Learning to “SEE”: Using Direct Observation in Teaching Trainees


 Linda L. Carr, Ph.D. CEO, Faculty Ed Solutions, LLC
Linda L. Carr, Ph.D. CEO, Faculty Ed Solutions, LLC

Know Do

Learning Objectives
• The benefit and application of direct observation in teaching trainees.
• How to observe trainees in their interactions with patients.
• Empowered to conduct more objective observations of trainees’ behaviors.
• Orient trainees to direct observation and feedback.


• Build meaningful feedback into the direct observation process.
• Require action planning after each direct observation.

See Slide Notes Feel
Crime Scene Challenge

You have 2 minutes to study the next photograph.
Pay attention to the details.
Do NOT write anything down until you project the next slide.
Set your stop watch for 2 minutes.


Answer Each Question Below
1. What color coffee mug was in the picture? Blue - Red - Yellow
2. When was the deadline? Yesterday - Today - Tomorrow
3. What time was on the clock on the wall? 10:40 - 11:05 - 1:55
4. How many sticky notes were on the whiteboard? 4 - 6 - 8
5. Which of the following was NOT in the picture? Stapler - Trash canPrinter
6. What was the name on the plaque on the desk? Bill - Brian - Carl
7. What color was the victim’s shirt? Black - Blue - Red
8. How many plants were in the picture? 0 - 1 - 2
9. What was the color of the marker in the desk drawer? Red - BlueGreen

10.Where was the book in the picture? On box - In trash can - Under body
When you’ve answered each question, go to next slide.
Check Your Answers
1. What color coffee mug was in the picture? Yellow
2. When was the deadline? Today

3. What time was on the clock on the wall? 11:05
4. How many sticky notes were on the whiteboard? 6
5. Which of the following was NOT in the picture? Stapler
6. What was the name on the plaque on the desk? Brian
7. What color was the victim’s shirt? Blue
8. How many plants were in the picture? 2
9. What was the color of the marker in the desk drawer? Green
10.Where was the book in the picture? On a box
How did you do?
Importance of Direct Observation
Lets trainees know their work is important
Checks to see if they are doing something correctly
Helps trainees develop competence in clinical skills


PEP2 Facilitator’s Module 3 (Observation), p. 3.4.

4 Rules for Observation
① Correct positioning
Minimize external interruptions ③ Avoid intrusions

E Holmboe, MD – Direct Observation by Faculty. In E. S. Holmboe & R.E. Hawkins (Eds.) (2008). Practical Guide to the Evaluation of Clinical Competence, p. 122.

②
④ Be prepared
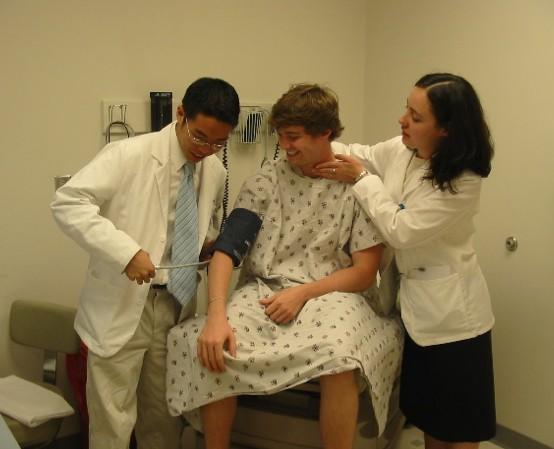
Principle of Triangulation for Direct Observation





E Holmboe, MD – Direct Observation by Faculty. In E. S. Holmboe & R.E. Hawkins (Eds.) (2008). Practical Guide to the Evaluation of Clinical Competence, p. 126.

Desk or Exam Table Patient
Trainee Faculty Observer
Benefits of Observation
Establishes a baseline
Reinforces the importance of the student
Can assess student’s abilities

Reminds you that evaluation is not your only job as a teacher
Prevents the halo effect
PEP2 Facilitator’s Module 3 (Observation), p. 3.4.
Vignette 5

A brief student-preceptor interaction.

PEP2 Clinical Vignette 5

Mechanics of Observation
Who is present?
What roles are they playing?
What is happening?
What tone (voice) are people using?

What activity (body language) is occurring?
What is the pattern, pace of the interaction?
Where is this happening?
Learn to focus on BEHAVIOR, not the person.
PEP2 Facilitator’s Module 3 (Observation), p. 3.5.
Requires planning ahead; reviewing your day’s schedule

May require communicatingthis withpatientsaheadoftime
How can you incorporate observation in your practice?
Informtrainee whatyouwill beobserving

Applications of Direct Observation
Assess the student’s clinical skills— interviewing style, technique and organization of PE

Distinguish specific parts of the encounter—opening, background history, explanation/management of plan, closure
Observe the student in hallway interactions with preceptors or clinic staff
PEP2 Facilitator’s Module 3 (Observation), p. 3.7.
14
Applications of Direct Observation, cont.
Look for specific behaviors regarding the process of the visit—putting patient at ease, communicating clearly, listening attentively

Separate the content issues—patient’s expectations, psychosocial context, appropriate exam
Observe how student communicates attitudes—body language, voice, pace, touch
15 PEP2 Facilitator’s Module 3 (Observation), p. 3.7.
Applications of Direct Observation, cont.
Observe effect of the interaction on the patient—Confusion? Satisfaction? Questions?

Organize, prioritize, and balance examples of positive and negative items prior to providing feedback
Differentiate between observation and interpretation—remember, the challenge in observation is withholding judgment.
PEP2 Facilitator’s Module 3 (Observation), p. 3.7.
Observation Tips
“Merely looking at the sick is not observing.”
-- Florence Nightingale
② Active Watching (the challenge in observation is withholding judgment)
③ Be Observed
④ Observe the Behavior (learn to focus on behavior and not the person)

PEP2 Facilitator’s Module 3 (Observation), p. 3.11.

① Do It!
Best Practice Tip
Daily record your LEARNER’S PERFORMANCE, noting:

1 thing DONE WELL
1 thing TO IMPROVE
YOUR PLAN to help her/him improve
See sample of Direct Observation form in notes.

Be intentional about observing your learners directly during patient visits/procedures and provide meaningful feedback.


LEARN – REFLECT - TEACH

What will you keep the same?
What will you do more of?
What will you do less of?
What will you stop doing?
What will you do differently & how will you do it?
What will you add?


 Linda L. Carr, Ph.D. CEO, Faculty Ed Solutions, LLC
Linda L. Carr, Ph.D. CEO, Faculty Ed Solutions, LLC

























