, but it has enormous growth potential in the future. Technological advances and regulatory initiatives are expected to improve market transparency and efficiency even further. The Indian derivatives market has grown significantly

since its inception in 2000, overtaking the cash market in terms of volume and contracts traded. The derivatives market's share of the total financial market turnover in India has almost doubled in the past decade, now exceeding 25%.
Products of derivative Markets.
Derivatives derive their value from an underlying asset, which can be stocks, indices, commodities, currencies, or even interest rates. The introduction of new products and reforms by SEBI (Securities and Exchange Board of India) has further boosted market activity.
Exchange Traded Derivatives (ETDs): These are standardized contracts traded on the exchange itself. Examples include futures and options on stocks, indices, and commodities.
• Equity Derivatives:
1. Futures: Contracts to buy or sell a specific stock/index at a predetermined price and future date.
2. Options: Right, but not obligation, to buy or sell a stock/index at a set price by a certain date.
3. Index Derivatives: Futures and options based on major indices like Nifty 50, Nifty Bank, etc.
• Commodity Derivatives: Contracts based on underlying assets like agricultural commodities, metals, etc.
• Currency Derivatives: Futures and options on various currencies for managing foreign exchange risk.
These are customized contracts negotiated directly between two parties, not traded on the exchange.
These platforms are electronically driven and fully automated, ensuring transparency and fast execution of trades.
Exchanges
• National Stock Exchange (NSE):-Leading exchange for equity derivatives, accounting for over 90% of market share.
• BSE India: The other major exchange offering equity and currency derivatives.
• MultiCommodityExchange(MCX): Largest platform for commodity derivatives.
• National Commodity and Derivatives Exchange (NCDEX): Another important commodity derivatives exchange.
The use of derivatives for hedging by corporations and institutions is increasing, which helps to maintain market stability. Since 2000-2001, market turnover has increased nearly 4600-fold, from Rs. 2365 crore in 2000-2001 to a staggering Rs. 11010482.20 crore in 2008-2009. The Indian derivatives market had a daily average turnover of around Rs. 8.5 lakh crore (approximately USD 102 billion).
Open Interest is estimated to be around Rs. 3.8 lakh crore (approximately USD 46 billion), indicating market participants' expectations and positions. The NSE-Nifty 50 F&O segment is the most actively traded, with an ADT of Rs. 5.5 lakh crore (approximately USD 66 billion). Similarly, the number of contracts traded has skyrocketed. The National Stock Exchange (NSE), which accounts for 99% of Indian derivatives trading, saw a record 58.54 billion contracts traded in the equity derivatives segment alone in FY23, nearly reaching the entire previous year's volume of 41.76 billion. Recent regulatory changes are SEBI implemented stricter margin requirements for certain derivatives contracts in August 2023, aiming to reduce volatility and leverage concerns.
Orders placed on the platform are matched automatically based on price and time priority. Buyers and sellers with matching orders are connected, and the trade is executed at the agreed-upon price. Derivatives trading involves leverage, meaning you only need to deposit a fraction of the contract value as a margin. However, this also amplifies gains and losses. If the price of the underlying asset moves against your position, your margin can be eroded, and you may be required to deposit additional funds to maintain your position. All trades executed on the platform are cleared and settled by a clearing corporation to ensure smooth delivery of contracts and minimize counterparty risk.
For the first time in 2018, the NSE's equity derivatives segment had a higher turnover than the NSE's cash market. This was a significant milestone. The volume of the derivatives market has surpassed that of
the cash market by a wide margin. While historical data is difficult to compare, recent statistics show a significant difference. Nifty futures and options contracts on the NSE recorded a turnover of Rs. 8.28 lakh crore in October 2023, dwarfing cash market activity. This dominance is also reflected in the trading velocity. India has a significantly higher ratio of derivatives trading volume to cash market volume than other major economies, indicating a vibrant and active derivatives market.


Improved liquidity and price discovery:- Derivatives may enhance underlying asset liquidity by bringing in more investors who can take positions without directly buying or selling the asset. As a result of the market reacting faster to new information and changes in supply and demand, price discovery may become more efficient.
Risk management:- Derivatives enable investors to hedge existing positions and better manage risk. Options, for example, can be used to limit potential losses on a stock holding, whereas futures can be used to lock in a future price for an asset.
Expanded investment opportunities:- Derivatives provide investors with a broader range of investment options and strategies. For example, they can be used to take leveraged positions, speculate on future prices, or build customized investment portfolios.
Increased market efficiency:- Derivatives can increase market efficiency by facilitating the transfer of risk and capital to those best suited to manage it. Lower transaction costs and a more stable market environment may result.
Increasedvolatility:- Derivatives, especially when used for speculation, can increase the volatility of the underlying asset. This is since large derivative positions can quickly magnify price movements in the underlying asset.
Systemic risk:- The derivatives market's interconnectedness can increase systemic risk, which means that problems in one part of the market can quickly spread to other parts. This was evident during the 2008 financial crisis, when the subprime mortgage market collapse triggered a domino effect that resulted in widespread financial instability.
Market manipulation:- If derivatives are not properly regulated, they can be used to manipulate markets. Short-selling derivatives, for example, can be used to drive down the price of an asset.

Lack of transparency: - The complexity of some derivatives can make it difficult to understand the risks involved, which can lead to problems for investors.
Although growth is undeniable, there are still worries regarding investor education and possible systemic risks due to high leverage. However, with ongoing regulatory efforts and market advancements, the Indian derivatives market is projected to maintain its robust growth trajectory, offering a platform for efficient risk control and advanced strategies for investment.

Corporate bonds have an inverse relationship to interest rates; their value decreases with an increase in interest rates and increases with a decrease in interest rates. Generally speaking, the percentage of price volatility increases with maturity. The significance of corporate bond funds is distinct. Investors might make a judgment by taking important risk considerations into account.
Because one will get the bond at face value, or par value, at maturity, holding the bond until maturity reduces the risk of price swings, often known as market risk or interest-rate risk. The bonds are less worthy because of the negative relationship between interest rates and bonds.
The highest-rated investment-grade bonds are designated as AAA bonds. These ratings are given by Indian credit-rating organizations such as CRISIL, ICRA, CARE, and India Ratings, following an evaluation of the risk associated with each bond as well as the issuer's operational and financial stability.
Below are the top 10 bonds rated AAA in the bond market in India:
Investment-grade bonds with an AA rating are highly regarded. PSU and corporate bonds in India are rated by several Indian rating agencies, including CRISIL, ICRA, CARE, and India Ratings. The bond rating of a corporation is determined by these rating agencies based on a variety of variables, including financial indicators such as leverage and interest coverage ratios.
These bonds are rated as investment-grade, and the coupon rate represents the interest rate paid by the issuer to the bondholder. Investors often consider such information when making investment decisions, taking into account factors like the issuer's creditworthiness, maturity date, and prevailing interest rates in the market.
Bonds with a AAA rating provide a dependable investment option with advantages for diversification, stability, and consistent income. These bonds are backed by issuers who maintain sound financial standing and sound management procedures. If you want to buy safe investment products, you can buy AAA-rated bonds.
These bonds are considered investment-grade, with an AA rating, suggesting a relatively high credit quality. Investors often look at factors like coupon rates, maturity dates, and the financial health of the issuer when considering such bonds for investment.
1. Government bonds issued by entities like PFC, IRFC, REC, and NHAI are typically considered safe investments due to their AAA ratings.
2. Treasury bills and Cash Management Bills are short-term debt instruments issued by the government for managing its short-term financial needs.
3. Investors often consider factors like coupon rates, ratings, and tenures when deciding to invest in government bonds as they play a crucial role in the fixed-income market and are considered relatively low-risk investments
The current yield in India's bond market short-term and long-term:
India Short-Term Government Bond Yield


▪ India: Month-end yield on short-term government bonds In September 2023, one year was recorded at 7.06 percent pa, up from 6.99 percent pa the month before.

▪ Data on India's Short-Term Government Bond Yields is available from May 1996 to September 2023 and is updated every month.
▪ The data set a record low of 3.46% pa in November 2020 and an alltime high of 13.01 percent pa in January 1998.
▪ CEIC Data reports on the yield on short-term government bonds.
The Year 2022:
The year 2022 presented challenges for the bond market, as reflected in the performance of the widely used bond benchmark, the Crisil Composite Bond Index. This index saw a modest increase of approximately 3 percent, which was notably lower compared to the returns of other major asset classes. Gold outperformed with a growth of about 14 percent, equities showed a 6 percent increase and even cash saw a 5 percent gain.
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) responded to economic conditions by raising policy rates by 225 basis points, bringing the rate to 6.25 percent. This move was part of a broader trend among major global central banks to address inflation concerns aggressively. The central banks, including the RBI, conveyed a commitment to combat inflation, even if it meant sacrificing some economic growth. This resulted in a notable rise in both domestic and global bond yields.
The impact of these developments was evident in the muted gains across various bond mutual fund categories. The environment of rising interest rates and central banks prioritizing inflation control created headwinds for bond investors, influencing the relative performance of different bond categories.
The Year 2023:
The assessment for 2023 is more favourable for bond investors, with the expectation of stabilized yields, an attractive yield environment, and a perceived value in bonds relative to equities. The dynamics of central bank policies and real yields in comparison to other emerging markets play a significant role in shaping this outlook.

Hedge funds is a type of Mutual Funds that is Funded by HNI’s (High Net worth Individuals), Institutional Investors and Accredited Investors. Usually is regulated by Fund managers in India It may also refer to Investment pools like Venture Capital Funds, Private Equity Funds and Commodity pools.
In India Hedge Funds is being Regulated by SEBI (Securities Exchange Board of India) in 2012 by Alternative Investment Funds Regulation.
Hedge Funds in India use different Trading techniques because of Multiple assets and Securities they invest like Fine/Modern Arts, Crypto Currency, Foreign Currencies, and even Patents.
They are total 3 types and 4 strategies Broadly used in Hedge Funds.
Types:
1) Offshore: Located in less tax environment countries regardless of home country

2) Domestic: Fund located within the country limited to investors subject to taxation.
3) Fund of Funds: Operates as a mutual fund that directs investment into diversified portfolio of multiple hedge funds
Strategies:
1) Long or Short Equity: Seeks to generate Returns by taking long and short positions in Individual tasks
2) Global Macro: In this they consider Macro Economic Factors like Interest rates and Forex rates to invest
3) Event Driven: If the company is going through significant corporate events such as Merger, Acquisition and bankruptcy.
4)Quantitative: Most important of all strategies as this uses Mathematical Models and Algorithms to identify Investment opportunities.

Tax Rate in India:
Right now in India hedge funds belong to category III AIF (Alternative Investment Funds) If the Annual Earnings exceed 5 Cr then the tax rate is 42.74% and If its below 5 Cr then 30% and also the Fees of Hedge Funds 2% Management Fees and 20% Performance Fees.
Hence the Risk and Return in the Hedge Funds and extremely Volatile and also because of the Low level Regulation in SEBI.
Top Performing Indian Hedge funds:


The world's largest stock market, accounting for approximately 42.5% of the global stock market, is the United States Stock Market. Right now, the U.S. stock market is valued at $46.2 trillion overall. Over the past few decades, U.S. stocks have frequently outpaced those of other wealthy countries. An investor's 1990 $100 investment in the S&P 500 would have grown to almost $2,000 in 2023, or four times the returns observed in other industrialized nations.
• Dow Jones Industrial Average (DJIA): 30 sizable, publicly traded corporations that are listed on the Nasdaq and the New York Stock Exchange (NYSE) are represented by the DJIA. The index is priceweighted. The DJIA has a market value of US$10.9 trillion. It is now trading at US$ 37,385.97 as on December 25, 2023.
• S&P 500 Index: 500 of the biggest publicly traded firms in the United States are included in the market capitalization-weighted S&P 500 index. It is a comprehensive indicator of the U.S. stock market's overall performance. S&P 500 Index market capitalization is $33.8 trillion USD. It is now trading for $4,754.63(as of December 25, 2023).
• Nasdaq Composite Index: All of the stocks listed on the Nasdaq stock market are part of the Nasdaq Composite. It is renowned for having a large concentration of stocks linked to technology and the internet.
The largest, most liquid, and most efficient equities markets in the world, the U.S. equity market will hold 42.9%, i.e., $45.5 trillion, of the $106.0 trillion global equity market valuation in 2023. This exceeds China's market share by a factor of 4.1. Over the past ten years, the U.S. market share has averaged 38.9%, peaking at 42.9% in 3Q23 and falling to 36.6% in 2015.
The Magnificent Seven:-
The Magnificent Seven stocks are a collection of prominent and profitable U.S. stock market firms, including Tesla, NVIDIA, Amazon, Apple, Meta Platforms, Microsoft, and Alphabet.
By December 15th, the return on the S&P 500 was primarily due to the Magnificent Seven. total weight of these businesses exceeds the total weight of top 7 corporations in S&P history.
Trillion
table shows the Top 5 Performing sectors in US Stock Market in 2023. Consumer Durables Sector has the best Performance. Investors are confident in long-term growth rates and are upbeat about the US consumer durables market. Compared to its three-year average PE of 10.6x, the industry is currently trading at a PE ratio of 14.8x.
Graph shows the Comparison between the Total market cap and Earnings and revenue of the Consumer Durable Industry performed very well in US stock market when compared to other sectors

Throughout 2023, interest rates have stayed consistently high. The goal of the Fed's interest rate increases was to reduce inflation and slow down the economy. The federal funds target rate, which the Federal Reserve (Fed) controls, was raised by the Fed through July and is now between 5.25% and 5.50%.
The aim is to avoid sending the economy into a recession by bringing inflation, which peaked at 9.1% in the middle of 2022, closer to its target of 2%. If interest rates move higher, stock investors become more reluctant to bid up stock prices because the value of future earnings looks less attractive versus bonds that pay more competitive yields today. Increasing interest rates can create a more challenging environment for stocks in the face of more attractive yields for certificates of deposit and other vehicles.

Since 2003, the size of the world's equities markets has almost tripled, reaching a total market capitalization of $109 trillion. The expansion of the money supply and exceptionally low interest rates have supported soaring asset values in all economies during the past few decades.

In 2024, the Magnificent Seven stocks, generative artificial intelligence, economy+, Presidential Elections will all be significant factors.
• Fed Rate Reductions
The Federal Reserve paused short of declaring that rate hikes will end at its December meeting, as policymakers scheduled 75 basis point reductions in interest rates for 2024. The Fed committee members anticipate reducing its key policy rate from the current range of 5.25% to 5.5% to 4.6% by the end of 2024, according to the most recent set of quarterly predictions. This is less than the September forecasts that stated the federal funds rate would end the next year at 5.1%.
• The Presidential Election
The stock market has a lengthy history of outperforming during presidential election years and even the years leading up to the election. Election years typically see a rise in stocks. The S&P 500 has never had a negative year in a year when there is a presidential re-election since 1952. The net market gain during the final two years of each of the 48 presidential administrations since 1833 was 772%, far more than the gain of 336.5% during the first two years of these terms.
• Regional Banking Crisis 2023
The regional banking crisis of 2023 sent shockwaves through the financial sector, with certain banks suffering substantial unrealized losses due to quickly increasing interest rates. Larger firms will be comparatively well-positioned to maintain their market share as regional banks lacking in scale will be disproportionately pressured to reduce cost bases and optimize loan composition, hence diminishing their ratings.
• Artificial Intelligence Stocks
Driven by the excitement about generative artificial intelligence, the year 2023 saw a surge in semiconductor, computer hardware, and software investments by tech businesses. Nvidia was the largest AI stock in 2023. The Magnificent Seven, C3.ai (AI), and Palantir Technologies (PLTR) are important AI stocks. The focus in 2024 will shift from AI's "creators" to AI's "adopters," spanning a wide range of sectors and industries, as businesses prioritize capital expenditures that increase productivity.
Despite persistent pressure from rising interest rates, Wall Street experts predict S&P 500 earnings will continue to rise in the upcoming quarters. Analysts predict that the S&P 500 will rise even more in the upcoming year. For the S&P 500, the average analyst price target is currently 5,038.15, indicating more gain in the upcoming 12 months.
The Dow Jones Industrial Average will probably lag in 2024 if investors' desire for growth and tech stocks doesn't abate. However, if the US economy enters a recession, investors might turn to blue-chip companies for protection. Salesforce, Microsoft, Intel, and other
technology stocks have been among the Dow's best-performing equities of 2023.
The NASDAQ index had an exceptionally good start to the year, but Treasury yields continued to rise until October. Although it will be difficult to match this year's performance, another 15% gain is a feasible goal, and the NASDAQ might very well touch the 19,000 mark in 2024. In 2023, the NASDAQ and interest rates showed minimal relationship. The NASDAQ index had an exceptionally good start to the year, but Treasury yields continued to rise until October.
Equity Derivatives:
Stock Options: Granting the option to purchase or sell a particular stock by a specific date at a predefined price, but not the duty to do so.
Exchanges: NYSE Arca, Nasdaq, CBOE
Stock futures: Contracts to purchase or sell a certain stock at a fixed price on a future date.
Exchanges: Nasdaq, CME, and CBOE
Index Derivatives:
Index Options: Comparable to stock options, but determined by an index of the market's performance, such as the S&P 500. Exchanges: Nasdaq, CME, and CBOE
Index Futures: contracts to purchase or sell a market index at a fixed price on a future date. Exchanges: CME and CBOE
Commodity Derivatives:
Commodity Options: Options to purchase or sell a particular good, such as maize, gold, or oil, at a set price by a given date. Exchanges: ICE, NYMEX, CME
Commodity Futures: are agreements to purchase or sell a certain good at a fixed price on a future date. Exchanges: ICE, NYMEX, CME
Currency Derivatives:
Currency Options: Options to buy or sell a particular pair of currencies by a given date at a fixed price. Exchanges: ICE, CME, CBOE
Currency Futures are agreements to buy or sell a particular currency at a fixed price on a future date. Exchanges: ICE and CME
Other Derivatives:
Interest Rate Swaps: Contracts to swap cash flows at various interest rates. Exchanges: ICE and CME
Credit Default Swaps (CDS) : A default or failure to repay a loan is referred to as a "credit default”. The "swapping" occurs when an investor "swaps" with another investor or insurance business the risk of receiving their net worth back. The buyer of a CDS pays the seller on a regular basis until the credit maturity date in order to swap their default risk. The seller agrees in the agreement to reimburse the buyer for all premiums and interest that would have been paid up until the date of maturity if the loan issued by the buyer of the CDS defaults.
Food Price Index comprises price indices for cereals, vegetable oils, meat, fish, sugar, and other foods.
Base Metals Price Index include price indices for iron ore, aluminium, cobalt, copper, nickel, tin, uranium, zinc, and lead.
Fuel Energy Index include price indices for coal, natural gas, propane, and crude oil (petroleum).

Fertilizer Index include prince indexes for potash, urea (carbamide), and DAP (diammonium phosphate).

November saw a 6.8% annual increase in the consumer price index, mostly due to increases in the costs of food, energy, and housing. The increase in core inflation, which does not include volatile categories like food and energy, was 4.9%, the most since 1991.
November saw an increase in food costs of 6.1% and home prices of 4.8% due to disruptions in the raw material supply that hindered construction activities.
After rising by 30% in October, energy prices increased by 33.3% in November. In November, gasoline prices increased by an astounding 58.1% from the previous year.
REASON FOR PRICE FLUCTUATIONS
The conflict in Ukraine has affected the world's energy sources, driving increasing the price of gas and oil and directly affecting the cost of gasoline.
Monetary policy: The pandemic-related low interest rates and quantitative easing programs of the Federal Reserve raised the money supply and may have exacerbated inflationary pressures.
Corporate profits: Some contend that despite the fact that costs haven't increased proportionately, firms are using the current circumstances to boost prices and profits.
Government spending: By raising the money supply and demand for products, recent stimulus plans intended to combat pandemic recovery may exacerbate inflation.

U.S. The loan market has developed dramatically over the last five years, formed by way of diverse financial and political occasions.
• From growing interest rates and exchange disputes to international pandemics and the conflict in Ukraine, permit’s take a more indepth examine the key factors and activities that have defined this dynamic landscape.
• Rising Interest Rates and Policy Regularity 2018-2019. The Federal Reserve, led by way of Chairman Jerome Powell, embarked on a direction of slow, focused hobby fee increases on to normalize the present financial coverage after the economic disaster after the financial disaster.
• This pushed up Treasury yields throughout the curve, affecting bond segments along with corporate, municipal and mortgages. The growing rate environment has pushed bond charges down, as
their constant coupon payments have come to be much less appealing relative to other higher yield issues
• In 2019-2020, Rising change warfare in the US. And China, as well as geopolitical uncertainty, have weighed on international economic increase and chance appetite.

• This aviation security situation drove investors into Treasury’s, inflicting yields to say no and bond expenses to upward push. In COVID-19 Pandemic, the global outbreak of COVID-19 has led to a slowdown within the financial system and considerable marketplace panic.
• The Fed replied via lowering the emergency rate to close to zero and beginning quantitative easing rules that flooded the market with cash.
• This triggered Treasuries to upward push sharply again, with the 10-12 months yield falling to a rock bottom of 0.5% by way of March 2020. Economic instable and inflation pressures 2021-2022 S&P U.S. This means the bonds issued by the US. the government considers it more secure.
• In the U.S the bonds are rated by the three agencies Moody's, Standard & Poor's, and Fitch. The top government bonds in the U.S according to the ratings there are TLT, BIL, IEF, SHY and corporate bonds are SPDR, Schwab, ISHARES, PIMCO
Compare the S&P Bond Index with the SPDR High Yield Bond Index.

Government bonds: Generally considered a safe haven, short-term funds (1-3 years) benefited from risk aversion during periods of market turmoil such as the onset of the pandemic in 2020. Initially, the yield a yield on these bonds fell, driving up inflation , and that too Before it went up when the Fed started raising rates.
Corporate bonds: High-quality, short-term corporate bonds with strong credit ratings reflected the Treasury’s attitude, providing some stability in times of uncertainty but substantial volatility in cheap corporate bonds in due to credit concerns about the issuers.


Long-term performance:
Government bonds: Cash dividends (10+ years) were initially lifted in 2018-19 on concerns of trade tensions and global growth, which lowered yields and raised inflation. However, the pandemic, and subsequent economic recovery, raised prices, pushing sales and yields up sharply in 2021-23.
Corporate bonds: Long-term corporate bonds, especially those issued by financially strong companies, offered higher yields compared to the Treasury but also carried higher credit risk Their performance varied across sectors, some benefited from the issues created by the epidemic, while others faced challenges.
A hedge fund is a group investment vehicle that makes profits by investing in securities or other financial instruments. Three-quarters of the Assets Under Management (AUM) in this industry worldwide are located in the United States. Out of the 5,383 active hedge fund managers and 5,523 active institutional investors, 3,405 and 3,319 respectively are based in the US. AIML, or artificial intelligence and machine learning, is another tool that fund managers are increasingly employing to boost returns and boost operational efficiency.

Over the forecast period (2023–2028), the US hedge fund market is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of more than 5%.
An industry benchmark for evaluating the overall health and performance of the hedge fund business is a hedge fund index. These indices are compilations of various hedge funds, frequently divided into groups according to investment approach, regional emphasis, and/or other factors. Following are the major Indices for hedge funds in United States.
• HFR Index
• Leading hedge fund indices
• Morningstar Index
• Barclay Hedge Fund Index
• Eureka hedge North American Hedge Fund Index

Hedge Fund Assets Under Management(AUM)
Bridgewater Associates $124,317,200,000
Renaissance Technologies $106,026,795,439
AQR Capital Management $94,523,700,000
Two Sigma $67,471,220,893
Millennium Management $57,670,000,000
Citadel $51,573,787,000
Tiger Global Management $51,000,000,000
D.E. Shaw $45,772,700,000
Coatue Management $42,338,946,229
Davidson Kempner $40,800,000,000

The Federal Reserve of the United States has executed an unprecedented series of eleven consecutive increases in the Federal Funds Rate over the past twelve meetings. This aggressive monetary policy includes four consecutive hikes of 0.75%, signifying the most rapid rate escalation since the early 1980s. Within a compressed timeframe of 16 months, spanning from March 2022 to July 2023, the Fed Funds rate surged by around 500 basis points. This dynamic shift in monetary policy implies a significant recalibration of strategies for hedge fund managers, who find themselves adapting to an altered economic landscape.
Against this backdrop, hedge funds have notably amplified their net short position in the US Treasury futures market, reaching an extraordinary level of approximately USD 800 billion by the close of November. This strategic positioning reflects a concerted effort by asset managers to shield themselves from the inherent risks associated with fluctuations in interest rates. In a counterbalancing manoeuvre, these financial entities have concurrently expanded their net long positions, indicating a nuanced and proactive approach to navigating the intricate challenges posed by the evolving economic environment.


The UK stock market, renowned for its longevity and reputation, hosts diverse companies, from global giants to smaller enterprises. It operates through various exchanges, primarily the London Stock Exchange (LSE) in the City of London is the dominant exchange, handling over 90% of UK stock market trading., The remaining exchanges like Aquis Exchange, BATS Europe: and Chi-X Europe combined account for less than 10% of the market share
The UK stock market features several key indices within the FTSE umbrella, each providing distinct insights into diverse market segments. The FTSE 100 mirrors economic shifts and growth prospects for mid-sized companies, impacting innovation and job creation.
Contrarily, the FTSE 250, while short-term volatile, offers long-term growth and diversification, often outperforming larger indices. Encompassing over 350 companies, the FTSE All Share Index offers a comprehensive view of nearly all of the UK market's capitalization. The FTSE 350 combines the FTSE 100 and FTSE 250, providing exposure to both large and mid-cap companies.
Furthermore, sector-specific indices within the FTSE 100, spanning Financials, Consumer Goods, Industrials, Healthcare, Energy, and Basic Materials, enable focused tracking of individual sector performance. Supplementary indices like FTSE AIM All-Share, FTSE SmallCap, FTSE Fledgling, and FTSE tech MARK 100 cater to growth potential, smaller Main Market companies, the smallest Main Market entities, and technology companies respectively.
Based on year-to-date (YTD) performance some sectors have emerged as frontrunners:
1. Technology :- The reasons were Shifting investor sentiment, strong earnings reports and increased demand for technology products and services. Some of the best-performing tech stocks in the UK YTD include ASOS (+107.5%), Ocado (+83.2%), and Deliveroo (+73.4%).
2. Communication Services:- The reasons were Increased reliance on communication technologies and Positive regulatory developments. Some of the top performers in the communication services sector include Airtel Africa (+123.6%), TalkTalk (+81.5%), and Vodafone Group (+55.4%).
3. Consumer Discretionary The reasons were Easing cost-of-living pressures and Pent-up demand. Some of the standout performers in the consumer discretionary sector include Rightmove (+80.5%), JD Sports (+70.3%), and Flutter Entertainment (+46.5%).
The UK stock market, represented by the benchmark FTSE 100 index, has experienced a period of up-and-down performance over the past five years (from December 2018 to December 2023).
• The FTSE 100 delivered a negative return of 4.56% in this period. However, the journey wasn't linear.

• The index reached an all-time high of 8,174.36 in May 2021, fuelled by economic recovery hopes and loose monetary policy.
• Subsequently, it plunged due to various factors:
1. The ongoing trade war between the US and China dampened investor sentiment.
2. The UK's withdrawal from the European Union created economic and political instability.
3. Central banks around the world, including the Bank of England, increased interest rates to combat inflation, making stocks less attractive compared to bonds.

The UK stock market, represented by the total market capitalization of companies listed on the London Stock Exchange (LSE), currently holds around 2.5% of the global market share. This translates to roughly $3.4 trillion in market capitalization as of December 2023.
Comparison to Larger Markets:
• The United States dominates the global stock market with a whopping 45.5% share, boasting a market capitalization exceeding $50 trillion.
• The second-largest market is China, representing around 12.5% of the global share with a market capitalization of approximately $14 trillion.
• Japan follows closely behind with a 7.4% share and a market capitalization of around $8 trillion

The UK Stock Market: December 2023 and Beyond
In December 2023, the UK stock market presents a complex scenario, blendingpositivefestivevibes with concerns about a looming recession and ongoing economic issues. The FTSE 100 exhibits modest growth fuelled by holiday spending, US market positivity, and a robust energy sector. However, persistent worries over inflation, escalating interest rates, and uncertainties impacting retail due to Brexit persist.
Central banks' measures against inflation and global tensions, especially the Ukraine conflict, influence investor sentiment. Holiday closeness might lessen trading activity, but the new year might usher in increased market fluctuations as the UK's global economic ties become clearer.
Investors are urged to conduct thorough research aligned with their risk tolerance and seek professional advice to navigate this uncertain period. Despite economic challenges, preparedness and guidance can position investors to seize opportunities in the UK stock market amidst its current challenges.
An increase in interest rates in the UK, whether prompted by the Bank of England or in response to changes by the US Federal Reserve, could bring multiple effects to the UK stock market.

• it might lead to reduced stock prices as higher rates often lure investors toward bonds, diminishing demand for stocks and causing their prices to fall.
• higher borrowing costs for businesses could hinder investments and slow economic growth, impacting companies' earnings and stock valuations.
• breed uncertainty and market volatility, making investors more risk-averse and leading to erratic stock price fluctuations. However, there could be positive consequences too.
• Elevated interest rates serve as a tool to combat inflation, potentially stabilizing the economy and bolstering long-term investor confidence in the market.

• It may attract foreign investments, benefiting companies with international operations by increasing their revenue in real terms.
• Certain sectors, like financial institutions, might also see advantages due to widened lending margins.
The US Federal Reserve's actions, especially alterations in the Fed fund rate, can indirectly influence the UK stock market through various channels. Changes in the Fed rate can sway global capital flows, affecting investor movement in and out of the UK market based on relative interest rates and economic situations. Moreover, a rising Fed rate can strengthen the US dollar, potentially making investments in
countries like the UK more expensive and impacting UK stock prices. Additionally, US monetary policy decisions can influence global investor sentiment towards riskier assets, potentially impacting UK stocks either positively or negatively.

The derivatives market in the United Kingdom is large and varied, providing a broad selection of products to satisfy the requirements of traders and risk managers. Contracts known as derivatives get their value from an underlying asset, which could be a currency, stock, bond, or commodity. They can be used as a risk hedge, to make predictions about future stock prices, or just to make money.
The following are a few of the most popular variants available in the UK -
1. Equity derivatives: These are linked to exchange-traded funds (ETFs), equities, or indices. Investors can utilize them to produce income through dividends, speculate on future stock prices, or act as a hedge against stock market volatility.
2. Interest rate derivatives: These products are connected to fixedincome securities or interest rates. They can give income through coupon payments, enable speculation on future interest rates, or offer insurance against interest rate risk.
3. Commodity derivatives: These are based on actual commodities, such as gold, oil, or agricultural products. They can be used to speculate on future prices, protect against volatility in commodity prices, or even make money by physically delivering the commodity.
4. Derivatives on currencies: These have to do with the rates at which currencies are exchanged. They are used by traders as a hedge against exchange rate risk, a way to make money from currency swings or to speculate on future exchange rates.
Derivative trading in the UK offers two avenues: over-the-counter (OTC) for bespoke contracts and regulated exchanges for standardized ones. Before engaging, understanding the risks is crucial, given the sophistication and potential financial losses associated with derivatives. Traders should approach derivative trading with caution and a deep understanding of market dynamics.
In the UK, derivatives get traded on two main exchanges: London Stock Exchange (LSE): This major exchange offers a wide variety of derivatives, like equity, interest rate, commodity, and currency options. It has platforms like SETS and Turquoise for trading.


1. Equity Derivatives:
I. Stock futures: Popular examples include FTSE 100 futures, IOB DR futures, and individual stock futures for major UK companies. These allow you to lock in the future price of a stock.
II. Stock options: You can choose between calls (right to buy) and puts (right to sell) on individual stocks or FTSE 100 and other UK indices. This flexibility can offer limited risk protection or leverage depending on your strategy.
III. Equity index futures and options: Track the performance of UK indices like the FTSE 100, FTSE 250, and FTSE All-Share, allowing you to speculate on the overall market direction.
2. Interest Rate Derivatives:
I. Interest rate futures and options: Based on future UK interest rates, enabling you to hedge against potential interest rate fluctuations or speculate on their movements.
II. SONIA futures and options: Specifically based on the Sterling Overnight Index Average (SONIA), the UK's benchmark for overnight interest rates.
3. FX Derivatives:
I. Currency futures and options: Allow you to lock in exchange rates for various currency pairs like GBP/USD, GBP/EUR, etc., protecting against adverse currency movements.
4. Commodity Derivatives:
I. Futures and options on commodities traded on UK markets, such as gold, silver, and Brent crude oil. These can be used for hedging or speculation on commodity prices.
5. Other Derivatives:
I. Structured products: Tailored investment vehicles combining derivatives and other instruments to achieve specific investment objectives.
II. Exchange-traded notes (ETNs): Debt securities tracking the performance of an underlying asset, like a UK index or commodity, but issued by a single institution
Intercontinental Exchange (ICE): This global group owns UK exchanges like the London Metal Exchange (LME) for metals and the International Petroleum Exchange (IPE) for European energy derivatives.
A) Equity Derivatives:

I. Single Stock Futures and Options: Trade individual UK and international stocks with various contract sizes and expiry dates.
II. Equity Index Futures and Options: Gain exposure to the performance of broad UK and European indices like FTSE 100, FTSE 250, EURO STOXX 50, etc.
B) Interest Rate Derivatives:
I. Short Sterling Futures and Options: Based on short-term UK interest rates.
II. Eurodollar Futures and Options: Based on US dollar interest rates, relevant for hedging international exposures.
III. Swap Futures and Options: Trade on future interest rate swap rates across various maturities.
C) Commodity Derivatives:
I. Energy: Futures and options on Brent and WTI crude oil, natural gas, electricity, etc.
II. Metals: Gold, silver, platinum, aluminium, copper, etc.
III. Agricultural products: Wheat, corn, soybeans, etc.
D) Freight Derivatives:
I. Dry Bulk Forward and Options: Hedge against movements in freight rates for dry bulk cargo shipping.
E) Other Derivatives:
I. Volatility derivatives: Trade on the implied volatility of underlying assets like equities and indices.
II. Climate change and ESG derivatives: Futures and options linked to climate change indices and ESG-focused assets..
Beyond these top two, smaller exchanges and platforms exist, but LSE and ICE dominate the scene. The exchange choice depends on factors like the underlying asset and target investor. Remember, not all derivatives are listed and some happen over-the-counter directly between parties.
Understanding UK Derivatives: How the Market Reacts to Change
The UK derivatives market is shaped by internal factors like regulatory shifts and market changes, alongside external influences such as global economic conditions and interest rate fluctuations. Regulatory adjustments, such as margin requirement changes, can impact liquidity, while global economic uncertainties and interest rate shifts affect investor behaviour. Commodity-linked derivatives are directly influenced by underlying commodity price changes. High-frequency trading and emerging platforms contribute to market efficiency.
Understanding these sensitivities is crucial for market participants to make informed decisions, manage risks, and identify opportunities. The interconnected nature of these factors, as depicted in the accompanying image, underscores the dynamic and intricate landscape of the UK derivatives market, emphasising the need for vigilance and adaptability.U.S. federal funds rate changes influence the UK derivatives market by affecting global borrowing costs, altering derivative appeal, and influencing currency exchange rates. Swift adaptation is vital for market participants to navigate effectively.
The UK bond market is one of the biggest in the world, worth more than $100 trillion.

There are various kinds of bonds in the UK bond market:
• The UK government issues Government Bonds (Gilts) to raise funds for public spending and debt management. They are considered low-risk investment bonds as they have a strong hand on the government’s creditworthiness. These bonds are issued to finance government expenditures and budgetary needs. They offer fixed interest payments at regular intervals and repayment of the principal amount at maturity.
• Corporate Bonds are issued by companies to raise capital for various purposes such as expansion, debt refinancing, etc. These bonds may have fixed or variable interest rates and can have different maturity periods. All the risk is associated with the creditworthiness of the companies. This may offer higher yields compared to Gilts but also vary in levels of risk.

• High-yield bonds issued by companies with lower credit ratings and higher yields also carry a greater risk of default. Yields on such bonds can reach up to 8%.
• Green Bonds are issued by companies or governments to finance environmentally friendly projects. It offers attractive yields with ethical investment principles.

• Index-linked Bonds are bonds that offer protection from inflation by having their principal and interest payments linked to a consumer price index. UK index-linked bonds currently offer yields of around 1.50%, providing a hedge against rising prices.
Investors choose between these bonds based on their investment goals, risk tolerance, and market conditions. The interaction of these two bonds contributes to the overall dynamic of the UK bond market. UK public holds some awareness of major credit rating agencies and understanding of their specific roles. Continuous education and transparency of agency practices might contribute to enhanced public knowledge in the bond market.
In the UK, there are various key players of credit rating agencies. Big three of them are Moody’s investors service Ltd (arguably most recognized globally), Fitch rating Ltd. (hold strong presence in finance and insurance), S&P Global Rating UK Ltd. and various others like ARC rating Ltd, DBRS Morningstar etc. According to the Fitch rating (Dec1, 2023), it affirms the UK at AA-; the outlook is negative. The global sovereign sector outlook is neutral, with fiscal risks in focus.



The UK bond market was a quiet haven in 2018-2020 with low yields and high demand for Gilts. It experienced a rollercoaster ride from 2021 onwards as rising inflation and interest rates caused yields to spike and the market to become volatile. The trend had significant fluctuations as the yield curve inverted in October 2023, signalling investor's concerns about future economic growth.
Currently, the short-term bonds (2 years and below) are hovering around 4% yield, indicating a rise from previous months but a slight dip from October’s peak, creating a moderate demand in the market. Whereas in long-term bonds (10 years and above) there is a yield of around 3.50%, showing a drop from earlier highs in 2023, creating an increased demand in the market.

The condition of the UK bond market in December 2023 is complex and evolving, marked by divergent trends across maturities and cautious optimism fuelled by recent improvements
The UK hedge fund market is a substantial and growing one, with assets under management (AUM) exceeding £1 trillion. It's expected to grow at a CAGR of over 8% in the coming years. The industry is relatively well-regulated, with the Financial Conduct Authority (FCA) overseeing its activities. This ensures transparency and investor protection.
Hedge funds utilize various strategies, including long/short investing, arbitrage, market timing, and activism. They can also invest in a wider range of assets compared to traditional funds, including derivatives, distressed debt, and private equity. Hedge funds typically charge a "2 and 20" fee structure, which comprises a 2% annual management fee and 20% of profits earned.
1. Capula Investment Management LLP
2. Man Group
3. Brevan Howard Asset Management
4. Lansdowne Partners
5. Arrowgrass Capital Partners

Types of hedge funds in the UK:
• Equity hedge funds focus on investing in stocks and aim to outperform the market through long/short strategies, activism, or other methods.
• Macro hedge funds seek to profit from macroeconomic trends through investments in currencies, commodities, and fixedincome instruments.
• Event-driven hedge funds: These funds capitalize on specific events such as mergers and acquisitions, bankruptcies, or spinoffs by taking long or short positions in the associated companies.
• Quantitative hedge funds: These funds rely on quantitative models and algorithms to make investment decisions, often employing high-frequency trading techniques.
• Credit hedge funds: These funds invest in debt instruments, including bonds and loans, and aim to profit fromcredit spreads and other fixed-income market opportunities.
The past five years (2018-2023) have been a mixed bag for UK hedge funds. The average UK hedge fund has delivered net annualized gains of 7.2% over the past five years, according to Barclay Hedge. This performance compares favourably to the S&P 500's return of 6.5% during the same period. However, it's important to remember significant performance dispersion within the industry. The top 50 UK hedgefunds collectively returned annualized gainsof over 15.5%, more than double the industry average.
Hedged equity strategies proved the most successful, generating average returns of 22.5% per year thanks to concentrated investments in key holdings. Interestingly, smaller and mid-sized funds outperformed larger ones due to their agility and ability to navigate less efficient markets.

Tokyo Stock Exchange (TSE) which is responsible for over 80% of the country's total market capitalization, Osaka Securities Exchange (OSE) focuses primarily on derivatives trading and growth companies both operate under the umbrella of the Japan Exchange Group (JPX), formed in 2013 through the merger of the TSE and OSE.
The Japan Exchange Group (JPX) ranks as the fifth largest stock exchange in the world by market capitalization. Its total market capitalization stood at roughly $6.54 trillion, this represents around 3.3% of the world's total market capitalization. JPX aims to provide a unified and efficient trading platform for investors in Japan and worldwide. Within Asia, JPX is a powerful force. It consistently ranks as the largest exchange in Asia by market capitalization and is crucial in channelling capital flows throughout the continent.
Indices representing TSE:

Nikkei 225: The most well-known Japanese stock market index, that tracks the performance of 225 blue-chip companies listed in the First Section of the Tokyo Stock Exchange. It serves as a crucial indicator of the market's overall health and performance and a major Asian equity benchmark with global consultation.
Technology dominates the Nikkei 225 landscape, commanding a towering 48%, while Consumer Goods occupy a significant 25%. Financials and Materials contribute 10% each, playing supporting roles alongside Transportation and Utilities (2%) and Capital goods/others (2%).
Among the Nikkei 225's heavyweights, SoftBank Group (4.2%) stands out, with Toyota (3.4%), Fast Retailing (3.3%), KDDI Corp. (2.2%) playing key roles.

Tokyo Price Index (TOPIX): The most comprehensive index of the TSE, tracking the performance of all companies listed in the First Section (large-cap).
Tech dominates the TOPIX landscape, with SoftBank and Sony spearheading a 35.5% weight. Consumer giants like Fast Retailing and Kikkoman holds a 18.2%. Banking powerhouses like Mitsubishi UFJ and Sumitomo Mitsui Financial Group hold a 16.8% weight, while automotive legends like Toyota and Hitachi anchor the Industrials sector at 11.3%. Materials, home to Nippon Steel and Asahi Kasei, rounds out the top 5 with 6.8%.

Apart from TSE, Osaka Securities Exchange (OSE),

the second largest stock exchange in Japan primarily focuses on trading futures and options contracts, unlike the TSE which deals mainly in spot trading of individual stocks. OSE includes two major indices:
JPX-OSE Mothers Index: Tracks the performance of around 80 highgrowth companies listed on the Mothers, a section dedicated to emerging and innovative companies within the OSE. Considered a benchmark for the growth segment of the Japanese stock market. Similar to the Nasdaq in the US, it features companies in sectors like technology, biotechnology, and e-commerce.
JPX-OSE Jasdaq Index: Represents the performance of roughly 300 companies listed on the Jasdaq, another section of the OSE focusing on small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs). Offers exposure to a broader range of companies compared to the Mothers Index, including more established SMEs alongside high-growth startups. Similar to the Russell 2000 in the US, it provides a way to invest in the potential future leaders of the Japanese economy
The Bank of Japan left its ultra-loose monetary policy unchanged at its final meeting this year on 19th December. The central bank decided unanimously that it would keep interest rates at -0.1%, while also sticking to its yield curve policy that references the 1% upper bound for 10-year Japanese government bonds as its limit. Yields for the 10-year Japanese government bond fell to 0.622%, and the Yen weakened 0.6% against the dollar to 143.70 after the decision. The Nikkei 225 closed 1.41% higher at 33,219.39, while the TOPIX closed up 0.73% at 2,333.81.

After declining in 2022, the Nikkei advanced around 28%, its fastest pace in a decade, to end 2023 at 33,464.17, reaching its highest yearend closing since 1989. This impressive comeback was fuelled by several factors, particularly the strength of export-oriented companies who benefited from the weak yen. With the U.S. Federal Reserve expected to cut rates and the Bank of Japan potentially ending its negative rate policy, the yen is anticipated to rise in 2024. This could pose a challenge for Japanese stocks, especially major players in the auto and electronics sectors, as exports could become less competitive and profit margins face potential contraction.
The Financial Services Agency (FSA) is in charge of the derivatives market regulation in Japan. After the US and Europe, Japan has the third-largest derivatives market globally. The notional value of all outstanding derivatives contracts in Japan as of June 2023 was $84 trillion, of which $75.2 trillion came from over-the-counter (OTC) contracts and $8.8 trillion from exchange-traded contracts.
Equity derivatives dominate the market, with interest rate and commodity derivatives following closely behind. Japanese financial

institutions, such as banks, securities firms, and insurance companies, dominate the market.
Various kinds of derivative products of that country which are available in Japan:
Nikkei 225 Futures and options (Large Contracts)
A significant Japanese stock index that serves as a benchmark for a number of financial products is the Nikkei Stock Average, which is the basis for Nikkei 225 Futures and options.
Nikkei 225 mini:
Under the terms of the Nikkei 225 mini stock index futures contract, traders pledge to purchase or sell 100 times the Nikkei Stock Average (Nikkei 225) at a certain price on a future date.
Nikkei 225 micro Futures:
An index futures contract based on the Nikkei Stock Average (Nikkei 225) called Nikkei 225 Micro Futures guarantees to purchase or sell under the following circumstances:
(1) Ten times the Nikkei 225
(2) on a particular future date
(3) for a contractual price that is now agreed upon
"Nikkei 225 micro Futures" was Introduced on May 29, 2023, which can be traded with even smaller amounts than Nikkei 225 mini, in response to the growing demand for more accurate risk management techniques against the backdrop of the trend toward smaller investments in the cash equity market.
Nikkei 225 mini Options:
A stock price index options contract on the Nikkei Stock Average (Nikkei 225) is called a Nikkei 225 mini Options contract.
More thorough risk management is made possible by the Nikkei 225 mini Options because the trading unit is one-tenth that of the Nikkei 225 Options.
Nikkei 225 Total Return Index:
The Nikkei 225 Total Return Index calculates the performance of the Nikkei 225 by taking into account changes in the component stocks' prices as well as the reinvestment of dividend income at the end of the ex-dividend period.
TOPIX Futures
Global investors have another asset to consider with TOPIX futures. Contracts for TOPIX Futures, like Nikkei 225 Futures, are traded through the pledge of collateral, or margin.

Mini-TOPIX Futures
A mini stock index futures based on TOPIX is called mini-TOPIX Futures.
Tenth of TOPIX Futures' contract size is what it is. SPAN is used to calculate the necessary margin. Margin is a requirement for investors to commit in order to trade mini-TOPIX Futures.
TOPIX Options
Only when the option expires may it be exercised. The base price for the price limit range calculation will be multiplied by the following rates to determine the price limit range. The price limit range will ideally be updated every three months (in March, June, September, and December).
JPX-Nikkei Index 400 Futures and options:
The stock index futures and options are based on JPX-Nikkei Index 400. The JPX-Nikkei Index 400 is made up of businesses that are very attractive to investors and that satisfy international investment standards, like effective capital use and investor-focused management viewpoints.
TSE Growth Market 250 Index Futures:
TSE Growth Market 250 Index Futures previously known as TSE Mothers Index Futures was derived from all common companies listed
on the TSE Mothers market and was free-float adjusted market capitalization-weighted. Despite the reorganization of the TSE Mothers market on April 4, 2022, TSE has modified the TSE Mothers index's calculation rules somewhat and is still using them.
TOPIX Core30 Futures:
It is a stock index Futures based on TOPIX Core30. The 30 most liquid and highly market capitalized stocks that are listed on TOPIX are used to construct TOPIX Core30.
RN Prime Index Futures:
Underlying index of Russell/Nomura Prime Index (RN Prime Index). The 1,000 largest stocks, as determined by free-float adjusted market capitalization, are included in the RN Prime Index. These stocks are chosen from all listed equities across all Japanese marketplaces. For this reason, The RN Prime Index is a good gauge of what is actually going on in the Japanese stock market.
TOPIX Banks Index Futures and Options:
TOPIX Banks Index Futures and Options stock index Futures based on TOPIX Banks Index. Only Flexible Options Trading offers TOPIX Banks Index Options. According to the industrial sectors as established by the Securities Identification Code Committee (SICC), the TOPIX Banks Index is the index of stocks in the bank sector based on TOPIX Sectors Indices (33 sectors).
S&P/JPX 500 ESG Score Tilted Index Futures:
It is an ESG index Futures based on S&P/JPX 500 ESG Score Tilted Index (0.5). A TOPIX 500-based index, the S&P/JPX 500 ESG Score Tilted Index (0.5) exhibits a tilt in the weights of its constituents away from freefloat market capitalization. This results in an over- or under-weighting of companies with varying S&P DJI ESG scores. This satisfies investors' need to increase their exposure to ESG factors while still having a wide range of varied investment options.
FTSE JPX Net Zero Japan 500 Index Futures:
It is an ESG index Futures based on FTSE JPX Net Zero Japan 500 Index. The FTSE JPX Net Zero Japan 500 Index is a TOPIX500-based index that uses an average 7% annual decrease in carbon emissions to get to net zero by 2050. Additionally, a 30% relative reduction in its climatic qualities is the goal of the indicators. Furthermore, in order to assess whether companies are gaining from the shift to a green economy, the indices achieve a notable increase in exposure to the green revenues of those companies.
Nikkei 225 Climate Change 1.5℃ Target Index Futures:
It is an ESG index Futures based on Nikkei 225 Climate Change 1.5℃ Target Index. The Nikkei 225 Climate Change 1.5°C Target Index is an index that is based on the Nikkei Stock Average (Nikkei 225), with constituent weights adjusted so that the index's overall GHG emissions (normalized by enterprise value) are 50% lower than the Nikkei 225 and will continue to decline by 7% in the years to come.
Sensitivity of that derivative market.
Interest Rate Sensitivity: The market is susceptible to any prospective changes in monetary policy due to Japan's historically low interest rate environment. For some positions, a sharp increase in interest rates could result in substantial losses.
A period of high interest rates would initially cause:
• Reduced contract values: The decreased appeal of holding future cash flows will cause the values of most derivatives, including swaps, futures, and options, to decrease. However traders who anticipate this can benefit from short positions in future contracts.
• Increased volatility: The rate hike-related market uncertainty could cause derivative contract prices to fluctuate more than usual(majorly towards the lower side).
Eventually, as interest rates decline, the opposite consequences will become apparent:
• Enhanced contract values: Future cash flows that are more appealing could increase the value of contracts.
• There could be continued volatility: Future rate changes could cause uncertainty, whichwould prolong the period ofhigh volatility.


Global Interconnectedness: Due to its integration with international financial markets, the Japanese derivatives market is vulnerable to outside shocks such as geopolitical upheavals and economic downturns.
Counterparty Risk: When one partyto a derivative contract default, the market is vulnerable to counterparty risk due to the reliance on OTC (over-the-counter) transactions.
Current Scenario and Future of Japan’s derivatives market:
Japan's extremely minimal rates and global trepidation are driving the market's volatility in the derivatives. OTC transactions are common, but laws are muttered. Technology expedites processes while simultaneously highlighting potential hazards. The times ahead?
Possible Future Patterns:
• OTC (Over-the-Counter) Derivatives Growth: Even though exchange-traded derivatives currently rule the market, over-thecounter (OTC) activity may increase because of its customization and flexibility options.
• PutSustainabilityFirst: Derivatives linked to sustainability, like ESGbased options, may become more popular as social and environmental issues gain more attention.
• Adoption of Blockchain Technology: Investigating blockchain technology for post-trade processing and settlement may result in cost savings and increased efficiency.

Imagine a massive marketplace where governments and businesses can borrow money from investors. That's the bond market in a nutshell. It's also known as the debt market, fixed-income market, or credit market, and it plays a crucial role in financing various activities, from infrastructure projects to corporate expansion.
Whousesthebondmarket?
• Governments: They issue bonds to fund public spending, like building roads or bridges. Japan, for example, boasts one of the largest government bond markets globally, with over $7.9 trillion in outstanding debt.
• Businesses: Companies issue bonds to raise capital for various purposes, such as acquiring other businesses, expanding operations, or simply staying afloat.
• Investors: Individuals, institutions, and even othergovernments can buy bonds to earn a steady stream of interest income. Bonds are
generally considered less risky than stocks, making them a popular choice for conservative investors.
Japan's bond market has been in the news lately due to its yield-curve control (YCC) policy. The Bank of Japan has been keeping interest rates near zero to stimulate borrowing and economic growth. This has made Japanese government bonds less attractive to investors, leading to decreased liquidity in the market. However, the recent expansion of the YCC target band may signal a shift in policy and potentially revive the market. The bond market is a complex and ever-evolving ecosystem, but understanding its basic principles can help you make informed investment decisions and gain insights into the global economy.
Japanese government bonds (JGBs) maturities range from two to forty years. Until the security matures, fixed coupon payments are made semi-annually, with the amount established at the time of issuance. Japanese government bonds (JGBs) are divided into four categories:

1. General Bonds, including bonds for debt financing and building.
2. Bonds issued under the Fiscal Investment and Loan Program (FILP) may be used to raise money for the Fiscal Loan Fund's investments.
3. Bonds for reconstruction.
4. Refunding bonds
• Japan Credit Rating Agency (JCR): The premier credit rating agency in Japan, JCR assesses the financial health of corporations and financial institutions. They cover over 60% of publicly rated Japanese companies and 70% of the financial industry. JCR also provides valuable economic and financial research, solidifying its role as a trusted advisor in the Japanese market.
• Rating and Investment Information, Inc. (R&I): Established in 1996, R&I is another prominent credit rating agency in Japan. They focus on providing credit ratings for structured finance products, assetbacked securities, and local governments. R&I's expertise in these areas makes them a valuable resource for investors and issuers alike.

• Japan Research Institute (JRI): While not strictly a credit rating agency, JRI plays a crucial role in assessing the creditworthiness of Japanese sovereign debt. Their research and analysis are highly respected by investors and policymakers alike, and they are often consulted on matters related to Japan's fiscal health.


• Moody's Investors Service: This global credit rating agency has a significant presence in Japan, providing ratings for a wide range of issuers, including corporations, financial institutions, and sovereigns. Moody's is a valuable source of independent credit analysis for investors around the world.

• Standard & Poor's (S&P): Another global credit rating agency with a strong presence in Japan, S&P provides ratings for corporations, financial institutions, and sovereigns. S&P's ratings are widely used by investors to make informed investment decisions.
There are two main categories of JGBs:
General Bonds and Fiscal Investment and Loan Program Bonds (FILP Bonds).
• Funding sources:
o General Bonds: Redeemed mainly with tax revenue.
o FILP Bonds: Redeemed and interest paid from recovered loans to FILP agencies.
• Market treatment: Both types are issued at the same interest rate and maturity, and are treated equally in the market.
Essentially, while the source of funds to redeem them differs, FILP Bonds and General Bonds are the same financial instruments from an investor's perspective.
General Bonds: General Bonds are a category of Japanese government bonds that can be further divided into four specific types: Construction Bonds, Special Deficit-Financing Bonds, Reconstruction Bonds, and Refunding Bonds. The revenue generated from these bonds is allocated differently depending on their purpose.
Construction Bonds and Special Deficit-Financing Bonds are issued under the General Account, meaning the revenue they raise is incorporated into the overall government revenue stream. This funding is used to support general government operations and infrastructure projects.
In contrast, Reconstruction Bonds are specifically issued to finance the recovery efforts following the Great East Japan Earthquake. The revenue from these bonds is directed to the Special Account for Reconstruction, ensuring it's dedicated to rebuilding efforts.

Refunding Bonds, on the other hand, are issued to raise funds for repaying matured government bonds. The revenue from these bonds is channelled into the Special Account of the Government Debt Consolidation Fund, aiming to manage and reduce overall government debt.
Fiscal Investment and Loan Program Bonds (FILP Bonds): Beginning in fiscal year 2001, the Japanese government introduced a new type of bond called Fiscal Investment and Loan Program Bonds (FILP Bonds) as part of a broader reform of the Fiscal Investment and Loan Program (FILP). These bonds are specifically designed to raise funds for investments made through the Fiscal Loan Fund.
While FILP Bonds share some similarities with other government bonds, they have a key distinction in how they are repaid. Traditional government bonds, such as Construction Bonds and Special DeficitFinancing Bonds, are ultimately redeemed using future tax revenues. In contrast, FILP Bonds are repaid through the recovery of loans made from the Fiscal Loan Fund to specific entities, such as Incorporated Administrative Agencies. This difference in funding sources is why FILP
Bonds are treated distinctly from General Bonds when reporting outstanding government debt.
Performance :-
Yields have risen for both 2-year and 5-year bonds as of December 21, 2023, compared to the previous day. This indicates a slight increase in borrowing costs for the Japanese government. However, yields have generally trended downward over the past week and year-to-date, suggesting a longer-term decline in borrowing costs. The larger increase in the 5-year yield compared to the 2-year yield might signal expectations for higher interest rates in the future.
The recent uptick in yields could reflect short-term market adjustments or reactions to specific economic or policy developments. The longer-term decline in yields is likely influenced by the Bank of Japan's accommodative monetary policy, which has kept interest rates low. The differential between 2-year and 5-year yields could suggest investors are anticipating some degree of monetary tightening in the coming years.

As of October 26, 2023, the current long-term and short-term bond yields in the Japanese economy are:
• 10-year Japanese Government Bond (JGB): 0.68%. It's important to note that this is slightly above the Bank of Japan's recent target band of plus or minus 0.5 percentage points around zero, representing a shift in the Central Bank's yield curve control policy.
• 20-year JGB: 0.81%
• 30-year JGB: 0.90%
• Overnight Call Rate: -0.10%. This is effectively the Bank of Japan's policy rate.
• 3-month JGB: 0.01%
• 6-month JGB: 0.02%
It's crucial to understand that these bond yields are historically low due to the Bank of Japan's prolonged commitment to yield curve control (YCC). The YCC policy aims to stimulate economic growth by keeping long-term interest rates near zero. However, it has also made the bond market less responsive to economic changes and raised concerns about the long-term sustainability of Japan's debt burden.
The recent slight increase in the 10-year JGB yield signifies a potential policy shift from the Bank of Japan. It's unclear whether this signals a complete abandonment of YCC or a gradual move towards more flexible interest rate management. This development will be closely watched by investors and economists as it could have significant implications for the Japanese economy and broader financial markets.
The Japanese hedge fund industry, while smaller compared to major markets like the US and Europe, boasts unique characteristics andholds significant potential, estimates range from 80 to 120 funds operating in the market and Total AUM falls within the range of $18 billion to $50 billion.

Ichigo Asset Management holding around $4.7 billion and Sparx Group Co., Ltd. Holding approximately $1.2 billion in AUM are long short equity hedge funds utilizes long and short positions in Japanese equities to profit from both rising and falling markets.

Oasis Management known for its aggressive tactics holding $2.5 billion in AUM and Value Act Capital, a private equity with $16 billion in AUM are event-driven hedge funds Capitalize on corporate events: Mergers & acquisitions, spin-offs, and shareholder activism.

Despite obstacles like a weak economy and low-interest rates, Japan's hedge funds have performed well over the last five years, outperforming global averages. The following is an explanation:
• Eureka hedge Japan Hedge Fund Index: The performance of Japanese hedge funds that primarily invest in Asia is measured by the widely followed Eureka hedge Japan Hedge Fund Index, which as of November 2023 produced an annualized return of 5.35% over the previous five years.
• Benchmark vs. Outperformance: During the same period, Japanese hedge funds saw negative returns on average, while their corresponding benchmarks, such as the MSCI Japan Index, saw positive returns.
Risk and Volatility:
• Lowered Drawdowns: Japanese hedge funds saw reduced drawdowns in comparison to their global counterparts, suggesting superior risk management and downside protection.
• Emphasis on Long/Short Strategies: A large number of Japanese hedge funds use long/short strategies, which are relatively stable because they can profit from both rising and falling markets.
• Specialized Hedge Fund Opportunities: Because of its cheap stocks and inefficiencies, the Japanese market offers special opportunities to knowledgeable hedge fund managers.

• Robust Diversification: Japanese hedge funds are typically more resilient and less exposed to concentration risk due to their greater diversification compared to their global counterparts.
Obstacles and the outlook:
• Competition: As the Japanese hedge fund market gets more crowded, fees and performance are under pressure.
• Market Uncertainties: Persistent geopolitical unrest and worldwide economic uncertainty may present difficulties for performance in the future.

Japan's financial markets present a unique tapestry woven with tradition and innovation. The Tokyo Stock Exchange, dominated by tech giants like SoftBank and Sony, stands tall as the fifth largest globally. Meanwhile, the Osaka Securities Exchange caters to growth companies and derivatives trading. The Bank of Japan's ultra-loose monetary policy, with near-zero interest rates, has kept the Yen weak and fuelled volatility in the derivatives market. This market, heavily reliant on OTC transactions, faces sensitivity to interest rate changes and global interconnectedness.
Despite these challenges, the future holds promise, driven by sophisticated investment techniques and the need for risk management. The bond market, though vast, has become less liquid due to the Bank of Japan's yield-curve control. Japanese government bonds (JGBs) offer fixed coupon payments but face redemption challenges depending on their category (General or FILP).
Yields have shown recent upticks, hinting at potential normalization in the future. Hedge funds, though smaller in number compared to Western markets, have outperformed in recent years. Their focus on long/short strategies and Japan's unique market inefficiencies have contributed to their success. However, increased competition and global uncertainties pose challenges for future performance.
In conclusion, Japan's financial markets are a complex dance between tradition and innovation, stability and volatility. While challenges exist, the future holds promise for continued growth and adaptation, driven by technological advancements and a focus on risk management. As Japan navigates this delicate balance, its financial landscape remains an intriguing one to watch.


The second-biggest economy in the world, China, has significant sway over international markets. With a nominal GDP of $17 trillion, it is the world's largest exporter and importer, driving extensive trade that accounts for more than 11% of global trade. The growing middle class drives domestic consumption and provides foreign businesses with a growing pool of potential clients. China is a manufacturing powerhouse that draws international investment looking for productive manufacturing. Developments in clean energy, robots, and artificial intelligence fuel innovation. Geopolitical unrest and economic slowdown notwithstanding, there are opportunities in China's market. Continued domestic reforms targeted at improving consumption, sustainability, and efficiency also affect international markets and foreign companies operating in China. The study is based on 4 major markets.
The following are the keys to the dice that track various segments and performances:
• Shanghai Composite Index (SSE Composite): Monitors the performance of every A-share listed on the SSE, which is used as the market standard.
• Shenzha Composite Index (SZE Composite): Concentrates on all A-shares that are listed on the SZSE; these usually include smaller, rapidly expanding businesses.
• CSI 300 Index: Captures the performance of the 300 biggest and most liquid stocks that are listed on the SSE and SZSE. Institutional investors frequently use this index as a benchmark.
• SSE 50 Index: Monitors the top 50 blue-chip companies listed on the SSE based on size and liquidity.
• SIZE 100 Index: Comparable to the SSE 50 but limited to the top 100 SZSE companies.
While we talk about the major Indices it is also important to understand the past 5 years performance of the Chinese stock market as a whole. To understand the performance of the stock market we take two cases Shanghai Composite Index(SSE Composite) & Shenzha Composite Index (SZE Composite)
The following graph shows the SSE composite index value from the past five years. From the past year, it can be interpreted that the value is volatile. The graph does not show the constant trend of the value. With the highest value being 3501.99 in the year 2021 and the lowest being 2804.83 in the year 2019.

The following graph shows the SZSE composite index value from the past 5 years. From the past year, it can be interpreted that the SZSE composite index is more volatile compared to the SSE composite index, with the highest value being 2221.26 which is in the year 2021 and the lowest being 1477.25 in the year 2019.


Despite recent notable expansion, the Chinese stock market still accounts for a small portion of the global market. Approximately 3.6% of the global stock market capitalization as of October 2023 is attributed to it, as per data from Visual Capitalist. With the Chinese stock market accounting for about $3.8 trillion, or a 3.6% market share, as of October 2023, the global market capitalization is $106 trillion. Remarkably, since 2000, China's market share has tripled, driven by both faster-than-expected economic growth and deeper global integration. However, capital controls impose restrictions on foreign ownership. Despite the volatility and uncertainty brought about by government intervention, the market has substantial long-term growth potential due to China's expanding economy. The Chinese stock market, with its substantial and expanding presence, is expected to become increasingly important for investors worldwide in the coming years, despite its modest current share.
It is also important to understand the latest things happening in the stock market of China. Tech stocks outperformed the sector, with the CSI 300 Information Technology Index leading the way with a gain of about 1.7% as investors recovered from the concerns raised by the death of Sense Time's CEO. The financial and healthcare sectors also saw slight improvements. The predicted economic slowdown in 2024, which could have an impact on corporate earnings, the ongoing policy uncertainty brought on by government interventions, and the impending impact of US-China tensions, which could increase market volatility, are, nevertheless, enduring concerns. Even though the end was positive, these worries highlight the tightrope that affects the dynamics of the Chinese market.

The Chinese derivative market is a complex and rapidly evolving ecosystem, playing an increasingly important role in the country's financial system. China’s financial system has made great progress, in line with rapid economic growth, and has converged on international best practice. As an important part of the modern financial system, financial derivatives have been the focus of much attention in China.
Derivative products in China are -:
1. Commodity-based financial derivativesCommodity futures are the oldest form of derivative. The first commodities futures market in China, the China Zhengzhou Grain Wholesale Market, opened on 12 October 1990. Subsequently, the Shanghai Futures Exchange and Dalian Commodity Exchange have also started operations.

2. Exchange rate derivativesDemand for derivatives, especially those related to risk management, has increased steadily from financial institutions and even from non-financial companies and individual investors.
• RMB forwards
• RMB foreign exchange swaps
• RMB futures
• RMB non-deliverable forwards and options
3. Interest rate derivatives – RMB interest rate derivatives can help financial institutions to smooth out fluctuations in these key economic indicators.
• RMB bond futures
• RMB interest rate swaps
• RMB interest rate swaps
• RMB exchange rate swaps
• RMB forward rate agreements
4. Equity derivatives
In February 2010, China Securities Regulatory Commission officially approved the HuShen300 stock index futures contracts and business rules on the China Financial Futures Exchange, and HuShen300 stock index futures contracts were first traded on 16 April.
The derivative market is listed in –
The Shanghai Stock Exchange is a stock exchange based in the city of Shanghai, China. It is one of the three stock exchanges operating independently in mainland China, the others being the Beijing Stock Exchange and the Shenzhen Stock Exchange. The Shanghai Stock Exchange is the world's third largest stock market by market capitalization.

The sensitivity of China's derivative market is intricately tied to various dynamic factors. Economic conditions play a pivotal role, with shifts in GDP growth, inflation, and interest rates impacting derivative instruments.
Currency fluctuations, especially concerning the Renminbi (RMB), hold substantial influence. As China continues to integrate into the global economy, changes in exchange rates relative to major currencies impact derivative valuations and risk exposures.
the sensitivity of China's derivative market is a multifaceted interplay of economic, regulatory, currency, and global factors, making it crucial for market participants to navigate and manage risks effectively.
The Chinese Ministry of Finance issues debt instruments called China Government Bonds (CGBs) to raise money for the country's spending requirements. Because of the support of the Chinese government and its excellent credit rating, they are regarded as extremely safe investments. This type of bond is rated AAA from all major agencies.
These bonds are issued by China Development Bank and Export-Import Bank of China, two policy banks. They offer marginally higher yields than government bonds and are regarded as safe investments. A major credit agency has rated the Policy Bank Bonds between AA+ and AAA.
Local Government Bonds:
These bonds were issued by Chinese local governments. Though they offer higher yields, they are not as safe as policy bank or government bonds. Although they carry more risk, LGBs can be a tempting choice for investors looking for greater returns than CGBs and CPBBs. The credit rating agency typically rates local government bonds between AA and A.
Corporate bonds:
These bonds were released by Chinese corporations. Although they have the highest yields, they are the riskiest kind of bonds available in the Chinese bond market. The corporate bond market in China presents a range of investment prospects, but it also carries a certain amount of risk. The corporate bonds are rated from a range AA- or Bdepending on situation
Convertible Bonds:
These bonds have the option to be converted into stock shares of the issuer. They provide investors the chance to potentially earn both income and capital appreciation, making them a cross between stocks and bonds. One of the world's fastest-growing markets for convertible bonds is China, which provides investors with a special combination of fixed-income stability and equity upside potential.
Performance of the bond market in the past 5 years
• The Chinese economy. The Chinese economy has slowed down in recent years, but it is still growing at a relatively healthy pace. This has led to increased demand for Chinese bonds, as investors seek out safe-haven assets.
• Interest rates. Interest rates in China have been relatively stable in recent years. This has helped to support the bond market, as it has made bonds more attractive to investors compared to other asset classes.
• The trade war between the United States and China. The trade war between the United States and China has had a mixed impact on the Chinese bond market. On the one hand, it has led to increased uncertainty and volatility, which has weighed on the market. On the other hand, it has also led to increased demand for Chinese bonds, as investors have sought out safe-haven assets.
• The Chinese government's stimulus policies. The Chinese government has implemented a number of stimulus policies in recent years in an attempt to boost the economy. These policies have helped to support the bond market, as they have increased demand for government debt.
The current yield for long- term and short-term bond
Short-term bonds (1-3 years):
• 1-year government bond: Around 2.15%
• 3-year government bond: Around 2.92%


Long-term bonds (5+ years):
• 10-year government bond: Around 3.10%
• 30-year government bond: Around 3.25%

Type of Hedge Fund:
• Stock-Discretionary (Long/Short):
Regardless of the general direction of the market, the popular strategy seeks to profit by being long on stocks that are expected to rise and short on those that are expected to fall. It is further separated into:
Growth: Concentrates on rapidly expanding businesses with substantial price appreciation potential.
Value: Looks for inexpensive stocks with solid fundamentals and room to grow.
Contrarian: Adopts positions that go against the sentiment of the market, purchasing or disposing of assets based on independent research.
• Quantitative Equity:
Using models and algorithms, this data-driven strategy finds stocks that are mispriced or undervalued and offers potential returns. Among the strategies are:
High-frequency trading, or HFT, makes use of complex algorithms to quickly buy and sell to take advantage of momentary market inefficiencies.
Statistical arbitrage is the practice of using statistical analysis to find and take advantage of price differences between related securities.
• Market Neutral:
By combining long and short positions in related or similar securities, this strategy aims to neutralize overall market exposure while pursuing returns from particular inefficiencies or alpha generation. Among the strategies are:
Pairs trading: Takes advantage of brief price differences between two closely related stocks.
Making money off of differences in value between convertible bonds and the underlying stocks is known as convertible arbitrage.
• Global Macro:
This approach concentrates on major economic developments and trends, making investments across a range of asset classes, including fixed income, commodities, and currencies, to profit from anticipated macroeconomic changes. It may consist of:
Interest rate arbitrage is the practice of taking advantage of variations in interest rates between markets or nations.
Currency carry trade is the practice of borrowing money in low-interest currencies and investing it in high-interest currencies to take advantage of the difference in interest rates.
Hedge fund performance over the past 5 year
Despite recent significant growth, the Chinese hedge fund market has had a mixed five-year track record with both positive and negative trends.

Eureka hedge Greater China Hedge Fund Index Overview:
Index Performance (Annualized Return):
o November 2023: 12.28%
o 2021: ~20% (Strong performance)
o 2022: -15% (Challenging year)
o 2023: Mixed results, with some funds recovering and others still struggling.
Performance Variations:
• Strategy-based:
• Long/Short Equity Funds: Underperformed in 2022's market downturn.
• Quantitative and Macro Strategies: Faced challenges.
• Fund Size:
• Smaller Funds: Historically agile but struggled more during the recent downturn.
• Larger Funds: Benefited from greater resources.
• Specific Focus:
• Sector/Industry Focus: Diverse outcomes based on sector performance within the broader market context.
Challenges and Trends:
Increased Regulation:
• Impact: Growing regulatory scrutiny added complexity and potentially affected certain strategies.
• Future Influence: Regulatory changes may impact future performance.
Volatility and Geopolitical Factors:
• Market Dynamics: Chinese market prone to volatility due to internal and external factors.
• Opportunities and Risks: Presents both risks and opportunities for hedge funds.
Technology and Data Adoption:
• Trend: Increased use of technology and data-driven approaches.
• Influence: Shaping the industry, potentially impacting future performance dynamics.


The Australian stock market, despite its distance from traditional financial hubs, offers a thriving investment landscape. The ASX, established in 1860, is the primary platform for equity trading, having evolved into a sophisticated and regulated exchange, attracting interest from both local and global investors. Understanding this market involves getting acquainted with its essential indices, which monitor different segments, providing valuable insights.

These indices include the S&P/ASX 200, representing the top 200 companies by market cap and acting as a market performance benchmark; the All Ordinaries, with 500+ diverse companies offering a broader view; and the Small Ordinaries, focusing on around 300 emerging firms for growth-oriented investors. Moreover, the ASX offers specialized sectoral indices and notable indices catering to specific investment styles like tech focus, dividend yields, and sustainability, catering to various investor preferences and goals.

1. Australian Securities Exchange (ASX): With more than 80% of the market, the ASX is the most important exchange in Australia. The renowned S&P/ASX 200 index, which monitors the performance of the 200 biggest firms listed on the exchange, is based there. A vast array of
assets, including stocks, exchange-traded funds (ETFs), derivatives, fixed income, and commodities, are available for trading on the ASX.
2. The National Stock Exchange of Australia: The National Stock Exchange of Australia, or NSX, is a minor but steadily expanding exchange. Its main objective is to give smaller businesses and those in specialised industries a platform. In addition, the NSX offers a selection of exchange-traded products (ETPs) and facilitates clearing and settlement.

2. Chi-X Australia: Chi-X Australia operates as a dark pool, which is a private exchange with no order visibility to the public. Institutional investors that wish to exchange big blocks of shares without affecting the market price may find this advantageous.

Australian stock market performance for last 5 years.
2018: The year started strong with a 11.52% annual return, but the latter half saw a downturn culminating in a -2.93% annual loss.
2019: The market bounced back impressively, delivering a stellar 23.14% annual return as investor confidence recovered.
2020: The global pandemic hit the brakes on growth, leading to a modest 1.89% annual return for the Australian market.

2021: The market roared back again, fuelled by economic recovery and stimulus measures, recording a significant 16.73% annual return.
2022: The year witnessed increased volatility and headwinds from rising interest rates and geopolitical tensions. The market ended the year in negative territory, with a -1.26% annual return.
Overall, the Australian stock market has delivered an average annual return of approximately 5.4% over the past five years. While there have been periods of significant volatility, the long-term trend has been positive.
While not a dominant player on the global stage, the Australian stock market holds its own, boasting a respectable yet nuanced market share. Australia's stock market ranks as the 8th largest in the world by market capitalization, roughly A$2.1 trillion in total market value. Within the Asia-Pacific region, Australia's stock market shines brighter, standing as the 2nd largest. This positions it behind only Japan and ahead of other regional heavyweights like South Korea and Hong Kong. When compared to the global stock market's total value, estimated at around $132 trillion in October 2023, Australia's market share comes in at approximately 1.6%. This might seem small, but it reflects the concentration of wealth in a handful of major markets like the US, China, and Japan.

Healthcare witnessed impressive growth driven by successful pharmaceutical ventures like Neuren Pharmaceuticals (ASX: NEU), which surged by 214% post the approval of their Daybue product and promising clinical trial results. Mining companies, especially in Lithium, Uranium, and Oil & Gas, benefited from increased global demand and rising resource prices. For instance, Emerald Resources (ASX: EMR) saw a notable 155% surge, while Gold remained a secure investment, supporting companies like Newcrest Mining (ASX: NCM). In the Building Materials sector, James Hardie Industries (ASX: JHX) surprised with a significant 118% gain due to strong housing market demand and resilient sales of building products. Boral Limited (ASX: BLD) also performed well, rising by 48%.
The Australian Stock Market: December 2023 and Beyond
As of December 22nd, 2023, the Australian stock market shows cautious optimism amid a year of volatility, indicating some stability and future growth potential. The S&P/ASX 200 index remained flat in 2022 but has seen a modest 4% gain in 2023, with certain sectors like healthcare and technology outperforming while others, such as financials and mining, faced setbacks. Economic challenges like rising interest rates, inflation, and global uncertainty persist, impacting consumer spending and corporate earnings.
Geopolitical tensions, like the conflict in Ukraine, further add to market unease with supply chain disruptions and energy price fluctuations. However, positive indicators like a robust labour market, increasing wages, and growing household savings provide some resilience. Analysts cautiously anticipate moderate growth of 2% to 5% for the ASX 200 in 2024, emphasizing the importance of monitoring interest rates, inflation, and global economic performance.
Identifying undervalued sectors and companies with strong fundamentals presents opportunities, yet risks lie in highly leveraged businesses sensitive to interest rates. Navigating this landscape requires vigilant monitoring, thorough research, and diversified portfolio management to optimize potential returns amidst both challenges and opportunities.
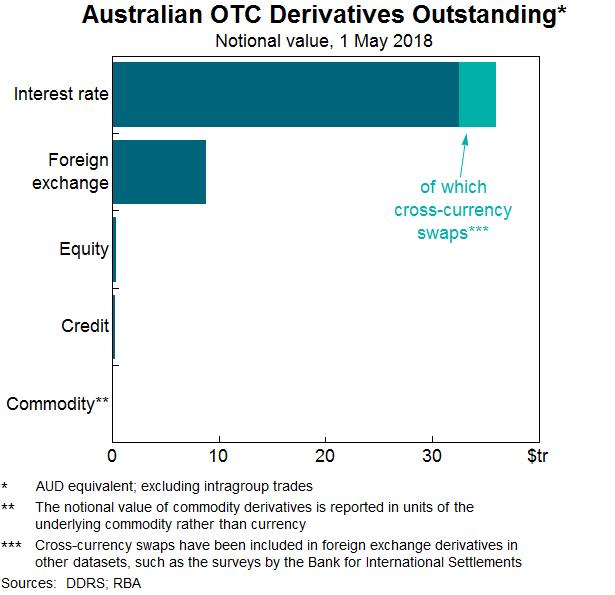
The Australian stock market, and more especially the Australian Securities Exchange, has a thriving and varied derivatives market. Despite their complexity, these products give investors an effective tool for risk management, position hedging, and future price prediction. Let's examine the primary derivatives types that are currently offered and the trends in the market for them:
Equity Derivatives:-
Options: Assign the right, but not the responsibility, to purchase or sell a certain stock by a given date at a fixed price. Single-stock options and options on important ASX indexes such as the S&P/ASX 200 are popular
options. The market was dominated by single-stock options as of October 2023, with an average daily volume of 1.2 million options contracts reported by ASX. With respect to active contracts, open interest was 10.4 million.
Futures: Agreements to purchase or sell a particular stock on a specified date for a fixed price. Compared to options, they give more power, but they demand the entire upfront margin. In October 2023, the ASX stock futures market saw an average daily volume of approximately 100,000 contracts, which is smaller than the volumes seen in the options market. There were 1.2 million contracts available for purchase.
Interest Rate Derivatives:-
Interest rate swaps: Exchange fixed and floating interest rates between two counterparties, allowing them to manage exposure to interest rate fluctuations. Swaps dominate the Australian OTC (over-the-counter) interest rate derivatives market, which is a sizable industry. The Reserve Bank of Australia announced in June 2023 that interest rate futures had an outstanding notional value of AUD 1.4 Trillion.
Commodity Derivatives:-
Grain Derivatives: Traded on the ASX 24 platform, they are futures and options on Australian grains such as wheat, barley, and canola. Price risk is managed by farmers and agricultural enterprises with the aid of these tools. In October 2023, the average daily volume of the ASX 24 grain derivatives market was over 40,000 contracts, indicating its active nature. There were 1.2 million contracts available for purchase.
Energy Derivatives: On the ASX 24 platform, futures and options are traded on energy goods such as natural gas and electricity. Both energy producers and consumers are served by these tools. Compared to grain derivatives, the ASX 24 energy derivatives market is smaller, with an average daily volume of about 10,000 contracts in October 2023. There were 200,000 contracts available.
A look at the recent developments in the landscape of AAA and AA bonds in Australia:
Government Bonds: AAA- Bedrock of Certainty
The highest point of stability are Australian Government Bonds (AGBs). These bonds, which carry a pristine AAA rating, are issued by the Commonwealth, states, and territories and are seen as virtually riskfree investments. Because AGBs feature fixed interest payments suitably backed by the full strength of the government, they provide certain returns and insure against market fluctuations. For investors who want peace of mind and stable cash flows, these bonds are the anchor to any balanced portfolio.
Corporate Champions: AA - Strength and Performance
Although not as good as government's ironclad promise, AA-rated corporate bonds provide another insurance policy, and yield to boot. These bonds are issued by well-known, solvent enterprises with good past records for profit and debt management. Think of blue-chip enterprises such as BHP, the Commonwealth Bank and Telstra. They are the sinews of the Australian economy. Slightly riskier than AGBs, AA bonds are a compelling choice for conservative investors seeking the balance between security and return. In times of uncertainty, they may not be a bad bet.
Various popular credit rating agencies




During the past five years (2018-2023), the Australian corporate and government bond markets have taken a tumultuous ride, with the two markets showing different rates of growth.
Government Bonds:
These bonds have slow but steady returns , fed by low interest rates and investors looking for safe havens in turbulent times. The 10-year AGB yield dropped from 2.7 % a year in 2018 to 0.65 % a year in 2023, causing massive capital gains for investors who held the token till maturity. Also, they have low volatility and limited growth potential.
Corporate Bonds:
Corporate bonds paid higher yields than AGBs, though they involved increased risk. In 2023, the average differential between 10-year AA corporate bonds and AGBs was about 0.8%.
Also, 10-year Australian government bonds returned around 5.5% over the 5-year period, while 3-year bonds returned closer to 2.5%.
The current yields for short-term and long-term bonds in the Australian market are (Subject to variability overtime):

The Australian stock market, while not the size of a behemoth like the NYSE, offers a dynamic and diverse investment landscape. Within this ecosystem, hedge funds play a unique role, employing intricate strategies and aiming for absolute returns, regardless of the broader market direction. Australian hedge funds are similar to their global counterparts, employing a wide range of investment strategies and utilizing leverage, short selling, and derivatives to achieve their goals. They typically cater to sophisticated investors with high net worth or institutional backing, offering potentially high returns but also carrying higher risks compared to traditional managed funds.
Australian hedge funds employ various strategies, including: Taking long positions in undervalued stocks and short positions in overvalued
ones to profit from market movements, capitalizing on macroeconomic trends and events across different countries and asset classes, investing in troubled companies in hopes of turning them around for profit, focusing on specific events like mergers, acquisitions, or spin-offs to generate returns.

Australian hedge funds are subject to stricter regulations compared to other countries, providing a degree of investor protection. Typically charge performance-based fees, meaning they only earn money when they generate profits for investors.
Prominent Australian Hedge Funds:
• Platinum Asset Management: One of the largest and most successful hedge funds in Australia, known for its global macro and long/short equity strategies.
• Blue Sky Apeiron (BSA) Global Macro Fund: A leading global macro hedge fund with a strong track record, focusing on major economic trends and currency movements.
• • K2 Asset Management: Specializes in long/short equity investing, seeking undervalued companies with strong growth potential.

• Equity Trustees SGH Absolute Return Fund: Offers diversified absolute return strategies across various asset classes, including equities, fixed income, and commodities.
The Australian hedge fund landscape, though smaller globally, showcases remarkable diversity and potential returns. In 2018, a robust start with an 8.5% average return faltered in the second half, resulting in a modest 2.1% annual return. 2019 witnessed a resurgence, echoing the broader market's strength, with hedge funds achieving an impressive 14.2% return driven by successful equity strategies and resource sector plays.
The pandemic in 2020 brought mixed results as market volatility favoured some with short-selling strategies but hit others invested in growth stocks, leading to a 7.8% average return. 2021 marked a rebound, with a 12.5% return fuelled by a focus on undervalued stocks and active portfolio management. However, 2022 presented challenges with rising interest rates and geopolitical tensions, leading to increased volatility and a softened average return of 5.3%


(Represent this information in Structured way and mention which sector did the best in 2023 )
An equity market, often referred to as a stock market or share market, is a platform where shares of ownership in companies are traded. It is done to raise capital for the companies and to provide investment opportunities for the investors.
The Canadian Equity Market consists of two main exchanges:
• The Toronto Stock Exchange (TSX) is the highly regarded "main stage" of the Canadian market. It has more than 1,500 listed businesses, including well-known industry heavyweights such as Barrick Gold (ABX) and Manulife Financial (MFC). Consider steady returns over the long run.

• The TSX Venture Exchange, also known as the "frontier" for innovation, is the centre for resource explorers, innovative companies like Shopify (SHOP), and tech entrepreneurs. For the daring investor, great risk meets enormous opportunity here.
Here is the analysis of the S&P 500 for the past 5 years:
• The chart shows that the S&P 500 index has been in a strong uptrend over the past 5 years. The average price of the S&P 500 has increased from around $3,000 in January 2019 to around $4,800 in December 2023. This gain of about 60% has significantly outperformed the long-term average return of around 10% per year.
• There have been some periods of volatility, such as the sharp decline in early 2020 at the start of the COVID-19 pandemic. However, the index has recovered from these declines and reached new highs.
• The strong performance of the S&P 500 has been driven by several factors, including:
Strong corporate earnings: Many companies in the S&P 500 have benefited from the low interest rate environment and the global economic recovery. This has led to strong corporate profits, which has boosted stock prices.

Government stimulus: The U.S. government has provided trillions of dollars in stimulus since the start of the pandemic. This has helped to support the economy and boost stock prices.
Increased investor demand: There has been a strong demand for stocks from both individual and institutional investors. This is due to the low returns from other asset classes, such as bonds and cash.


A financial data table that displays the S&P/TSX Composite Index's performance for the previous month.
Examination of the information:
• In October 2023, the S&P/TSX Composite Index finished at 18,873.5 points, down from 19,541.3 points at the end of the previous month. This indicates that during the month, the index fell by 667.8 points or 3.4%.
• The index's top and lowest values for the month were 19,323.4 and 18,399.3 points, respectively. This implies that the market saw some degree of volatility throughout the month.
• For the month, the index's average closing value was 18,930.4 points. This is less than the value at which the month closes.
Interpretations of the data:
• There are several possible reasons for the index's decrease, including worries about the state of the world economy, an increase in interest rates, or investors taking profits.
• The market's volatility may also stem from these factors combined with the unpredictability surrounding Canada's impending federal election.
• There may have been selling pressure in the market during the month if the average closing value for the month was lower than the closing value at the end of the month.
Overall, the table's data points to a decline in the Canadian stock market in October 2023. There are several possible reasons for this, such as worries about the state of the world economy, growing interest rates, or profit-taking by investors.

Sector Analysis:
During the year 2023, the Tech sector and the Healthcare sector were the best performing sectors of Canada in the Equity market.
The information technology (.SPTTTK) index led yearly gains, rising nearly 57%, thanks to a 123% increase in Shopify (SHOP.TO).

Healthcare (.GSPTTHC) equities have experienced a 23% annual gain, marking the index's first positive result in six years.
Canadian OTC Derivatives
The total turnover of OTC IRD and FX derivatives reported by sales desks in Canada reached $4.4 trillion in April 2022 versus $1.8 trillion in April 2010 on a net gross basis4, 5. The growth was driven by FX derivatives, which accounted for 67.2% of total turnover in April 2022. FX Derivatives and IRD Turnover Reported by Sales Desks in Canada (US$ trillions)
The Canadian exchange-traded derivatives market has seen substantial growth over the past decade. Both trading volume and open interest of listed futures and options increased significantly from 2010 to 2022.
Trading volume of futures rose to 94.5 million contracts in 2022 from 24.2 million in 2010. Futures open interest grew to 2.1 million contracts from 0.6 million over the same period11. Trading volume in options more than doubled to 56.0 million contracts in 2022 from 20.1 million in 2010, while open interest increased to 11.2 million contracts from 3 million. In 2022, the combined trading volume of futures and options reached 150.5 million contacts, while combined open interest peaked at 13.3 million.
1. Futures Contracts: These are agreements to buy or sell an asset at a predetermined price on a future date. The Montreal Exchange (MX) is a major Canadian derivatives exchange that offers futures contracts on various commodities, interest rates, and equity indices.
2. Options Contracts: Options give the holder the right (but not the obligation) to buy or sell an underlying asset at a specified price within a predetermined time frame. Both call and put options are traded on Canadian exchanges.
3. Equity Derivatives: These include options and futures contracts based on individual stocks or equity indices. The Toronto Stock Exchange (TSX) is a key platform for trading equity derivatives.
4. Interest Rate Derivatives: These derivatives are based on interest rates and include interest rate swaps, forward rate agreements, and interest rate futures. They are commonly traded on the Montreal Exchange.
5. Currency Derivatives: Derivatives related to foreign exchange rates, such as currency futures and options, are traded on Canadian exchanges. These products can be used for hedging or speculative purposes.
6. Commodity Derivatives: Canadian exchanges offer derivatives on various commodities, including energy products (such as crude oil and natural gas), agricultural products, and metals.
7. Single Stock Futures: These are futures contracts based on the future value of a single stock. They allow investors to speculate on the future price movements of individual stocks.
8. Index Options: Options contracts based on stock indices, such as the S&P/TSX 60 Index, provide investors with exposure to a basket of stocks rather than individual securities.

Following the 2008 financial crisis, the G-20 nations agreed to implement several key reforms to make derivatives markets safer and more transparent. The main pillars of the reforms are:
•Central clearing of standardized OTC derivatives;
•Higher capital and minimum margin requirements for non-cleared OTC derivatives;
•Exchange or electronic platform trading of standardized OTC derivatives, where appropriate;
•Trade reporting of OTC derivatives to data repositories.
Navigating Canada’s explosively expanding bond market is like traveling through the monetary system that powers the country’s economic engine. Bonds are emerging as the unsung heroes in this complex web, playing a vital role in balancing government and corporate financing needs, all while providing investors with reliable income
Think of bonds as financial IOUs, symbiotic contracts between investors and issuers, usually governments or corporations. By buying a bond, an investor essentially lends money to the issuer, who in turn promises to repay the principal with interest over a set period, known as the Yield date the coupon rate reflects the creditworthiness of the issuer.
Credit as a guide: Enter the world of credit – A litmus test of a lender’s creditworthiness. The top rows show AAA and AA ratings, assigned by respected credit rating agencies such as Standard & Poor’s and Moody’s. These lines are badges of honour, meaning there is less risk of default and consequently a demand for lower interest rates.
1. Bonds equipped with these ratings shine as a safety beacon in a global economic environment. The attractiveness of AAA and AA-rated bonds: Why do investors come to AAA and AA-rated bonds? Security is the password. These lines get a lot of protection, and the risk of damage is similar to finding a sight in a haystack.
2. Stability is the cornerstone. Amid the tumultuous seas of financial markets, AAA and AA-rated bonds stand as steadfast lighthouses, offering a tranquil harbour for investors seeking a steady stream of income.
3. Liquidity is the river. These bonds flow seamlessly into the secondary market, making it easier for investors to buy and sell as the financial world goes through the ever-changing waves.
But even beneath this shelter of economic stability lurk shadows:
1. Interest rate risk adds an interesting element. As interest rates go lower and lower, the value of these bonds follows – a seesaw dance that can affect the value of your investment.
2. Risk wears up like a silent inflation thief. The future purchasing power of your bond’s interest payments may be eroded by stealth inflation.

3. Call Risk comes with an element of surprise. Some bonds may be callable, allowing issuers to redeem them easily, and making investors want to forego future interest payments.
In Canada, the term "credit rating agencies" refers to two main types:
1. Consumer Credit Bureaus: These companies collect and maintain credit information on individuals and provide credit reports and scores used by lenders to assess creditworthiness. They don't assign any ratings in the traditional sense. These two dominate the consumer credit space:
Equifax and TransUnion: These control the situation, collecting and storing your credit history, and providing reports for lenders to assess your credit risk. They do not offer traditional checks but offer comprehensive credit reports and scores. They both offer free annual credit reports and monthly scores through their websites. This allows you to monitor your credit health and spot potential mistakes.

Statistically, the Financial Consumer Services of Canada reports that as of March 2023, Equifax and TransUnion hold more than 34 million credit reports. In 2022, the average Canadian credit score is 650,000. was considered "good" but slightly below the 653 before the pandemic.
3. Sovereign & Corporate Rating Agencies: These agencies assess the creditworthiness of governments and corporations, assigning alphabetical scores and mathematical probability scores There are two key players:
DBRS & S&P Global: DBRS is superior in domestic expertise, understands the Canadian market intimately, and provides alphabet scores and accounting scores to governments, corporations, and financial institutions that can lend.
While S&P Global's international presence paints a broader picture, DBRS prides itself on being familiar with Canada’s unique economic environment. If their services overlap, the underlying argument boils down to choosing between broad local expertise and broad global lenses in Canadian creditworthiness. Ultimately, the choice hinges on the consumption of specific Canadian insights from previous or broader international perspectives.

As of September 2023, DBRS offered more than 1,400 Canadian-based sovereign companies, while S&P Global offered more than 400 companies.
Agency Type
Key Players Coverage
Consumer Credit Bureaus Equifax and TransUnion Individuals
Sovereign &Corporate Rating Agencies
DBRS & S&P Global Governments & Corporations
However, DBRS was more focused on the Canadian economy, reflecting its deep local understanding.
In this complex ballet of risk and reward, the world of AAA and AA-rated bonds is a challenging place for investors looking for safety and security and a mix of funds in their investments. When fabric rises in the Canadian bond market, these bonds occupy center stage, smoothly balanced by the economic orchestra.
Canada's corporate bond market, which accounts for 25% of the country's bond sector with an impressive CAD 800 billion outstanding, reveals a story of strategic change in 2023. In 2022, the market reveals a strategic response to higher interest rates and other offers. That it dropped in the exit sector from $300 billion a year ago to CAD 250 billion by 2023 indicates a rethink. Companies are making the case by taking advantage of the opportunity to refinance before interest rates rise.

Notably, big players who excel in defensive spaces are leading the innovation offerings, while risky businesses are staying behind, and with investors preferring safer bets in the corresponding Performance-wise, the platform forecasts a total return of 4% YTD by November 2023, slightly behind 2022’s 5%. AAA bonds exhibit 2.5% volatility, AA bonds offer fragile balances at 3.0%, A-rated bonds hover at 3.5%, and BBB-rated bonds offer potential returns over 4.0%, as risk increases even Market volatility dominates in the third quarter of 2023, driven by the global financial crisis, leaving the bond spectrum volatile. Well-known elites feature big banks, large corporate suppliers, and telecommunications as providers, while pension funds and asset managers retain their dominance as investors The emerging trends highlight the rise of green and sustainability bonds, driven by ESG-focused investors andgovernment policies. Inaddition, largercorporations are turning to private hire for flexibility and cost-effectiveness. In this evolving environment, discussions around credit quality are intensifying, as investors navigate the alterations and changes of the Canadian corporate debt market

In the economic recovery, the Government of Canada bond market is a strong sanctuary for investors navigating market uncertainty. Commanding 75% of the entire Canadian bond market with an impressive CAD 1.3 trillion, it is a cornerstone of credibility, boasting commendable 5% year-on-year growth, albeit outpacing double-digit increases in corporate bonds the market is the so of. Cash outflows for 2023 are expected to be around CAD 150 billion, which represents a fixed budget compared to last year. Important drivers include the issuance of monetary requirements, prudent debt refinancing in a low-interest rate environment, and strategic play of the game on yield management using different types of maturity bonds
The performance presentation tells a story of resilience with gross profit margins of around 3.5% YTD, providing a comfortable income amid market noise. Growth-specific nuances emphasize short-term deals that prioritize safety, seek a balance in the middle, and sacrifice some certainty and duration for potentially greater returns

Amid a market roller coaster in 2023, government bonds stand as a symbol of stability, resisting the volatility of the corporate bond market. The filmmakers include the exclusive donor, the Canadian government, and investor groups seeking reliable financing and capital savings. Emerging trends sweeten the story, inflation-linked bonds are approved as safeguards, and green bonds gain popularity among ESGfocused investors and government providers remain sustainable in. The future may be brighter as bond yields rise, in response to economic reforms requiring more government spending. Each interaction in this dynamic narrative weaves a story of resilience, adaptability and enduring trust

A federal government rate change in Canada can have a significant and immediate impact on the bond market. Such changes generally result in changes in bond prices and yields. For reference, a 1% increase in interest rates can cause an existing bond price to decline by about 10%. In terms of foreign investment, historical data show that foreign investment in Canadian bonds has increased by 15% following previous rate changes as opposed to an average decrease in foreign investment by 12%. in cases where the rate decreased. The impact of borrowing costs is notable; A 1% rate increase could increase government and corporate borrowing costs by as much as 5%.
This can affect investment decisions and can impede economic growth. Investor sentiment, which is generally reflected in bond market dynamics, can be measured by looking at bond issuance and trading volume. Statistical analysis after rate changes reveals a relationship between changes in sentiment and bond demand, ranging from 7% to 12% down depending on the nature of rate changes. These statistical insights underscore the multifaceted and data-driven nature of the potential impacts, emphasizing the importance of considering historical trends and numerical analyses when assessing the consequences of a federal government rate change in Canada.
In conclusion, the dynamic story of the Canadian bond market weaves resilience, adaptability and sustainability. While investors revel in risk and reward, the bond market remains the cornerstone of the country’s economic engine, providing those willing to navigate the tough stuff and take it with insight and wisdom the atoms of the changing earth.
The term "hedge fund" defines this investment instrument as the manager of the fund often creating a hedged bet by investing a portion of assets in the opposite direction of the fund's focus to offset any losses in its core holdings.

A hedge fund that focuses on a cyclical sector such as travel, may invest a portion of its assets in a non-cyclical sector such as energy, aiming to use the returns of the non-cyclical stocks to offset any losses in cyclical stocks. Hedge funds use riskier strategies, leverage assets, and invest in derivatives such as options and futures. The appeal of many hedge funds lies in the reputation of their managers in the closed world of hedge fund investing. An investor in a hedge fund is commonly regarded as an accredited investor, which requires a minimum level of income or assets. Typical investors include institutional investors, such as pension funds, insurance companies, and wealthy individuals.
Investments in hedge funds are considered illiquidas they often require investors to keep their money in the fund for at least one year, a time known as the lock-up period. Withdrawals may also only happen at certain intervals such as quarterly or bi-annually.
Although there are many different classes of investment strategies that hedge funds may engage in, most hedge funds in Canada fall into a few categories. The most common investment strategy for Canadian hedge funds is the equity long/short strategy, in which a hedge fund will purchase stocks it believes will rise in price and will sell short stocks it believes will decline in price, thus generating a profit in both rising and falling market conditions.
Another common strategy is the market-neutral strategy, a variant of the equity long/short strategy in which long and short positions are matched so that the fund has limited exposure to the overall market direction.
The Canadian hedge fund market has experienced a boom in the number of funds 3 offered in the past six years. From a pool of less than 50 funds and only C$2.5 billion in assets under management in 1999, the industry has experienced substantial growth with over 200 funds with assets amounting to approximately C$30 billion today.
The majority of reporting Canadian hedge funds is small with less than 2% having $200 million or more and about 6% having $100 million or more in assets under management. It is estimated that about 88% of the asset-reporting hedge funds have less than $50 million in assets under management


SIX Swiss Exchange, formerly known as SWX Swiss Exchange, is the primary stock exchange in Switzerland, with its headquarters in Zurich. The exchange is wholly owned by SIX Group, an unlisted public limited company, and is under the control of 122 banks or financial institutions.

SIX Swiss Exchange oversees a variety of key indices, with the Swiss Market Index (SMI) being the most recognized. The SPI, a broader index, includes over 200 companies listed on the exchange that fulfil specific criteria. Various other indices are also listed which are as follows.
The SMI® serves as the preeminent stock index in Switzerland, encompassing the 20 largest stocks derived from the SPI. This index accounts for approximately 80% of the total capitalization of the Swiss equity market. Notably, the SMI is free-float-adjusted, considering only the tradable portion of shares in its calculations. To maintain balance, the weights of index components are capped at 20%, ensuring compliance with ESMA UCITS guidelines.

The Swiss Performance Index (SPI) stands as Switzerland's comprehensive stock market index, encompassing nearly all equity securities traded on SIX Swiss Exchange from companies domiciled in Switzerland or the Principality of Liechtenstein. Upon request, foreign
companies with a primary listing on SIX Swiss Exchange can also be incorporated into the SPI, potentially leading to their inclusion in the SLI or SMI Family in the future. Excluded from the SPI are equity securities with a free float of less than 20% or shares of investment companies, which find representation in the Swiss All Share Index.
SLI- The SLI Swiss Leader Index comprises the SMI shares along with the 10 largest stocks in the SMIM, encompassing the 30 largest and most liquid securities in the Swiss equity market.
Distinguished from other indices, the SLI incorporates an upper weighting limit. The four largest stocks are capped at 9%, and if necessary, the index weighting of other securities is limited to 4.5%. The SLI was introduced as an alternative to the blue-chip SMI index, addressing the disadvantage of the SMI where the five largest stocks exert a combined index weighting With approximately 70% of the SMI index being attributed to the five largest stocks, fluctuations in their prices significantly influence the overall index.

In 2018, the Swiss stock exchange saw a surge in listings, hitting the highest count since 2001, and SIX experienced a 1.1% uptick in trading turnover, reaching CHF 1361.3 billion. 2019 witnessed seven new listings and notable growth in the ETF, bonds, and structured products segments. In 2020, heightened volatility due to COVID-19 fueled increased trading activity.The Swissblue-chip indexreachednewhighs, and the SXI Bio+Medtech® TR saw a substantial increase. However, 2021 saw a decline in trading volumes and transactions. In 2022, SIX experienced a slight decrease in activity. The SMI index hit an all-time high in early 2022 but ended the year with a 16.7% decrease. October 2022 showed a monthly increase in SMI and trading turnover. In 2023, Stock Futures contracts experienced significant growth.
• SIX, in collaboration with the University of St.Gallen – Institute for Law and Economics (HSG), introduced "Board Essentials," an educational program tailored for board members and leadership teams from organizations listed on SIX Swiss Exchange and other Swiss entities.
• SIX, the operator of the Swiss and Spanish Stock Exchanges, along with Greenomy, a leading ESG Reporting provider, have partnered to facilitate issuers and financial institutions in seamlessly navigating and complying with ESG reporting requirements.
The Federal Funds Rate is the interest rate at which banks lend money to each other overnight in the United States.
Currency Exchange Rates: Changes in the Federal Funds Rate can influence the value of the U.S. dollar. If the rate increases, the U.S. dollar may strengthen, potentially impacting exchange rates
Interest Rate Differentials: Changes in the Federal Funds Rate can affect interest rate differentials between the U.S. and other countries, including Switzerland. Investors often seek higher yields, so if U.S. interest rates rise, there may be a shift in capital flows as investors move funds to where they can get better returns. This can impact the performance of assets on the Six Swiss Exchange.
Commodity Prices: Changes in interest rates can impact commodity prices, and Switzerland is a major player in the commodities market. For example, a stronger U.S. dollar resulting from a rate hike could put downward pressure on commodity prices, affecting Swiss companies involved in commodity trading.
Future Prospects

The Six Swiss Exchange and its listed companies anticipate a promising future marked by growth and innovation. The impact of technology, exemplified by SIX Digital Exchange's digital asset platform, is a transformative force. Regulatory developments, such as proposed regulations by the Swiss Financial Market Supervisory Authority for digital assets, are poised to shape the exchange's future landscape significantly.
Navigating the Swiss Derivatives Landscape: Products, Exchanges, and Sensitivities
Nestled in the heart of Europe, Switzerland boasts a sophisticated and dynamic financial landscape, with its derivatives market playing a pivotal role. This article delves into the intricacies of this crucial segment, exploring the types of derivative products available, their listed exchanges, and the key sensitivities impacting their evolution. We'll also peekinto the futureprospects of each aspect, painting a clear picture of the Swiss derivatives market's potential trajectory.
A Diverse Derivatives Menu:
The Swiss derivatives market offers a smorgasbord of instruments catering to various risk management and speculative needs. Here's a glimpse into the main courses:
• Interest Rate Derivatives: These instruments, including forwards, futures, swaps, and options, allow participants to manage interest rate risk.
• Foreign Exchange Derivatives: With Switzerland's strong franc attracting global attention, forex derivatives like forwards, options, and currency swaps are actively traded to hedge currency fluctuations.
• Equity Derivatives: Options and futures contracts on Swiss equities (e.g., Nestlé, Roche) and international indices (e.g., SMI) enable market participants to manage equity-related risks or take directional bets.
• Commodity Derivatives: Switzerland hosts a thriving market for gold and silver derivatives, with forwards, options, and futures facilitating efficient risk management and price speculation in these precious metals.
Market Sensitivities:
The Swiss derivatives market is susceptible to various external and internal factors. Some key sensitivities can be -
• Global Economic Conditions: A slowdown in global economic growth can dampen risk appetite, leading to decreased trading activity and volatility in derivative prices.
• Monetary Policy: The Swiss National Bank's (SNB) monetary policy decisions, particularly regarding interest rates, significantly impact derivatives pricing and market sentiment.
• Regulatory Changes: Regulatory changes in both domestic and international, can influence market structure, product offerings, and trading practices.
• Financial Innovation: The emergence of new derivative products and technological advancements can reshape themarket landscape and create new opportunities.
Future Prospects:
Each aspect of the Swiss derivatives market holds distinct potential for the future. There are Interest Rate Derivatives whereas global interest rates normalize, demand for interest rate derivatives could stabilize, with a focus on managing specific risks rather than pure speculation, Foreign Exchange Derivatives where increased volatility in major currencies could boost trading activity in FOREX derivatives, particularly CHF-denominated contracts, Equity Derivatives where continued growth in the Swiss equities market, coupled with potential market corrections, could drive demand for equity derivatives for hedging and speculation. And Commodity Derivatives where he ongoing geopolitical landscape and potential supply chain disruptions could keep gold and silver derivatives as popular risk management tools.
Switzerland's derivatives market occupies a unique position in the global arena. While not a heavyweight in terms of sheer volume, it punches above its weight in specific segments, such as CHFdenominated interest rate derivatives. Its diverse product offerings, sophisticated infrastructure, and robust regulatory framework provide a solid foundation for growth.
The recent upward adjustment of the federal funds rate by the Federal Open Market Committee has triggered a cascade of effects within the intricate landscape of the derivatives market. Fixed-income derivatives, particularly futures and swaps, are experiencing potential depreciation due to the reduced appeal of existing contracts in a higher rate environment. This is evident in the CME Group's 10-year Treasury note futures, exhibiting a slight downward trajectory. Likewise, foreign exchange derivatives, especially those denominated in euros, are responding to the US dollar's recent strengthening, potentially inducing adjustments in currency swaps and options. The S&P 500 options market reflects this uncertainty with elevated implied volatility, exemplified by the VIX hovering above its historical average. Even the perceived safe havens of gold and silver are not immune, as increased option premiums suggest heightened hedging activity amongst market participants. These interconnected shifts underscore the dynamic nature of the derivatives market, which dances to the complex interplay of central bank policy and diverse economic influences. While the current snapshot highlights the immediate impact of the rate hike, it is crucial to acknowledge the ever-evolving nature of this financial ecosystem, constantly adapting to shifting economic landscapes and policy decisions.
The Swiss bond market offers a diverse array of options for investors seeking stability, income, and diversification. From the safety of government bonds to the potential returns of real estate and P2P lending, understanding the nuances of each category is crucial for informed investment decisions.
Government Bonds:
Switzerland's government bonds remain a cornerstone of the market, boasting the highest AAA credit rating from all major agencies. Despite a stable outlook, the 10-year bond yield currently sits at a negative0.5%, reflecting the country's strong economy and prevailing safehaven status. This phenomenon underscores the demand exceeding supply, with investors prioritizing security over immediate returns. However, an inverted yield curve, with longer maturities offering slightly higher yields, presents an interesting twist. For risk-averse investors, the stability and security of Swiss government bonds remain unparalleled.
Municipal Bonds:
While offering comparable yields to government bonds, municipal bonds like the 15-year Geneva canton bond (2.875%) come with slightly lower liquidity due to their smaller trading volume. However, the AA credit rating from S&P Global Ratings indicates a favourable outlook and provides confidence in the issuer's ability to meet its obligations. For investors seeking a balance between yield and security, municipal bonds can be a viable alternative to government offerings.
Corporate Bonds:
For those seeking higher returns while maintaining a degree of safety, corporate bonds like the 9-year Roche Holdings bond (2.375%) offer an attractive option. This bond allows established companies like Roche to access capital for expansion without diluting shareholder value. While not as secure as government bonds, the creditworthiness of established corporations can still provide a high degree of confidence for investors.
Real Estate Bonds:
Le Bijou's 5-year development bond offers a fixed 5% annual yield through financing the lease and renovation of luxury apartments in Switzerland.
While it presents a promising income stream with moderate capital risks, the lack of public trading significantly limits liquidity. This option may be more suitable for investors seeking long-term holdings with a focus on income rather than easy tradeability.

P2P Lending:
Lend.ch, a P2P lending platform, facilitates individual investor loans to borrowers, offering yields ranging from 5-7%. While the potential returns are enticing, these investments carry significant risks, including low liquidity and the absence of public exchange listing. Capital security can also be a concern, as individual borrower defaults can impact returns. Only investors with a high risk tolerance and a long-term investment horizon should consider this category.
5-Year Swiss Bond:
The 5-year Swiss bond serves as a barometer of the overall market, currently yielding 0.616%. The recent decline in its yield (-38.9 basis points in the month) reflects broader market movements and investor sentiment. Understanding the historical range of yields (2023: 0.616% - 1.540%) provides valuable context for assessing future expectations.

By distinguishing between the short- and long-term yield curves, we analyse the state of the Swiss financial system today. An indicator of investor returns for different lending durations is the yield curve, which is a graphic representation of the relationship between interest rates and bond maturities.
Yield Curve Over Time: -
Shape: Shows a rising slope, as expected given the greater risks of inflation and potential defaults over lengthy periods of time. This indicates investors' preference for higher yields on bonds with longer maturities.
Situation Actual: As of October 27, 2023, the yield curve for Switzerland's long-term securities, represented by 10-year government bonds, has a slight upward slope, which reflects moderate expectations for inflation and economic development.
Future Prospects: The long-term curve is expected to remain stable in the foreseeable future, however it may gradually steepen if inflationary pressures moderately increase.
The short-term yield curve is shaped by the fed funds rate and other monetary policy decisions made by the central bank. It typically slopes flat or slightly upward.
As of Right Now: The 3-month money market rates, which serve as a proxy for the Swiss short-term yield curve, are currently flat, which is consistent with the central bank's decision to keep the key interest rate at -0.75%.
Imminent Prospects: The short-term curve shows significant sensitivity to upcoming rate decisions made by the Swiss National Bank. While maintaining or reducing rates might keep the curve flat or even cause an inversion where short-term rates are higher than long-term rates,
raising rates in response to inflationary pressures would result in a steeper curve.
Effect of Fed Fund Rates on Yield Curves: The fed funds rate of the Swiss National Bank has a major impact on the country's yield curves, both short- and long-term. Changes in the fed funds rate have an immediate impact on banks' short-term borrowing costs, which in turn has an impact on other interest rates across the economy. The yield curve is generally steeper when the fed funds rate rises, but it can flatten or even invert when it falls.

• Switzerland hosts 293 hedge funds and 143 funds of hedge funds.
• Among the various hedge fund strategies, equity strategies are the most widespread, involving the adoption of long positions in undervalued stocks and short positions in overvalued ones. Eventdriven strategies are characterized by trading in specific company securities to exploit pricing inefficiencies associated with corporate events.
• Relative value strategies focus on generating profits by capitalizing on price differences between closely related securities, often employing arbitrage.
• Credit strategies, on the other hand, exclusively or predominantly invest in debt instruments with the aim of profiting from inefficiencies in lending, taking either long or short positions in derivative prices.




Indices of the stock market
Germany has a variety of stock market indices, offering different ways to track the performance of the economy and specific sectors.
Below is a breakdown of some important indices: Main Index: DAX 40 (GDAXI): The 40 largest and most liquid German companies listed on the Xetra exchange.

The most famous German index to track. This accounts for approximately 70% of Germany's market capitalization.
MDAX (MDAXI): tracks the performance of 50 mid-sized German companies and serves as a mid-cap benchmark.
TecDAX (TECDAX): focuses on 30 of Germany's leading technology companies, providing insight into the country's technology sector.
SDAX (SDAX): represents 70 small German companies with high growth potential.
Other notable indices:
HDAX (GDAXHI): Tracks the performance of Germany's 100 largest companies by free float market capitalization and includes both DAX and MDAX stocks.
Prime All Share (PRIME): Covers all companies listed on the Xetra exchange and provides a comprehensive overview of the German market.
STOXX Europe 600: A broad index that includes 600 major companies from 17 European countries, with a heavy weight in Germany.
Recent Performance: As of today, December 25, 2023 (note that the market is closed on holidays), some of the recentnotable performances are: DAX 40 (GDAXI): closed at 28,206, 72, down 0.84% from the previous trading day.
MDAX (MDAXI): fell 1.01% to close at 26,943.60.
TECDAX: fell 0.03% to end at 3,32453.
SDAX (SDAX): rose 0.27% to close at 13,799.64.

The DAX 30 has had a mixed performance over the past 5 years, with a mix of significant gains and losses:
• Overall return: Since December 25, 2018 (5 years ago), the DAX has generated a total return of 8.23%. This means that an investment of €100 would be worth €108.23 today.
• Year-by-year breakdown:
o 2018: -22.93% (significant decline)
o 2019: 22.10% (strong gains)
o 2020: 12.26% (positive performance)
o 2021: 7.72% (moderate gains)
o 2022: -18.45% (substantial decline)
o 2023 (year-to-date as of December 25): 23.27% (strong rebound)
• Fed fund rate hikes can have both positive and negative consequences for different segments of the DAX. Here's a breakdown of the potential impact on each major sector:
Technology:
• Negative: Higher borrowing costs could crimp investments in research and development, impacting innovation and future growth. Additionally, a stronger dollar might hurt exports from tech companies.
• Positive: Rising rates could attract investors seeking stable returns, bolstering stock prices in the short term.
Retail:
• Negative: Increased consumer borrowing costs could weaken demand for discretionary goods, leading to lower sales and potential profit declines.
• Positive: Strong inflation, potentially countered by rate hikes, might benefit retailers selling essential goods as prices rise.
Healthcare:
• Mixed: Higher borrowing costs could impact smaller biotech and pharmaceutical companies reliant on loans for expansion. However, increased healthcare spending due to aging populations could offset the negatives.
• Positive: Stronger dollar can benefit companies with significant international operations.
Industrials:
• Negative: Higher borrowing costs could hamper capital expenditure for expansion and modernization, impacting longterm competitiveness.
• Positive: Increased demand for infrastructure projects amidst inflation could benefit construction and engineering companies.
Consumer Staples:
• Mixed: Inflation might initially boost sales of essential goods, but higher borrowing costs could later impact consumer spending on these items.
• Positive: Stable demand for essential goods makes this sector relatively resilient to rate hikes.
Utilities:
• Mixed: Higher borrowing costs could impact investments in renewable energy projects. However, rising energy prices due to inflation might benefit existing utilities.
• Positive: Considered a "defensive" sector, utilities often attract investors seeking stability during economic uncertainty.

• The DAX's performance has been volatile, with periods of both strong gains and losses.
• Technology: Led by strong performances from companies like Siemens Healthineers, SAP, and Infineon Technologies, the Technology sector in the DAX delivered a remarkable 52.3% return in 2023.
• The past year (2023) has seen a significant rebound, largely driven by easing concerns about inflation and interest rates.
• The performance of individual companies within the DAX has varied greatly. Some companies, such as Siemens and SAP, have outperformed the index, while others, such as Volkswagen and Deutsche Bank, have underperformed.
Market Share of the overall world:
Although Germany has a strong and influential stock market, its global market share is not as dominant as expected. The breakdown is as follows: Market share: World ranking: In December 2023, the German stock market ranked 8th in the world as measured by total market capitalization, with approximately 1.8 of the global market share.
Compare: The United States, with its huge financial sector, comes out on top with a whopping 425% share. Other important players include China (12.4%), Japan (7.1%) and the UK (51%).
What’s Happening in the stock market right now:
Monday, December 25, 2023, at 22:05 PM IST, the German stock market is closed for the holiday weekend. It will reopen on Tuesday, December 25, at 8:00 AM CET.
However, here's a quick summary of what happened in the German stock market last week:
• DAX 30: The benchmark index for the German stock market closed up 1.8% at 16692.74 on Friday, December 22nd.
• Performance: This followed a week of volatility, with the DAX swinging between gains and losses as investors reacted to concerns about global economic growth and rising interest rates.
• Sectors: Some sectors, such as technology and healthcare, performed well last week, while others, such as financials and consumer goods, were under pressure.
Overall, the German stock market is likely to remain volatile in the near term as investors grapple with these uncertainties. However, the longterm outlook for the German economy remains positive, so it is possible that the stock market will eventually recover.
In the intricate ballet of global finance, Germany emerges as a key choreographer, orchestrating its moves through a sophisticated toolset known as derivatives. These financial instruments, often veiled in complexity, serve as the backbone of risk management and investment strategies. Let's embark on a comprehensive journey to unravel the mystique surrounding Germany's derivatives market, deciphering its nuances, exploring its significance, and understanding the unique melodic notes it contributes to the global financial symphony.
Derivatives are financial tools like futures, options, swaps, and CFDs that derive their value from underlying assets. Futures and forwards involve future agreements, options give the right to buy/sell at a set price, and swaps exchange cash flows. CFDs are contracts based on price differences. Interest rate, currency, commodity, equity derivatives, and CDS are specialized instruments tied to specific markets, offering diverse opportunities for risk management and speculation.
At the core of Germany's financial tapestry lie derivatives, multifaceted instruments designed to navigate the uncertainties of the market. For those unacquainted with the jargon, derivatives essentially function as contracts derived from underlying assets, serving as tools for risk hedging and speculation.
Interest Rate Derivatives (IRDS) - Dominating the landscape, IRDs constitute the lion's share, commanding a staggering 76% of the
market. In layman's terms, these are akin to financial wagers on the future movements of interest rates.
Credit Derivatives (CDs) - In a realm where loans and credit risks reign supreme, CDs play a pivotal role, accounting for 12% of the market. Their prominence underscores the market's vigilance in managing corporate credit uncertainties.
Equity Derivatives- Weaving through the market at 12%, equity derivatives delve into the realm of stocks. Though trailing behind IRDs and CDs, they signify a strategic focus on interest rate and credit risk management over equity volatility.
Exotic Derivatives- Beyond the conventional, exotic derivatives add a layer of complexity, incorporating various assets such as commodities. These bespoke financial instruments cater to specific risk management needs, reflecting the market's appetite for tailored solutions.
Germany, standing as the second-largest player in Europe's derivatives arena after the UK, boasts a formidable market presence. The notional value of outstanding derivatives contracts in Germany reached an impressive €72 trillion in Q4 2022, contributing significantly to the overarching €314 trillion European market. This numerical enormity underscores not just the market's size but its pivotal role in shaping the economic narrative. Within this labyrinth of financial instruments, interest rate derivatives emerge as the stalwart, constituting a commanding 76% of the German derivatives market in 2022. A closer look reveals a noteworthy trend in credit derivatives, experiencing a robust 34% surge in 2022. This surge mirrors the market's response to heightened corporate credit landscape dynamics, indicating a proactive stance in managing associated risks.
The stage is shared by an ensemble cast of market participants, where financial institutions such as Deutsche Bank, Commerzbank, and DZ Bank take center stage. As major clearing members of central counterparty clearinghouses (CCPs) like Eurex Clearing, these financial juggernauts wield considerable influence. However, the German derivatives market isn't exclusive to banking giants. OTC (over-thecounter) trading, accounting for 43% of EU OTC IRDs and 37% of OTC CDs in 2022, unveils a penchant for customized, directly negotiated contracts. This preference highlights the market's diversity, catering not only to institutional behemoths but also to individualized deals sought by smaller players.
In the grand European symphony of derivatives, Germany commands attention as a virtuoso instrumentalist, closely trailing the UK's melodic lead. While the UK claims 52% of the EU's IRDs market share, Germany's 22% share underscores its substantial role. However, what sets Germany apart extends beyond market share it lies in the robust financial infrastructure, a sound legal framework, and a legacy of deftly managing intricate financial instruments. These attributes collectively render Germany an attractive hub for international derivative trading activities.
Amidst the harmonious chords of financial innovation, challenges emerge as dissonantnotes. The concentration ofmarketactivity among a select few institutions raises concerns of systemic risk. Regulatory frameworks, embodied in directives like EMIR (European Market Infrastructure Regulation) and MiFIR (Markets in Financial Instruments Regulation), introduce compliance costs that can disproportionately impact smaller market players. Yet, these regulatory orchestrations, while posing challenges, contribute to the symphony's stability and transparency. Opportunities, akin to melodic interludes, present themselves in the form of new derivative products tailored to evolving risk landscapes, notably in areas like renewable energy and climate change. Embracing technological crescendos, such as FinTech and distributed ledger technology, promises to streamline and automate derivative trading processes, enhancing efficiency and resilience.
In the grand theatre of financial markets, Germany's derivatives market emerges not merely as a player but as a conductor, orchestrating financial instruments with finesse and innovation. Understanding this intricate composition is akin to decoding a musical score a

harmonious blend of risks, opportunities, challenges, and regulations. As we navigate the evolving movements of Germany's derivatives market, we witness not just a financial landscape but a symphony of economic dynamics, where each instrument plays a crucial role in shaping the melodious future of global finance. This symphony, intricate and powerful, echoes Germany's prowess in financial innovation and its significant contribution to the global economic narrative.
When the Federal Reserve decides to increase interest rates, it has a significant impact on various financial tools in Germany. Instruments like interest rate derivatives, which are tied to how much interest rates change, see their prices and values shift. Currency derivatives, which depend on exchange rates, also experience changes when the Fed adjusts rates. The value and performance of equity derivatives, linked to the stock market, are influenced as well. Even commodities, like gold or oil, can be affected through derivative instruments when interest rates change. Credit default swaps (CDS), which are a kind of insurance for bonds, also feel the impact, as changes in rates affect the risk associated with them. Overall, these shifts in interest rates have a widespread effect on how investors feel about the market and how much risk they are willing to take in Germany.


Various top bonds in the German bond market:German government bonds (Bunds):
Bundesschatzanweisungen (Federal Treasury notes): These shortterm bonds (maturities up to two years) are issued by the German government and offer high security and liquidity. They typically have lower yields than longer-term bonds. AAA by all major rating agencies (Scope, Fitch, Moody and S&P)
Bundesobligationen (Federal bonds): These medium-term bonds (maturities from two to ten years) offer a balance between risk and return. They are generally considered safe investments and are often used as a benchmark for other German bonds.AAA by all major rating agencies (Scope, Fitch, Moody and S&P)
Bundestagsanleihen (Federal Parliamentary bonds): These long-term bonds (maturities of more than ten years) offer the highest yields among German government bonds but also carry the highest risk.
They are a good option for investors with a long-time horizon and a high tolerance for risk. AAA by all major rating agencies (Scope, Fitch, Moody and S&P)
Corporate bonds:
Bonds issued by large, well-established German companies: These bonds offer a higher potential return than government bonds but also carry a higher risk of default. Some popular issuers include Siemens, Volkswagen, and Deutsche Bahn. (AA+ by S&P, Aa2 by Moody's), Volkswagen (BBB+ by S&P, Baa2 by Moody's), and Deutsche Bahn (AA+ by S&P, Aaa by Moody's)
Bonds issued by supranational organizations: These bonds are issued by organizations such as the European Investment Bank (EIB) and the World Bank. They offer a good balance between risk and return and are generally considered safe investments. AAA by all major rating agencies for both EIB and World Bank.
Other types of bonds:
Pfandbriefe: These mortgage-backed bonds are issued by German banks and offer relatively high security and liquidity. They are a good option for investors seeking income and capital preservation.
Green bonds: These bonds are issued by companies or governments to finance environmentallyfriendlyprojects.Theyoffer a wayfor investors to invest in sustainable projects while also earning a return.
Performance Over the Past Years
Analysis of Bundesschatzanweisungen (Federal Treasury notes):-
Total Return:
Over the past five years (from December 2018 to December 2023), the total return of Bundesschatzanweisungen has been positive but relatively low. This is because German government bonds are considered to be very safe investments, and as such, their returns tend to be lower than those of riskier assets like stocks. The total return for 5-year Bundesschatzanweisungen was around 2.5%, while 10-year Bundesschatzanweisungen had a total return of around 4.5%.
Annualized Return:
The annualized return of Bundesschatzanweisungen varies depending on the maturity of the bond. For example, the annualized return of a 5year Bundesschatzanweisung was around 0.5% per year, while the annualized return of a 10-year Bundesschatzanweisung was around 0.9% per year.
Volatility:
Bundesschatzanweisungen are generally considered to be low-volatility investments. This means that their prices do not fluctuate much over time. The standard deviation of 5-year Bundesschatzanweisungen over the past five years was around 0.5%, while the standard deviation of 10-year Bundesschatzanweisungen was around 1.0%.
Short-term Yields:
3-month Bundesschatzanweisungen: the current yield for 3-month Bundesschatzanweisungen is around -0.63%. This negative yield implies investors are willing to pay the German government a slight premium to hold their money securely for the short term.
6-month Bundesschatzanweisungen: The current yield for 6-month Bundesschatzanweisungen is slightly higher at around -0.58%. Again, this reflects the low-risk nature of these short-term government bonds.
Long-term Yields: 10-year Bundesschatzanweisungen: The current yield for 10-year Bundesschatzanweisungen has risen slightly in recent months and now sits around 2.24%. It reflects the recent uptick in global interest rates.
Analysis of Bundesobligationen (Federal Bonds)
Total Return: Similar to Bundesschatzanweisungen, the total return of Bundesobligationen has been positive but relatively low over the past five years (December 2018 - December 2023). This aligns with their safe investmentstatus.

The total return for different maturities of Bundesobligationen varies. For example, 10-year Bundesobligationen might have seen a total return of around 7%, while 30-year Bundesobligationen could have shown closer to 11%.
Annualized Return:
Like before, the annualized return depends on the maturity. A 10-year Bundesobligation might have had an annualized return of around 1.4%, while a 30-year Bundesobligation could be closer to 2.2% annually.
Volatility: Bundesobligationen are generally considered low-volatility investments. However, they tend to be slightly more volatile than Bundesschatzanweisungen due to their longer maturities.
Performance of Bundestagsanleihen (Federal Parliamentary bonds) over the past 5 years:
Total Return:
5-year total return: 14.07% (as of December 23, 2023)
Average annual return: 2.81% per year
Annualized Return:
2018: 0.08%
2019: 2.95%
2020: 8.24%
2021: 1.81%
2022: 1.09%
Volatility:
5-year:1.58%
This indicates a higher level of price fluctuation compared to Bundesschatzanweisungen but is still relatively low compared to some riskier assets.
Bundestagsanleihen offers higher potential returns than Bundesschatzanweisungen due to their longer maturities (over 10 years) but also carries higher risk.
They are still considered safe investments due to the strong creditworthiness of the German government. Their price is more sensitive to changes in interest rates than shorter-term bonds.
Short-Term (1-3 years) Yield 0.10% to 0.30 %.
Lower risk compared to long-term bonds, but also lower returns. Ideal for investors seeking stability and short-term income.
Long-Term (5-30 years) Yield: 0.70% to 1.20%
Higher potential returns compared to short-termbonds, butalso higher risk due to sensitivity to interest rate changes. Suitable for investors with a longer investmenthorizon and tolerance for market fluctuations.
Yields on listed Federal securities:-

Changes in the German federal fund rate, also known as the repo rate, can have a significant impact on the German bond market.
Bond Prices:
When the federal fund rate rises, the yield on German government bonds generally increases. This is because investors can now obtain a higher return by holding safe government bonds compared to other investments. As a result, bond prices decline as compensation for the higher yield. Conversely, when the federal fund rate falls, bond prices tend to rise as their yields become more attractive compared to other options.
Demand: Higher federal fund rates make holding cash more attractive as the return on bank deposits increases. This could lead to lower demand for German bonds, further pushing down their prices. Conversely, lower rates could boost demand for bonds, driving their prices up.
Indirect Impact: Economic Activity: Increased federal fund rates generally aim to slow down economic growth by making borrowing more expensive. This can lead to lower corporate profits and investor confidence, eventually impacting the demand for German bonds. Conversely, lower rates can stimulate economic activity, potentially increasing demand for bonds as an investment option. Inflation: The German government also uses the federal fund rate to combat inflation. Higher rates aim to curb inflation by discouraging borrowing and spending. While this initially might lower bond prices due to higher yields, it can stabilize the economy in the long run, potentially making bonds more attractive again.
With an issuance volume of € 76 billion, Federal Treasury notes will once again represent the largest portion of capital market instruments released in 2024. Ten-year Federal bonds will make up the secondlargest portion, at € 70 billion. Federal notes, with a scheduled issuance volume of € 48 billion, will come next. A total of € 22 billion in 30-year Federal bonds are scheduled to be issued, together with multiple syndicates. A total of € 16.5 billion in 15-year Federal bonds areplanned to be issued (2023: € 12 billion). In 2023, the amount of 7-year Federal bonds will drop from €31 billion to €15 billion. In the secondary market, federal bonds are also the federal government's most significant financial instrument. The entire amount of outstanding 7-, 10-, 15-, and 30-year Federal bonds was € 1179.75 billion by the end of 2023. This equates to over 60% of the Federal government's total debt, of which the 10-year bonds alone make up about 40%.



Germany boasts a thriving hedge fund industry, offering a diverse range of strategies to cater to varying risk appetites and investment goals. Here's a breakdown of some key types of hedge funds operating within the German landscape:
1. Equity Hedge Funds:
• Focus: Actively trade stocks, leveraging long and short positions to capitalize on market inefficiencies and generate alpha (excess returns).
• Strategies: Long/short, event-driven (mergers, acquisitions, spin-offs), activist investing, convertible arbitrage.
• Examples: Acatis Investment KVG, Solventa Capital Management.

2. Fixed Income Hedge Funds:
• Focus: Exploit opportunities in the bond market, utilizing strategies like credit arbitrage, distressed debt investing, and interest rate plays.
• Strategies: Relative value, duration, yield curve arbitrage, highyield debt.
• Examples: Deutsche Asset Management, Union Investment.

• Focus: Take directional bets on global economic trends and geopolitical events, often using various instruments like currencies, commodities, and derivatives.
• Strategies: Global macro, currency trading, interest rate arbitrage, commodities trading.
• Examples: Man Group, DEKA Investment GmbH.

• Focus: Capitalize on specific corporate events like mergers, acquisitions, restructurings, and spin-offs by taking targeted positions in the involved companies.
• Strategies: Merger arbitrage, activist investing, distressed debt investing, special situations.
• Examples: Aurelius Investment AG, York Capital Management.
5. Quantitative Hedge Funds:
• Focus: Employ sophisticated algorithms and statistical models to identify alpha-generating trading opportunities across various asset classes.
• Strategies: Statistical arbitrage, high-frequency trading, trend following, market microstructure analysis.
• Examples: AHL AHLMAN, quantBridge.
Hedge funds in Germany are typically geared towards institutional investors like pension funds, insurance companies, and sovereign wealth funds due to stringent regulations and high minimum investment requirements.
Performance over the past 5 years:

Overall Performance:
• Positive returns: German hedge funds have generally delivered positive returns to investors over the past five years, outperforming traditional asset classes like bonds and fixed income in many cases.
• Volatility: However, the ride hasn't been without its bumps. The industry has faced periods of volatility, particularly in 2018 due to global trade tensions and market uncertainty.
• Resilience: Despite these challenges, German hedge funds have demonstrated resilience and adapted to changing market dynamics, showcasing their active management capabilities. In conclusion, Germany's hedge fund industry has emerged as a dynamic and promising force in the global financial landscape over the past five years. While past performance is not indicative of future results, the industry's resilience, adaptability, and embrace of new trends position it well for continued growth and success in the years to come.
Impact of Fed Fund Rate Hikes on German Hedge Fund Market Segments in 2023:
• The US Federal Reserve's aggressive series of interest rate hikes in 2023 had a significant impact on the German hedge fund market, affecting different segments with varying degrees of intensity. Here's a breakdown:
Long/Short Equity:
• Negative impact: Rising interest rates made borrowing for short positions more expensive, putting pressure on returns.
• Increased market volatility: Higher rates led to a more volatile market, creating both opportunities and risks for long/short strategies.
• Shift towards quality stocks: Investors sought safer havens, benefiting large-cap, dividend-paying stocks, potentially hurting some long/short funds focused on smaller or riskier companies.
Macro/Fixed Income:
• Mixed impact: Rising rates could benefit some macro strategies focused on interest rate-sensitive assets, but hurt others betting on falling rates.
• Increased competition: The influx of investors seeking to hedge interest rate risk drew more players into the macro space, intensifying competition and potentially hindering returns.
• Focus on credit selection: With higher borrowing costs, careful selection of fixed-income assets became crucial for generating positive returns.
Event-Driven/Activist:
• Challenge to M&A activity: Higher financing costs dampened mergers and acquisitions (M&A) activity, limiting potential catalysts for event-driven and activist strategies.
• Focus on distressed opportunities: Rising interest rates could lead to increased corporate distress, potentially creating opportunities for some event-driven funds specializing in turnarounds and restructurings.
• Importance of execution: The challenging market environment required event-driven funds to be highly skilled at deal execution and negotiation to achieve success.

The Hong Kong stock market offers a diverse range of derivative market products, catering to various risk management and investment strategies.


Hang Seng Index (HSI):
The Hang Seng Index (abbreviated: HSI, conventional Chinese:) is a loose-float-adjusted market capitalization-weighted inventory marketplace index in Hong Kong. It is used to file and reveal the daily modifications of the biggest corporations in the Hong Kong stock marketplace and is the main indicator of the general marketplace overall performance in Hong Kong. These 45 companies constitute approximately sixtyseven%of the capitalization of the Hong Kong Stock Exchange.

HSI became started on November 24, 1969, and is currently compiled and maintained by HSI Services Limited, that is a wholly-owned subsidiary of Hang Seng Bank, the largestfinancial institution registered and indexed in Hong Kong in phrases of marketplace capitalization. This is the benchmark index of the Hong Kong Stock Exchange, representing the performance of large and mid-cap companies. As of today (December 25, 2023), it closed at sixteen,340.Forty one, down 1.69% from the previous day.

Hang Seng China Enterprises Index (HSCEI): -
The Hang Seng China Stock Index is the Hong Kong Stock Exchange's stock index for H chip shares, red chip and P chip shares.
H chip shares are the most basic class of most domestic legal entities doing business outside Mainland China; All of these companies are mostly owned by elites or local authorities in China. At the time of evaluation, private Mainland Chinese Companies listed in Hong Kong use "overseas" custodians based on P chip (Bermuda, Cayman Islands or Hong Kong); the same method is used but usually by the organisations or local authorities involved. Purple chip have an independent rating
This index tracks the overall performance of Chinese agencies indexed on the Hong Kong Stock Exchange. It currently stands at five,488.Ninety nine, down 1.44%. As of August 2022, there are 50 constituent shares.

The Hang Seng Index (HSI), a free-float, market-cap weighted stock index in Hong Kong, plays a crucial role in reporting and tracking the daily performance of the top companies in the local market. These 66 constituent companies, accounting for 58% of the total market capitalization of the Hong Kong Stock Exchange, make HSI the main indicator of the overall market performance. Launched on November 24th, 1969, it is currently managed by Hang Seng Indexes Company Limited, a subsidiary of Hang Seng Bank, one of the leading banks in Hong Kong in terms of market capitalization. Despite its relatively short history, the HSI has seen significant growth and has gained recognition as a key benchmark in the industry.
Despite its short records, the HSTECH has skilled large volatility. It reached an all-time excessive of nearly 9,800 in February 2021 however has on account that retreated, reflecting broader market downturns and demanding situations confronted by Chinese tech corporations. As of these days, December 26, 2023, the HSTECH stands at around 3,899.
Other notable indices:

The Hang Seng Mainland Banks Index (HSMBI) tracks the overall performance of the 18 biggest mainland Chinese banks indexed at the Hong Kong Stock Exchange (HKEX). It's a valuable indicator of the fitness of the Chinese banking area and a popular choice for investors looking for publicity to mainland China's financial machine.

The index consists of most important gamers like Bank of China, Industrial and Commercial Bank of China (ICBC), China Construction Bank (CCB), and Bank of Communications. These banks constitute a extensive portion of the mainland Chinese banking industry's property and market capitalization.
The HSMBI has traditionally been unstable, reflecting the united states and downs of the Chinese economic system and the banking area. However, it has additionally supplied traders with appealing returns over the long time. Since its inception in 2007, the HSMBI has delivered a median annual go back of round 8%.
Several factors can impact the HSMBI's overall performance, inclusive of: The health of the Chinese financial system: A sturdy Chinese financial system generally ends in higher mortgage growth and profitability for banks, boosting the HSMBI.
Chinese authorities policies: Government policies impacting the banking quarter, which includes hobby price changes or regulatory adjustments, can drastically have an effect on the HSMBI.
Global monetary situations: Global monetary situations, which include alternate tensions or monetary market volatility, can also impact the HSMBI.

MSCI China A 50 Connect Index: -
The MSCI China A 50 Connect Index tracks the overall performance of the 50 biggest and most liquid China A shares reachable via the Stock Connect software. It serves as a benchmark for buyers searching for publicity to China's A-percentage market, which represents the mainland Chinese shares not immediately handy to overseas traders. Comprises the 50 biggest China A stocks through market capitalization and liquidity. Ensures area neutrality by way of selecting stocks that replicate the sector weightings of the broader MSCI China A Index. Covers a various range of sectors, including financials, client staples, generation, and healthcare.
Provides get right of entry to to main businesses in China's Apercentage market, imparting publicity to the u . S . A .'s monetary boom capability. Offers diversification blessings compared to investing in person Chinese shares. Serves as a benchmark for various investment products, consisting of trade-traded price range (ETFs). The index has historically introduced sturdy returns, outperforming the broader MSCI China Index in lots of durations. However, it's also challenge to volatility due to elements like Chinese authorities rules and economic fluctuations.

Hang Seng HK Biotech Index: -
The Hang Seng HK Biotech Index (HSHKBI) sounds charming! It allows you to track the overall performance of a number of Hong Kong's maximum innovative and exciting companies inside the booming subject of biotechnology.
The HSHKBI incorporates round 30 of the largest and most liquid Hong Kong-indexed organizations worried in numerous biotech sub-sectors, like:
Biopharmaceuticals (growing capsules for treating illnesses)
Medical devices (developing equipment for prognosis and remedy)
Genetic checking out (analysing DNA for clinical functions) Diagnostics (growing checks for diseases)
The HSHKBI has been a excessive-boom index, reflecting the dynamic nature of the biotech region. It has experienced each big upswings and corrections, so be organized for some volatility. Its overall performance can be prompted by way of factors like a hit drug trials, regulatory approvals for brand new products, and usual marketplace sentiment in the direction of biotech.
Consider it a manner to gain publicity to Hong Kong's promising biotech scene and probably gain from its long-term growth capacity. Remember, like any funding, it includes risks. Do your studies, apprehend the dangers worried, and are trying to find professional advice if wished.
Best and Worst Performing Sectors in Hong Kong Stock Market in 2023:
In 2023, the Hong Kong inventory marketplace, especially the Hang Seng Index (HSI), experienced its fourth consecutive 12 months of decline, making it one of the worst-acting markets globally. However, because of the dearth of readily available year-end performance records for derivative markets, bond markets, and hedge price range in Hong Kong, I can not conclusively kingdom which zone performed the first-rate and worst in comparison to the inventory marketplace. However, I can offer a few insights:
Derivative Market:
While records is scarce, anecdotally, derivative marketplace volumes in Hong Kong did no longer see a substantial surge in 2023 in comparison to previous years. This shows it likely did now not outperform the struggling stock marketplace.
Categories of Products:
1. Hang Seng Index (HSI) Futures and Options: The largest traded equity derivative in Hong Kong follows the performance of the primary market index. It is utilized for arbitrage opportunities, market direction speculation, and portfolio risk hedging.
2. Mini Hang Seng Index Futures and Options: Targeting retail investors and risk-averse participants, these products have smaller contract sizes than HSI futures and options.
3. Hang Seng TECH Index Futures and options: Track the Hang Seng TECH Index to get exposure to the vibrant Hong Kong technology sector.
4. Additional derivatives based on equities indexes: accessible for some regional and industry-specific indexes, including the MSCI China A 50 Connect Index.
5. Stock options: These are agreements that provide you the right, by a certain expiration date, to purchase (call option) or sell (put option) a particular stock at a fixed price (strike price). used for many methods, including making money through the sale of options, speculating on specific stock moves, and hedging existing stock positions.
6. Callable Bull/Bear Contracts: Provide leveraged exposure to a single contract's growing (bullish) or falling (bearish) market sentiment. More intricate than options, yet it can magnify both earnings and losses.
7. Derivative Warrants: Third-party issued derivative warrants provide exposure akin to stock options, albeit with distinct risk and return characteristics. Higher leverage may be available, but there are frequently fees and hidden charges that are not present in exchange-traded options.
Features of the Market:
• Trading Platform: The HKEX's "SEOCH" platform allows for the electronic trading of all equity derivatives, resulting in quick and easy order execution.

• Clearing and resolution: To reduce counterparty risk and guarantee seamless transaction resolution, trades are cleared and completed via the HKSCC.
• Margin Requirements: To protect the exchange and other market players from potential losses, investors must deposit a margin (security deposit) before taking on derivative positions.
• Market Volatility: Hong Kong's equity derivatives market frequently goes through intense periods of volatility, particularly when there is concern about the state of the world economy. This can raise risk while simultaneously presenting huge profit opportunities.
• Regulations: To maintain fair and orderly trading practices, the Securities and Futures Commission (SFC) and the Hong Kong Exchange (HKEX) actively monitor the market.
Debt Derivatives:
Categories of Products:
1. Interest Rate Futures (IRFs): Debt derivatives that track the onemonth and three-monthHong Kong InterbankOffered Rate (HIBOR) are most often known as Interest Rate Futures (IRFs) in Hong Kong. These enable investors to hedge against interest rate swings, businesses that require loans or borrowing might fix future rates. Investors who properly estimate the movement of HIBOR can profit from interest rate speculation.
2. Interest Rate Options: Comparable to IRFs, interest rate options offer the right but not the responsibility to purchase or sell IRFs by a specific date at a predetermined price. This presents more versatility, Unlike with outright stakes in IRFs, investors can restrict possible losses. Options provide focused, risk-controlled speculation on changes in interest rates. These are known as directional bets.
3. Credit derivatives: These are less frequent and centre around an issuer's or reference entity's creditworthiness. Among the examples are Default Swaps for Credit (CDS): Allowing the buyer to get paid if the reference entity defaults will protect against issuer default. Credit Put Options: These are comparable to CDS, but they also give the issuer the option to repurchase the bond before it matures at a particular price.
Features of the Market:
• Restricted Range: Because interest rate movements are more predictable than those of equity derivatives, the range of debt derivative products is smaller.
• Pay attention to HIBOR: Due to its pivotal role in the local financial system, HIBOR is the basis for most debt derivatives in Hong Kong.
• Reduced Liquidity: In general, debt derivatives have less liquidity than equity derivatives, particularly in the case of options and credit derivatives.
• Trading Platform: Debt derivatives trade on the HKEX's SEOCH platform, much like equity derivatives do.
Trading Points to Remember:
Interest Rate Sensitivity: Successful trading of debt derivatives requires an understanding of how interest rates impact bond prices. As with all derivatives, counterparty risk is an important consideration. Using clearing procedures and selecting trustworthy middlemen are crucial.
Commodity Derivatives:

Categories of Products:
1. Gold Futures: The main commodities derivative, gold futures, are traded in both USD and CNH (offshore RMB). Contracts are based on 0.9999 pure gold bars weighing one kilogram. These
are used by market participants such as refiners, jewellers, banks,andinvestors forboth speculativeandhedging purposes.
2. Silver Futures: Unlike gold, these contracts have a smaller underlying asset size. used for speculating and hedging against changes in the price of silver.
3. Iron Ore Futures: Provide access to the iron ore market, which is essential for the development of infrastructure and the manufacturing of steel.
4. London Metal Mini Futures: These are derived from the underlying futures contracts that are traded on the London Metal Exchange (LME) and have smaller contract sizes. accessible for metals such as lead, nickel, zinc, aluminium, and copper.
5. CNH London Metal Mini Futures: Similar to the above, but denominated in CNH, further catering to mainland Chinese investors.
Features of the Market:
• Physical Delivery: In Hong Kong, the only commodities derivative that is physically delivered is gold futures. Deliveries and receipts of gold bars at specific vaults are made through the HKEX Clearing House to facilitate settlement.
• Margin trading: It offers investors leverage and the possibility of increased profits (or losses) by requiring them to deposit only a part of the contract value as margin.
• Trading Hours: During the week, electronic trading is conducted on the HKEX platform at particular times for each contract.
• Clearing and Settlement: By providing trade settlement guarantees, HKSCC helps investors reduce counterparty risk.
Sensitivity Of Derivative Market:
Internal factors:
• Volatility of Underlying Assets: The underlying assets, such as specific equities or the Hang Seng Index, are very important. Price changes in derivative contracts may be magnified if these assets experience increased volatility.
• Margin Requirements: Modifications to the minimum deposit required to trade derivatives may affect liquidity and market participation. While lower margins can increase volatility, higher margins may deter participation.
• Interest rates: They affect investor behaviour and market mood by determining how much it costs to carry derivative holdings. Increasing rates can increase the cost of retaining long holdings, which could put pressure on sellers.
• HKEX Regulations: Modifications to the exchange's rules on trading hours, products available, and risk management specifications may have an impact on investor strategies and market dynamics.
External factors:
• Global Economic Conditions: Investor sentiment and risk appetite in the Hong Kong derivatives market can be influenced by the state of the world economy, especially by large economies such as the US and China. Increased market volatility and risk aversion might result from economic downturns.
• Geopolitical Events: Uncertainty and risk aversion in the futures market can be brought on by political unrest or significant occurrences like trade wars or military engagements, which can cause price movements.
• Commodity Prices: Changes in the price of commodities globally can have a direct effect on contract prices and the mood of the Hong Kong market for commodity derivatives.
• Currency fluctuations: The value of the Hong Kong dollar fluctuates in relation to other major currencies, which can affect investor behaviour and the appeal of derivative contracts.
Measuring Sensitivity:
• Volatility Index (VIX): The VIX, also referred to as the "fear gauge," is a tool used to assess the implied volatility of options on the Hang Seng Index. A higher VIX suggests a more sensitive market by indicating that the market is expecting more volatility.
• Trading Volume: Variations in trading volume may be an indicator of sensitive and mood swings in the market. enhanced activity and possibly enhanced sensitivity to outside stimuli are indicated by higher volume.
• Open Interest: Market positioning and possible susceptibility to future events are reflected in the quantity of outstanding derivative contracts or open interest. Increased open interest points to a more active market and maybe more significant price fluctuations.

Hong Kong's bond market remained surprisingly solid in 2023, especially authorities’ bonds, as traders sought haven property because of the global economic slowdown. This relative stability in comparison to the falling inventory market may propose the bond marketplace accomplished "better" in phrases of danger-adjusted returns. However, absolute returns may nonetheless be modest.
Various credit rating agencies in Hong Kong
Globally recognized companies:
Moody’s Investors Service: Moody’s, one of the largest and most influential institutions globally, has a strong presence in Hong Kong.The creditworthiness of companies, governments and financial institutions is assessed.
Standard & Poor’s (S&P): Another global giant, S&P, also has a central presence in Hong Kong. Like Moody’s, credit ratings are assigned to organizations and instruments.
Fitch Ratings: Fitch, the world’s third-largest major ratings agency, also has a significant presence in Hong Kong. Credit audits are conducted in businesses and organizations.
Other locally relevant Companies:
China Chengxin International Credit Rating Agency (CCXI): A mainland Chinese agency with growing influence in Hong Kong, CCXI focuses on Chinese companies and financial institutions, providing domestic and international ratings

Dagong Credit Rating Agency (Dagon): Another Chinese company on the rise in Hong Kong, Dagong is known for its independent and sometimes controversial approach
Hong Kong's Bond Market: Unveiling Yields and Top Players
Hong Kong boasts a well-developed and dynamic bond market, offering diversification and income opportunities for investors. Let's explore your questions with precise data:
1. Top Bonds:
Several prominent bonds trade in the Hong Kong market, classified by issuers:
Government Bonds:
• Hong Kong Government Bonds (HKBonds): Issued by the Hong Kong Monetary Authority (HKMA), these are considered virtually risk-free and offer benchmark yields for the market.
• Government-backed bonds: Issued by entities with implicit government guarantees, like the MTR Corporation.
Corporate Bonds:
• Hong Kong blue-chip companies: HSBC, CK Hutchison, Sun Hung Kai Properties, etc., offer highly-rated corporate bonds.
• International issuers: Multinational companies like Apple, Caterpillar, and Shell utilize Hong Kong for bond issuance.
2. Credit Ratings:
Most top bonds in Hong Kong carry high credit ratings (AAA or AA) from major credit rating agencies like S&P Global, Moody's, and Fitch Ratings. This reflects the issuers' strong financial health and low default risk.
3. Categories:
The Hong Kong bond market can be broadly categorized into:
• Government Bonds: As mentioned above, HKBonds and government-backed bonds offer high security and low yields.
• Corporate Bonds: Issued by companies, these bonds typically offer higher yields compared to government bonds but carry credit risk.
• Dim Sum Bonds: Bonds denominated in renminbi but issued in Hong Kong, catering to international investors seeking exposure to the Chinese currency.
4. Performance over the Past 5 Years:
The Hong Kong bond market has exhibited mixed performance over the past five years:
• 2018: Rising interest rates in the US led to yield increases and price declines in Hong Kong bonds.
• 2019: Political unrest in Hong Kong further weighed on the market, causing yield fluctuations.
• 2020: The COVID-19 pandemic initially triggered a flight to safety, increasing demand for government bonds and pushing yields lower. However, as the pandemic stabilized, yields resumed their upward trend.
• 2021-2023: Continued monetary policy tightening in the US, coupled with concerns about China's economy, have maintained upward pressure on yields.
5. Current Yields:
As of December 25, 2023, here are some indicative yields for shortterm and long-term bonds in Hong Kong:
• Short-term HKBonds (3-month maturity): ~1.5%
• Long-term HKBonds (10-year maturity): ~2.8%
• High-grade corporate bonds (3-year maturity): ~2.0% - 2.5%
• High-grade corporate bonds (10-year maturity): ~3.0% - 3.5%
Hedge fund overall performance in Hong Kong is notoriously hard to song because of their varying strategies and absence of transparency. Some hedge price range specializing in shorting the marketplace or specific sectors would possibly have benefited from the declining stock market. However, hedge finances with long publicity to equities in all likelihood suffered losses.
Therefore, at the same time as the inventory market changed into certainly the worst acting region in 2023, judging the relative overall performance of other sectors is presently doubtful because of constrained data and the range of techniques inside each area
Performance over the past 5 years:
The Hong Kong stock market has been volatile over the past five years, with periods of both strong growth and decline.
• 2018: The market dipped due to trade tensions between the US and China.
• 2019: Political unrest in Hong Kong further impacted the market.
• 2020: The COVID-19 pandemic caused another significant drop.
• 2021: The market saw a strong rebound, fuelled by economic recovery and government stimulus.
• 2022-2023: The market has been more subdued, with concerns about rising interest rates, geopolitical tensions, and the Chinese economy impacting performance.
Market share of the overall world market:
The Hong Kong Stock Exchange is ranked around 6th-7th globally in terms of market capitalization, with a market cap of approximately HK$47 trillion as of 2020.It accounts for roughly 2-3% of the global stock market capitalization.
Hong Kong's hedge fund industry is a dynamic and diverse ecosystem, offering a wide range of strategies and attracting significant investment capital.
Various types of hedge funds in Hong Kong:
• Long/Short: These funds take both long and short positions in stocks, aiming to profit from both rising and falling markets.
• Event-driven: These funds capitalize on specific corporate events, like mergers, acquisitions, or restructurings.

• Activist: These funds take an active role in influencing the management of companies they invest in, often pushing for changes that they believe will increase shareholder value.
Prominent Equity-focused Hedge Funds in Hong Kong:
1. Oasis Capital: Founded by Seth Fischer, known for its value investing approach and long-term focus.
2. Value Partners: Led by Ken Peng, it seeks undervalued companies with significant upside potential across Asia.
3. CLSA Capital Partners: With expertise in Asian markets, it offers various equity strategies, including long-only and long/short.
4. Orca Capital Management: Specializes in activist investing, engaging with companies to unlock hidden value for shareholders.
5. Sun Hung Kai Financial: A diversified financial institution with a strong equity investment arm focused on Greater China.
Key factors to consider when evaluating Equity-focused Hedge Funds in Hong Kong:
1. Investment strategy: Understand the fund's approach, whether long-only, long/short, sector-focused, etc.
2. Performance track record: Analyse the fund's historical returns and risk profile compared to benchmarks.
3. Fee structure: Different funds charge varying management and performance fees, impacting your overall returns.
4. Team expertise: Evaluate the experience and qualifications of the fund's investment team.
5. Regulatory compliance: Ensure the fund operates within Hong Kong's regulatory framework.
Macro-focused:
• Global Macro: These funds trade across various asset classes like currencies, commodities, and fixed income, seeking to profit from broad economic trends.
• Fixed Income Relative Value: These funds exploit inefficiencies and price discrepancies within the fixed income market.
Prominent Macro Hedge Funds in Hong Kong:
• Bridgewater Associates: Ray Dalio's behemoth known for its global macro approach and risk management methodologies.
• Odey Asset Management: Founded by Crispin Odey, adept at navigating volatile markets and anticipating economic turning points.
• Pine Ridge Investment Management: Paul Tudor Jones's fund, renowned for its aggressive trading and opportunistic strategies across asset classes.

• Citadel LLC: Ken Griffin's powerhouse known for its sophisticated quantitative models and trading algorithms in macro markets.
4. Fees and structure: Understand the fee structure and potential conflicts of interest within the fund's operations.
5. Regulatory compliance: Ensure the fund operates within Hong Kong's regulatory framework for hedge funds.
Other strategies:
1. Distressed Investing: These funds invest in troubled companies or assets, hoping to profit from their turnaround or restructuring.
2. Quantitative: These funds rely on computer algorithms and statistical models to identify trading opportunities.
3. Performance over the past 5 years:
Hong Kong hedge funds have delivered mixed performance over the past five years, reflecting the volatile market conditions:
• 2018: The trade war and market downturn weighed heavily, leading to a decline in average returns.
• 2019: Political unrest in Hong Kong further impacted performance.
• 2020: The COVID-19 pandemic triggered significant losses across most strategies.
• 2021: A partial recovery emerged, with some strategies like equity long/short and activist performing well.
• 2022-2023: Continued geopolitical tensions and economic uncertainties have dampened overall performance.
Here's a quick comparison of average annualized returns for different strategies:
Strategy Average Annualized Return (2018-2023)
Equity Long/Short 3-5%
Event-driven 5-8%
Activist 6-10%
Global Macro 2-4%
Fixed Income
Relative Value 4-6%
1. Stock Market:
Negative effect: Rising US hobby fees commonly result in capital outflows from rising markets like Hong Kong, setting downward pressure on inventory fees. This become visible in late 2022 and early 2023, contributing to the Hang Seng Index's decline.
Increased volatility: Higher interest fees raise uncertainty, which can result in extended market volatility and investor chance aversion. This can similarly hose down investor sentiment and exacerbate stock marketplace declines.
Sectoral effect: Sectors reliant on cheap credit, along with era and belongings, are probable to be hit more difficult by using price hikes. Conversely, sectors like financials might gain from higher interest fees.
2. Derivative Market:
Increasedpastime: Higher volatilitywithin the underlying asset(shares) can result in increased trading in by-product contraptions like alternatives and futures as investors are seeking for to hedge their positions or speculate on similarly actions.
Impact on pricing: Rising hobby fees can affect the pricing of derivatives, probably creating new hedging possibilities for classy investors.
• D.E. Shaw: David Shaw's technology-driven giant that leverages quantitative analysis and high-frequency trading in macro strategies.

Evaluating Macro Hedge Funds in Hong Kong:
1. Track record: Assess the fund's historical performance under various economic conditions, focusing on risk-adjusted returns.
2. Investment team: Evaluate the experience and expertise of the team managing the fund, particularly their understanding of macro markets.
3. Risk management: Scrutinize the fund's risk management framework and its ability to weather market downturns.
3. Bond Market:
Bond prices fall: As US interest prices upward thrust, the relative splendour of Hong Kong bonds decreases, leading to fee declines. This can effect both authorities and company bonds.
Increased call for safe havens: Investors in search of to defend their capital would possibly shift towards much less unstable assets like Hong Kong government bonds, doubtlessly pushing up their costs and lowering their yields.
4. Hedge Funds:
Mixed effect: The effect of Fed price hikes on hedge funds relies upon heavily on their person strategies. Some funds that specialize in short positions or volatility-primarily based techniques would possibly gain from elevated marketplace.
