


PUBLISHING
Firstview Media Ventures Pvt. Ltd.
EDITING
Sadhana Shenvekar Mohan Gupta editorial@firstviewgroup.com
CONTENT
Sadhana Shenvekar Mohan Gupta Avanti Deshpande
Rajasri Alagar publishing@firstviewgroup.com
DESIGNING
Neha Barangali Radha Buddhadev
Rajesh Mishra design@firstviewgroup.com
ADVERTISING
Smriti Charan Andrew Ferreira advertise@firstviewgroup.com
CIRCULATION
Sadhana Shenvekar
SUBCRIPTION
subscribe@firstviewgroup.com
ADVERTISE WITH US
Contact: Smriti Charan e: smriti@firstviewgroup.com

06


L




14


22



27

CONTENT FEATURED INTERVIEW 6-8 IN CONVERSATION 9-27 RESEARCH INSIGHTS 28-33
Chief Executive Officer, Energyneering Zimbabwe EPCM
12 Tichafa Chireka
(Solar)
Melusi Tshabalala CEO, Mesama Energy
Regional
Director
Brian M. Omega
Managing
(East Africa), Soventix East Africa Ltd. 08
K Verma Managing Director, PowernSun
Réchard Area Sales Director Sub-Saharan Africa, Elum Energy
Gabriel
Manager, Alternative Energy, REREC Kenya
09 Eng. Jonathan Mbutu
23
VP Commercial, Rensource Energy
Michael Iwu
Executive
16 Joshua B. Narh
Chairman, Energy Chamber
of Ghana
Frank Spencer
Regional
Director - Southern Africa, Cainmani
26
Executive
28 Africa’s Solar Surge: Racing to Achieve 16 GW of PV Capacity by 2023’s End 29 Empowering Africa: A Policy Perspective On Accelerating Solar And Storage Deployment 30 Empowering Sustainable Urbanization In Africa: The Integration Of Solar, Storage, And Smart Infrastructure 31 Innovations In Battery Technology: Driving The Future Of Energy Storage In Africa 32 Revolutionizing Renewable Energy: Advancements In Solar And Storage Technologies Reshaping Africa’s Energy Landscape 33 Solar Gold Rush: Navigating The Financial Landscape Of Investing In Renewable Energy Projects In Africa
Edington Tapera Mazambani
Chief
Officer, ZERA
20
Director
Engineering, Renewvia
Nicholas Selby
of
Solar Africa

Featured | Interview
Powering Progress: Navigating Solar and Storage Solutions in SubSaharan Africa - Insights, Innovations, and Regulatory Perspectives

Can you discuss current solar and storage market trends and challenges in Sub-Saharan Africa?
It’s difficult to speak about a trend for a region that covers over 40 countries which each face different situations in terms of grid reliability, electrification rate, electricity tariff policies, and operational constraints.
We can, however distinguish sub-regional trends:
South Africa was the first to experience a surge in solar-diesel applications due to a massive load shedding issue. It was also adopted way earlier BESS and it is currently the most mature market for storage applications.
Nigeria started solar-diesel integration later, due to the change of policy on diesel subsidies. The hybridisation market is still dominated by PV/DG integrations, though the demand for BESS projects is increasing fast.
Eastern Africa countries rely mostly on geothermal and hydro sources, and generally speaking, have a way more reliable grid. Therefore most of the solar hybrid projects address remote areas that are not electrified, that leading to most solar hybrid projects being off-grid PV/DG/BESS.
As trends are different from a sub-region to another, the whole Sub-Saharan region, however has in common the challenges. High interest rates and operational hurdles impede market growth. Logistical constraints, security issues, and a shortage of skilled workers
Gabriel
Réchard
Area Sales Director Sub-Saharan Africa Elum Energy
KEY HIGHLIGHTS
• Dynamic Market Trends: Understanding Sub-Regional Variances and Common Challenges.
• Competitive Edge: Local Engagement, Global Expertise, and Longevity in Solutions.
• Tailored Solutions for Growth: Scalability, Flexibility, and Regional Customization
further complicate matters and deter investors.
Moreover, the lack of a structured regulatory framework and policy uncertainty pose significant barriers. Without clear policies, securing financing for solar projects becomes challenging, hindering progress. Additionally, the absence of an organised electricity market complicates the distribution of electricity generated from solar and storage systems. Addressing these challenges requires collaborative efforts and policy reforms to foster a conducive environment for market growth.
How does Elum Energy stay competitive in the Sub-Saharan Africa market for solar and storage solutions?
Elum Energy maintains its competitive edge by combining local engagement, industry expertise, and a global perspective. We prioritise hiring local talents and collaborating with regional distributors to streamline logistics, ensuring efficient delivery and tailored
The lack of a structured regulatory framework and policy uncertainty pose significant barriers. Without clear policies, securing financing for solar projects becomes challenging, hindering progress.
solutions for diverse customer needs. Our active involvement in the local ecosystem, such as our PV training program with ACES Academy speaks to our dedication to understanding and addressing the specific needs of the African market.
Furthermore, our compatibility with other equipment and emph asis on longevity distinguish us in the industry. With extensive experience in solar-dieselstorage integration, we offer reliable solutions designed to evolve with your project over time.

06 SOLARQUARTER ANNUAL EDITION 2024 | SOLAR & STORAGE AFRICA LIVE EXPO SPECIAL ISSUE
Featured | Interview

Our focus is on standardization rather than customization, as scalability is essential. Considering the significant increase in electricity demand across the continent, we aim to offer a one-size-fits-all solution suitable for all models.
Additionally, we leverage our international identity to bring global knowledge and insights to our solutions. Drawing from diverse markets, we anticipate challenges and offer comprehensive solutions for sustainable growth. Unlike competitors with a background in the generator controller industry, our roots in the solar sector provide us with a nuanced understanding of industry demands.
How does Elum Energy customise its offerings to meet customer needs in Sub-Saharan Africa?
Our focus is on standardisation rather than customization, as scalability is essential. Considering the significant increase in electricity demand across the continent, we aim to offer a one-size-fitsall solution suitable for all models. This approach is particularly relevant for SubSaharan Africa, where PV/DG systems were initially introduced to address energy needs.
Elum Energy emphasises system scalability, enabling seamless integration of battery storage into existing PV/DG setups. This approach ensures flexibility and future-proofing for customers,
allowing for easy upgrades as energy needs evolve. Local partnerships with EPCs, particularly in South Africa and Nigeria, bolster on-the-ground presence and support efficient project implementation.
Additionally, we offer customizable solutions to fit unique regional requirements. For example, the DNP3 protocol, designed specifically for the City of Cape Town, enhances communication efficiency in energy systems. Similarly, while our Eskom API EMS is yet to be released, Elum anticipates its integration to optimise battery performance in the future, aligning charging cycles with grid schedules for enhanced ROI.
What distinguishes African EMS, and are there specific considerations for the African market?
Our focus is on standardization rather than customization, as scalability is essential. Considering the significant increase in electricity demand across the continent, we aim to offer a one-size-fits-all solution suitable for all models. This approach is particularly relevant for Sub-Saharan Africa, where PV/DG systems were initially introduced to address energy needs.
In specific regions like the City of Cape Town, we utilize the DNP3 protocol, tailored to enhance communication efficiency in energy systems. Additionally, we’re developing the Eskom API EMS, designed to optimize battery performance by leveraging load shedding data. Integrating these features into our EMS enables better decision-making for battery charge and discharge cycles, ultimately enhancing ROI.
Moreover, as our systems are designed with scalability in mind. We can easily integrate
batteries into existing PV/DG setups, ensuring adaptability as energy needs evolve. To further support our operations, we foster local partnerships with EPCs, particularly in regions like South Africa, to ensure efficient project implementation and on-the-ground support.
How can regulatory frameworks and policies be structured to promote the integration of BESS and PV systems? What incentives are effective in this regard?
To encourage the adoption of PV systems, it’s crucial to establish frameworks allowing C&I entities to sell excess PV production. This step is essential as it incentivizes PV ownership by enabling owners to earn revenue from exporting electricity to the grid. Similarly, for BESS integration, creating a market for battery services is imperative. In regions like South Africa, where incentives exist for peak shaving, BESS owners are rewarded by the grid, driving investment in battery technology.
Furthermore, differential tariffs for peak and off-peak periods can significantly boost the profitability of BESS installations. By leveraging arbitrage opportunities, batteries can be charged during lowcost periods and discharged during peak periods, maximizing cost savings.
For these frameworks to be effectively utilized, it is imperative to have a complete understanding of them. BESS owners should be fully informed about the potential benefits of their investments and how controllers like ours can optimize their returns. Additionally, addressing technical challenges such as supplying battery services for frequency regulation is essential for grid stability and maximizing the value of BESS installations.
07 SOLARQUARTER ANNUAL EDITION 2024 | SOLAR & STORAGE AFRICA LIVE EXPO SPECIAL ISSUE
Empowering Africa’s Solar Revolution: Navigating Challenges and Seizing Opportunities with PowernSun’s Innovative Solutions

Could you provide insights into the challenges and opportunities faced by solution providers in the African solar market, given your prominent position in the industry?
Solar Industry have been witnessing ungenuine products influencing inferior efficiency in solar projects. Power n Sun deals with TIER 1 products supplied mostly by public listed companies who are not only committed to the business, but also keen on consumers’ value for money for long term. Our business volume supports us to help our channel partners & consumers to enjoy the best solar solutions at a competitive price in the market.
PowernSun is introducing Pns One, a revolutionary software solution designed specifically for the African solar market. How do you plan to introduce effectively and promote this software, considering the diverse needs of solar businesses throughout the region?
Yes. PnS One is indeed a revolutionary software with its unique feature to bring all departments of EPC / Installer to work on a single platform. PnS one helps an installer to trace a project’s activity from its Enquiry till O&M activity including project schedule and its payment schedule. We have planned to introduce the software at the upcoming solar show to be held in March in Johannesburg. We also have seminars to be conducted in various locations to train the individuals for effective utilization of the software.
LK Verma
Managing Director
PowernSun
KEY HIGHLIGHTS
• PowernSun leads with top-tier solar solutions, ensuring long-term value for African consumers.
• Pns One streamlines African solar projects with tailored promotion and comprehensive training.
• PowernSun advances regional needs with Pns One, ensuring data security while boosting off-grid solutions.
Given the diverse market conditions across Africa’s solar landscape, how does PowernSun intend to customize Pns One to meet the unique requirements of solar enterprises in different countries?
With PnS One, one can get generation forecast and its payback period within few hours of project lead generation with AI technology. This broadly helps an Installer to reduce the survey timings and hence the project timings. PnS One is specifically designed with respect to business dynamics in respective countries. PnS One facilitates the users to access the country specific Brands & products along with country specific stock availability.
Access to reliable electricity remains a significant challenge in many parts of Africa. How does Pns One contribute to enhancing efficiency and streamlining processes, especially in off-grid and rural electrification projects?
PnS One helps the end user (up to rural consumer of electricity) to find the nearest
With PnS One, one can get generation forecast and its payback period within few hours of project lead generation with AI technology. This broadly helps an Installer to reduce the survey timings and hence the project timings.
PnS approved solar installer available in his / her location. This accessibility helps the consumer to have a qualified installer for his / her solar solutions and have value for the money.
Data security and privacy are critical concerns in the power industry. How does PowernSun ensure the integrity of data when implementing Pns One in Africa, considering the varying regulatory environments?
Individual users have their own unique user ID with password protection. PnS One has internal data security system as firewalls which operates 24/7 and raises an alarm for any breach or any suspicious activity and act immediately including blocking the account. PnS One’s cloud based function helps the user to access the required data & details from any part of the world with network connectivity.

Featured | Interview 08 SOLARQUARTER ANNUAL EDITION 2024 | SOLAR & STORAGE AFRICA LIVE EXPO SPECIAL ISSUE
Solar Energy Revolution in Africa: Market Progress, Challenges, and Future Strategies

How is solar energy adoption perceived in Africa, particularly Kenya, from a market perspective, and what initiatives promote solar access in these regions?
There has been consistent progress on perception of solar adoption in Africa. Looking at the changes in the last 10 years or so which I have been actively involved in the industry, the progress has been impressive. The technology can now be considered mature and widely accepted and used in the continent. Most of the countries in the regions have in place policies and regulations governing the development of solar in their countries, from small systems (solar home systems) to large grid connected systems.
Over the time, tertiary learning institutions have also warmed up to the solar energy industry. Most of the universities and colleges are now offering tailor made courses in renewable energy. This has been critical in capacity building and development of the industry.
Further, Africa is endowed with solar energy resource and most of the countries receive more than 4.5 daily peak sunshine hours. This makes investment in solar more attractive in the region.
At the early stages of the solar industry development in Kenyan, the solar energy industry received a lot of government support, including fiscal policy interventions some of which are still ongoing.
Kenya’s development blueprint, Vision 2030, seeks to transform Kenya into a newly industrializing, middle-income country providing a high quality of life
Eng. Jonathan Mbutu
Manager, Alternative Energy
Rural Electrification & Renewable Energy Corporation Kenya
KEY HIGHLIGHTS
• Solar energy adoption in Africa, particularly in Kenya, has seen remarkable progress due to government support, technological advancements, and favorable policy frameworks.
• Solar solutions like mini-grids and solar home systems are empowering marginalized rural communities in Africa by providing cost-effective and sustainable access to electricity, thus enhancing socio-economic development.
• Emerging technologies such as IoT and AI are shaping the future of the solar sector, while collaborative partnerships among stakeholders are crucial for integrating solar solutions into Africa’s energy landscape, ensuring resilience, equity, and sustainability.
to all its citizens by 2030 in a clean and secure environment. Vision 2030 identifies energy as a key enabler required to achieve the goals of the blueprint. Further, the Kenya National Electrification Strategy (KNES) 2018, envisages the country will achieve Universal Access by 2027. This will be achieved by grid extension and development of mini-grids in the areas far from grid. The facilities which cannot be economically connected through minigrids will be electrified through standalone systems. Through the updated Nationally Determined Contributions (NDC) plan submitted in December 2020, Kenya has made commitment to lower its Green House gasses by 32% of the BAU scenario by 2030. This will majorly be achieved by enhanced investment in renewable energy in all socio economic sectors. The Climate Change (Amendment) Bill, 2023 sets a framework to identify past, current and projected sector-based greenhouse gasses emission profile. The bill also creates a regulatory framework for governing carbon markets in the country which will enhance carbon trading in the country, hence creating more funding opportunities.
The country has put together a number of policy and regulatory frameworks which promote development of renewable energy including, the energy Act 2019, the clean cooking strategy, solar PV Regulation 2012 (currently under review), and Energy Management Regulation 2012 (currently under review). A series of other regulations which will have a significant contribution in the renewable energy
sector are also under various stages of development, including net metering regulations, mini-grids regulations and renewable energy fund regulations. All these have played a critical role in the development of the renewable energy industry in the country.
What are the main challenges rural and marginalized communities encounter in accessing reliable energy in Africa, and how do solar solutions, like mini-grids, address these challenges in the market?
It is estimated that sub-Saharan Africa accounts for 75% of people without electricity in Africa. Most of these people leave in rural areas and are located more than 50km from the grid. This makes electricity connection through the grid an expensive option amidst competing government needs. Further, rural communities are sparsely populated with low energy demand this complicates the process of connecting them to the grid. Therefore, solar energy presents a more economical option of electrification.
Traditionally, the strategy of most of the African countries for increasing access to electricity has focused on national grid extension. Other available options, such as off-grid solutions in rural areas, have been pursued with lower priority. With rapidly improving technologies, off-grid solutions including solar home systems and mini-grids are now well-placed to
InConversation
09 SOLARQUARTER ANNUAL EDITION 2024 | SOLAR & STORAGE AFRICA LIVE EXPO SPECIAL ISSUE
InConversation
As we enter the Energy 4.0 phase, we expect more focus on electrification, de-carbonization, decentralization and digitalization of the global energy sector. Some of the enabling technologies for Energy 4.0 are renewable energy technologies, modern power electronics, bidirectional power flows, IoT, big data and cloud computing.
provide affordable electricity services, especially in rural areas.
How does technology improve the efficiency and affordability of solar energy systems in remote areas of Kenya and Africa, and how do emerging technologies drive market growth?
Under the Fourth Industrial Revolution (4IR), major world economies are harnessing the speed, scope, and systems impact of the
Intelligence (AI), smart cities, electric mobility, high-speed internet, mobile communications, autonomous vehicles, nano-technology, 3-D printing, block chain technology, big data, augmented vision, virtual reality, Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV) and biotechnology.
As we enter the Energy 4.0 phase, we expect more focus on electrification, de-carbonization, decentralization and digitalization of the global energy sector. Some of the enabling technologies for Energy 4.0 are renewable energy technologies, modern power electronics, bidirectional power flows, IoT, big data and cloud computing. In addition, the drive towards affordable energy, higher productivity and reduction of greenhouse gasses will assume center stage, leading to greater innovations to support energy access and renewable energy technologies.
Decentralization will play a critical role in electrification of rural communities going forward. This concept involves electricity that is generated nearby to where it will be utilized, instead of at a large plant elsewhere and sent through the national grid. Decentralized energy systems provide promising opportunities for deploying renewable energy sources locally available as well as for expanding access to clean energy services to remote communities. Most of times this electricity replaces traditional biomass which is a high greenhouse gasses emitter.
There has been a number of notable solar projects in Kenya and the continent. In Kenya I would wish to highlight the following projects some of which I have been part of:
Garissa 54.6MW Solar Plant - Kenya
The Garissa Solar Plant which is the largest grid connected solar power plant in East & Central Africa. The project is located in Balambala Constituency, Garissa County about 20 kilometers from Garissa Town. The solar farm sits on 85 hectares of land and consists of 206,272# 265Wp solar panels and 1,172# 42kW inverters. The solar power plant was completed and connected to the Grid in November 2018.
The project has been instrumental in contributing to the Government agenda of affordable and clean energy. To date the project has generated in excess of 460,000 MWh.
Government Funded Solar Mini-grids
The Government of Kenya through Rural Electrification and renewable Energy Corporation has implemented TwentyEight (28) solar mini-grids across counties of Wajir, Turkana, Marsabit, Mandera and Garissa. The projects consist of solar PV sytem with battery storage and a back up diesel generator to ensure quality and reliable power supply to the customers.
The projects are serving in excess of 5,000 customers and provide other socio economic benefits to communities living in these areas in education, health, entrepreneurship, employment, communication, water pumping and food preservation. This translates to major carbon emission reduction for the country because previously the

10 SOLARQUARTER ANNUAL EDITION 2024 | SOLAR & STORAGE AFRICA LIVE EXPO SPECIAL ISSUE
InConversation

connected customers used kerosene or biomass fuel as a source of light. This translates to approximately two tons per year per connection of carbon dioxide emission reduction in addition to other health and socio-economic benefits.
Solar for schools
The Government through Rural Electrification & Renewable Energy Corporation has provided solar powered electricity to about 5,000 primary schools and secondary schools to facilitate the government Digital Learning Programe.
The primary schools were installed with 1.68kW solar PV system consisting of 240W lighting system and 1,440W laptop / tablet charging system. The secondary schools were installed with 3kW solar PV system with 9,600AH, 48V battery storage system. The main components of the secondary school systems are 300W solar panels, 4,000W Inverters-charger and 2v400AH batteries.
These projects have been a great support to education in the beneficiary schools because the students can conduct evening studies more conveniently. This is expected to improve the performance of the beneficiary schools significantly. Teaching primary pupils digital literacy skills is crucial because they need to be able to understand the technology that they use early, this will help them use it safely and effectively. In addition, this prepares them to future careers which will be majorly digital.
Kenya Off-Grid Access Program
The Government of Kenya is implementing the Kenya Off-Grid Solar Access Project for underserved counties (K-OSAP) funded by the World Bank. The Project Development Objective is to increase access to modern energy services in underserved counties of Kenya. The project is being implemented in fourteen
(14) underserved counties in the north, northern eastern and coastal parts of Kenya. These counties are Garissa, Isiolo, Kilifi, Kwale, Lamu, Mandera, Marsabit, Narok, Samburu, Taita Taveta, Tana River, Turkana, Wajir and West Pokot. The Project is being implemented by the Ministry of Energy and Petroleum (MoEP), Kenya Power and Lighting Company (KPLC) and Rural Electrification and Renewable Energy Corporation- REREC.
The project has Four components, as follows;
Component 1: Mini-grids for Community Facilities, Enterprises, and households
Component 2: Standalone Solar Home Systems, and Clean Cooking Solutions for Households
Component 3: Standalone Solar Systems and Solar Water Pumps for Community Facilities
Component 4: Implementation Support and Capacity Building
Other notable solar projects in the continent include: Kaxu 100MW CSP Solar project in South Africa, Yeleen 208MW Solar Power Project in Burkina Faso, Ouarzazate 510MW Solar Power Station (OSPS) in Morocco among others. These projects gives a sneak preview of the potential of solar energy in the continent.
What is the market vision for solar energy’s role in Africa’s transition to sustainable and resilient energy systems, and how do stakeholders plan to collaborate to integrate solar solutions into the broader energy landscape, promoting resilience, equity, and sustainability?
Solar energy will play a very critical role in the 100% access to electricity in Africa. The high potential of solar energy resources in Africa presents a better return on investment compared to other continents. This is expected to continue attracting more investors and stakeholders to finance solar projects.
Funding remains a major challenge towards development of solar energy and universal access to electricity in the continent. This calls for collaboration of various stakeholders both International Donor Agencies and lending intuitions for the projected targets to be achieved.
Investment in solar energy presents other additional benefits including reduction of greenhouse gasses which helps in climate change mitigation. In many occasions, statistical analysis has linked electricity connectivity to improved health, economic and social conditions.
It is my feeling that Africa should be the one leading research and development in solar and other renewable energy technologies, including battery energy storage. This is because the continent is highly endowed with these resources and has overtime developed the prerequisite human capacities to lead in this front. As at now the continent continue to import most of the solar systems which makes the cost of deployment high. This is compounded by the depreciation of the local currencies to the foreign currencies witnessed in recent time. The effect of this to long term project is significant and sometimes can lead to cost variations.

11 SOLARQUARTER ANNUAL EDITION 2024 | SOLAR & STORAGE AFRICA LIVE EXPO SPECIAL ISSUE
Energyneering Zimbabwe EPCM Has Achieved Several Milestones In Advancing Solar Energy Projects In Zimbabwe.

Could you provide an assessment of the current state of the solar energy industry in Zimbabwe, and expound upon the role and impact of Energyneering Zimbabwe EPCM within this domain?
The solar energy industry in Zimbabwe has seen significant growth in recent years, driven by factors such as increasing energy demand, declining solar technology costs, and a growing awareness of the need for sustainable energy solutions. Energyneering Zimbabwe EPCM has played a pivotal role in this growth by providing expertise in engineering, procurement, construction, and management (EPCM) services for solar energy projects across the country. The company has contributed to the expansion of solar infrastructure, enabling more communities and businesses to harness clean energy and reduce their reliance on fossil fuels. We have tailored our solutions offering to suit C&Is as well as the NGO community.
What are the most notable accomplishments and pivotal moments for the company in advancing solar energy projects and infrastructure throughout Zimbabwe?
Energyneering Zimbabwe EPCM has achieved several milestones in advancing solar energy projects in Zimbabwe. These include the successful completion of large-scale solar installations for commercial and industrial clients, the implementation of innovative financing models to make solar energy more accessible, and the establishment
Tichafa Chireka
Chief Executive Officer
Energyneering Zimbabwe EPCM (Solar)
KEY HIGHLIGHTS
• Energyneering Zimbabwe EPCM have recently developed a combo box (that provides power and purify water), this was in mind of the current Cholera outbreak.
• Energyneering Zimbabwe EPCM employs a comprehensive approach to project management, starting from project inception to final operational phases.
• Energyneering Zimbabwe EPCM continually explores innovative technologies and methodologies to enhance the efficiency and efficacy of its solar engineering endeavours.

of strategic partnerships with local stakeholders to promote solar adoption. We have recently developed a combo box (that provides power and purify water), this was in mind of the current Cholera outbreak.
How does Energyneering Zimbabwe EPCM approach the management and execution of solar energy projects? Specifically, how does the company ensure the successful implementation and finalization of solar initiatives, from their inception to operational phases?
Energyneering Zimbabwe EPCM employs a comprehensive approach to project management, starting from project inception to final operational phases. This involves thorough feasibility studies, meticulous planning, efficient procurement processes, rigorous quality control measures during construction, and
Energyneering Zimbabwe
EPCM has played a pivotal role in this growth by providing expertise in engineering, procurement, construction, and management (EPCM) services for solar energy projects across the country. The company has contributed to the expansion of solar infrastructure, enabling more communities and businesses to harness clean energy and reduce their reliance on fossil fuels.
InConversation
12 SOLARQUARTER ANNUAL EDITION 2024 | SOLAR & STORAGE AFRICA LIVE EXPO SPECIAL ISSUE
InConversation

ongoing monitoring and maintenance to ensure the long-term performance of solar initiatives. The company’s experienced team and adherence to international standards contribute to the successful implementation and finalisation of solar projects.
Could you delve into
Energyneering Zimbabwe EPCM’s strategies and initiatives aimed at promoting sustainability and integrating eco-conscious practices into its solar projects?
Energyneering Zimbabwe EPCM is committed to promoting sustainability and integrating eco-conscious practices into its solar projects. This includes optimising the design and layout of solar installations to minimize environmental impact, employing energy-efficient technologies, and prioritizing the use of renewable materials and resources. Additionally, the company actively engages with local communities to raise awareness about the benefits of solar energy and promotes initiatives for environmental conservation and social responsibility.
Can you shed light on some of the innovative technologies or methodologies that
Energyneering Zimbabwe EPCM has adopted to enhance the efficiency and efficacy of its solar engineering endeavors?
Energyneering Zimbabwe EPCM continually explores innovative technologies and methodologies to enhance the efficiency and efficacy of
its solar engineering endeavours. This includes advancements in solar panel technology, energy storage solutions, smart grid integration, and digital monitoring systems. By leveraging these innovations, the company aims to maximise the performance and reliability of solar energy systems while reducing costs and environmental impact.
What is your strategic vision for Energyneering Zimbabwe EPCM in the coming years? Additionally, how do you intend to navigate and capitalize on the evolving opportunities and challenges within Zimbabwe’s solar energy market?
Our strategic vision for Energyneering Zimbabwe EPCM in the coming years
Energyneering Zimbabwe EPCM is committed to promoting sustainability and integrating ecoconscious practices into its solar projects. This includes optimising the design and layout of solar installations to minimize environmental impact, employing energyefficient technologies, and prioritizing the use of renewable materials and resources.
is centred on expanding our presence in the solar energy market, driving innovation, and fostering sustainable growth in collaboration with our partners. We intend to capitalise on emerging opportunities such as government incentives for renewable energy, increasing demand for off-grid solutions, and advancements in solar technology. To navigate challenges such as regulatory uncertainty and market competition, we will prioritise agility, adaptability, and strategic partnerships to maintain our position and drive positive change in Zimbabwe’s solar energy sector. We are also working with international financing partners, to improve the perception of Zimbabwe in the global place, so that investment in renewable energy can flow.

13 SOLARQUARTER ANNUAL EDITION 2024 | SOLAR & STORAGE AFRICA LIVE EXPO SPECIAL ISSUE
How Tapping Into Decades Of International Experience From Parent Company Is Supporting His Vision To Realize High Value Projects & Deliver On Partner Commitments

What are the current trends driving solar energy adoption in Africa, especially post events like Solar + Storage Africa 2024?
There are no specific trends driving adoption of solar energy in Africa
The trends – IMO - are based on individual jurisdictions and the uniqueness that comes with this.
While some commonalities exist. We need to be alive to the fact that certain aspects, such as; the difference in the consumer grid tariff and reliability of the grid are country specific.
What could be a motivating factor to transition in Kenya may not be the same as say in Tanzania, Uganda, Madagascar, Somalia, Rwanda.
Having said that, we still see some common trends; Cost of Energy, Grid unreliability or the complete Lack of Grid network.
Peak demand management that necessitates the need to have a hybrid system.
Strained transmission network and hence the need to deploy solar parks closer to consumers to maximize the ever-increasing demand for energy downstream.
Importantly however, we are witnessing an increasing number of consumers eager to onboard a cleaner source of power to their current energy mix.
This greatly underscores the local efforts to enhance sustainability.
Brian M. Omega
Regional Managing Director (East Africa) Soventix East Africa Limited
KEY HIGHLIGHTS
• Soventix E.A i s a subsidiary of Soventix GmbH. A Turnkey solution provider in the development and realization of medium and large-scale solar power facilities
• With a Centralized Centre of Excellence, a team track record 5000+ Projects ranging from a size of kWp to multi MWp with proven experience in project development and execution
• Soventix GmbH successfully delivered as EPC a Floating PV in 2023.
Can you highlight key milestones that have shaped Soventix East Africa’s reputation in the African solar energy sector?
Soventix has developed a strong team that has delivered and continues to deliver very interesting projects in collaboration with our partners in Africa
In 2023. We delivered several MWs of projects with most if not all, delivered within the agreed frameworks of cost, quality and time.
Three Special projects come to mind.
Located in Madagascar, this Ground Mounted Fixed Tilt projects with hybrid integration on local mini-grid consisting of a HFO, BESS and Wind(Ongoing). That project has been in operation for a year.
With the level of performance and the consequent benefits to our customer,
we have been contracted Phase II Expansion
In Germany, Soventix delivered 5.6MWp Floating PV (See Photo on next page)
We anticipate more traction on the Floating PV Space within the next years in Africa
Located in Madagascar, t h i s Ground Mounted Fixed Tilt projects with hybrid integration on local mini-grid consisting of a HFO, BESS and Wind(Ongoing). That project has been in operation for a year.

InConversation
2.5MWp Single Axis Tracker with 1 KM 33kv Overhead Line to Interconnection Point currently under construction in Kenya
14 SOLARQUARTER ANNUAL EDITION 2024 | SOLAR & STORAGE AFRICA LIVE EXPO SPECIAL ISSUE
InConversation

In addition to the 2 projects already in Operation, Soventix is currently building a project in Somalia, which is - in fair terms - a very challenging environment to deliver a project.
Our ability to look beyond challenges highlights the commitment we have to our partners as an EPC in EA. Wherever the project is, Soventix will build.
How does Soventix East Africa navigate regulatory complexities and market conditions to ensure successful project implementation across Africa?
As a business, you encounter unique regulatory complexities in each market. My wish would be to standardize to some
Our partnership network and inhouse capabilities has a clear understanding of the market-specific regulatory framework governing the renewable sector. This heavily supports the company to work within the existing regulatory frameworks at development or building phase of projects
extent some regulations especially in East Africa. Doing this would partly improve the ease of doing business. The Pro’s would heavily outweigh the Cons.
Our partnership network and inhouse capabilities has a clear understanding of the market-specific regulatory framework governing the renewable sector. This heavily supports the company to work within the existing regulatory frameworks at development or building phase of projects
We are capable to support from concept, initial development phase to actual project realization.
How does Soventix East Africa integrate sustainability and technology into its projects, and could you provide examples?
Sustainability: Transitioning any consumer to a clean source of energy always deserves a pat on the back. Especially, consumers heavily reliant on Fossil Fuels as their main source of energy.
Specifically, Soventix is adapting the sourcing by evaluating as part of the purchasing process how sustainable a supplier’s operations.
There are conversations ongoing that are centered on prioritizing some equipment based on technology. For example. Vacuum as opposed to SF6 gas as an extinguishing medium in RMU’s.
Sustainability: Transitioning any consumer to a clean source of energy always deserves a pat on the back. Especially, consumers heavily reliant on Fossil Fuels as their main source of energy.
What is Soventix East Africa’s vision for driving solar energy adoption and sustainability in Africa, and how will it leverage expertise and partnerships to address continent-wide challenges?
The plan is to keep doing what we are good at: EPC, O&M. We want our partners and potential customers to focus on their main mandate as IPPs, Developers, Manufacturers while we do the rest.
We are partnering with local contractors. Training and sharing our wealth of experience in the industry.
Challenges? Financing Is number one. Gaps in Project Development and the required Technical Skills. Cost & Ease of doing business.
Visit us at: www.soventix.com
15 SOLARQUARTER ANNUAL EDITION 2024 | SOLAR & STORAGE AFRICA LIVE EXPO SPECIAL ISSUE
InConversation
Energy Chamber Of Ghana Employs To Promote Sustainable Energy Solutions

How do you perceive the current state of solar technology advancements in Africa, and what potential do you see for further growth and innovation in this sector?
Africa has shown significant potential for the growth of solar technology due to its abundant sunlight and the need for sustainable energy sources. Several factors contribute to the perception of a positive outlook for solar technology in Africa.
Renewable Energy Initiatives: Many African countries have recognized the importance of renewable energy and have implemented policies and initiatives to promote its development. These initiatives often include incentives for solar projects and the establishment of solar farms.
Off-Grid Solutions: Given the challenges of extending centralized power infrastructure to remote areas, off-grid solar solutions have gained traction. These systems can provide electricity to rural and off-grid communities, contributing to increased energy access.
Innovative Financing Models: Some regions have explored innovative financing models to make solar technology more accessible. This includes pay-as-you-go systems, which allow users to pay for solar services in installments, making them more affordable for a broader population.
International Collaboration: Various international organizations and initiatives have supported solar projects in Africa.
Joshua B. Narh
Executive Chairman
Energy Chamber of Ghana
KEY HIGHLIGHTS
• Energy storage technologies play a crucial role in addressing Africa’s evolving energy landscape by addressing several challenges and contributing to a more reliable, sustainable, and resilient energy infrastructure.
• To promote renewable energy and sustainability in Ghana, collaboration among various stakeholders is essential.
• The Energy Chamber of Ghana’s mission is to advance sustainable energy solutions in the country and the broader African continent.
Partnerships with developed nations and international bodies have facilitated the transfer of technology and expertise.
Local Entrepreneurship: There has been a rise in local entrepreneurship focusing on solar technology. This includes the development and manufacturing of solar panels as well as the implementation of solar solutions tailored to local needs.
As for the potential for further growth and innovation,
Technological Advancements: Continued advancements in solar technology, such as improvements in efficiency, energy storage solutions, and new materials, can enhance the viability and affordability of solar power.
Scale-Up of Projects: Scaling up successful solar projects and increasing their integration into the energy mix can contribute to further growth. This involves not only expanding capacity but also improving the efficiency of existing installations.
Policy Support: Ongoing government support, including favorable policies, incentives, and regulatory frameworks, is crucial for fostering a conducive environment for the growth of solar technology.
Community Engagement: communities in the development and implementation of solar projects can ensure that solutions are tailored to specific needs and enhance the overall acceptance and sustainability of these initiatives.
Research and Development: investment in research and development
can lead to breakthroughs in solar technology, making it more efficient, cost-effective, and adaptable to diverse conditions.
As the Executive Chairman of the Energy Chamber of Ghana, how is your organization promoting sustainable energy solutions in the country and across the African continent?
Below is what the Energy Chamber of Ghana employs to promote sustainable energy solutions:.
Advocacy and Policy Influence: Engage with government bodies and policymakers to advocate for the development and implementation of favorable policies that support sustainable energy practices.
Collaborate with relevant stakeholders to shape energy regulations and standards that encourage the adoption of renewable energy sources.

16 SOLARQUARTER ANNUAL EDITION 2024 | SOLAR & STORAGE AFRICA LIVE EXPO SPECIAL ISSUE
InConversation

Capacity Building: Conduct training programs, workshops, and seminars to enhance the skills and knowledge of professionals in the energy sector, focusing on sustainable and renewable technologies.
Support educational initiatives to build a workforce skilled in renewable energy technologies.
Industry Collaboration: Foster collaboration between the public and private sectors, as well as with international organizations, to share best practices, research, and technologies in sustainable energy.
Promotion of Renewable Energy Sources: Actively promote the use of renewable energy sources such as solar, wind, and hydropower through awareness campaigns, incentives, and partnerships with renewable energy providers.
Investment Facilitation: Facilitate investments in sustainable energy projects by connecting investors with viable opportunities, providing a platform for dialogue, and fostering a conducive investment environment.
Community Engagement: Engage with local communities to raise awareness about the benefits of sustainable energy and involve them in decision-making processes related to energy projects.
Monitoring and reporting: Establish mechanisms to monitor the progress of sustainable energy initiatives, track key performance indicators, and report on the impact of these efforts on both a local and regional scale.
International Partnerships: Forge partnerships with international
organizations, NGOs, and other countries to leverage resources, share experiences, and benefit from global initiatives aimed at promoting sustainable energy.
These strategies contribute to the Energy Chamber of Ghana’s mission to advance sustainable energy solutions in the country and the broader African continent.
Can you discuss specific initiatives or projects aimed at integrating renewable energy sources like solar power into Ghana’s energy mix, and what impact do you foresee these initiatives having on the region?
Scaling up the Renewable Energy Program (SREP): The Scaling-up Renewable Energy Program is a World Bank initiative aimed at increasing the deployment of renewable energy in developing countries. Ghana has been a participant, and projects under this program have included the development of solar power plants.
The Renewable Energy Master Plan (REMP): Ghana developed a Renewable Energy Master Plan to guide the integration of renewable energy into the country’s energy mix. The plan includes targets for the share of renewable energy in the total energy generation capacity. Solar power is a significant component of this plan.
Grid-Scale Solar Projects: Ghana has undertaken several grid-scale solar projects. For example, 50 MW Solar plant. This plant was launched in April 2021 and is connected to Ghana’s National Interconnected Transmission System (NITS) is one of the projects that aims to contribute to the national grid. These projects are often developed in collaboration with international
organizations, private investors, and government agencies.
Renewable Energy Act: The government of Ghana has put in place policies and regulatory frameworks to support the development of renewable energy. The Renewable Energy Act provides a legal basis for promoting and regulating renewable energy projects, including solar power.
Investment and International Cooperation: Ghana has sought international cooperation and attracted investments to support its renewable energy goals. Partnerships with organizations like the International Finance Corporation (IFC) and the African Development Bank (AfDB) have been crucial in financing and implementing solar projects.
The impact of these initiatives on the region could be significant.
Energy Security: Introducing solar power can enhance energy security by diversifying the energy mix and reducing dependence on traditional sources. Solar energy is abundant in Ghana, and harnessing it can contribute to a more resilient and sustainable energy infrastructure.
Economic Development: The deployment of renewable energy projects can stimulate economic development by creating job opportunities and fostering a growing renewable energy sector.
Environmental Benefits: Solar power is a clean and environmentally friendly energy source, contributing to efforts to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and combat climate change. This is particularly crucial as countries globally aim to transition to more sustainable energy systems.
Rural Electrification: Many initiatives focus on extending electricity access to rural areas through off-grid and minigrid solar solutions, addressing energy poverty, and promoting soc io-economic development in underserved regions.
While these initiatives represent positive steps, their successful implementation and impact depend on various factors, including effective policy frameworks, regulatory support, and private sector involvement. It’s essential to check the latest sources for updates on these projects and their outcomes.
17 SOLARQUARTER ANNUAL EDITION 2024 | SOLAR & STORAGE AFRICA LIVE EXPO SPECIAL ISSUE
InConversation
The government of Ghana has put in place policies and regulatory frameworks to support the development of renewable energy. The Renewable Energy Act provides a legal basis for promoting and regulating renewable energy projects, including solar power.
With the increasing importance of energy storage solutions, particularly in Africa’s evolving energy landscape, how do you view the role of energy storage technologies in addressing the region’s energy needs?
Energy storage technologies play a crucial role in addressing Africa’s evolving energy landscape by addressing several challenges and contributing to a more reliable, sustainable, and resilient energy infrastructure. Here are some key ways in which energy storage can positively impact the region:
Grid Stability and Reliability: Energy storage helps stabilize and smooth out fluctuations in power generation, especially from renewable sources like solar and wind. This is vital for maintaining a stable and reliable electrical grid.
Intermittent renewable integration: Africa has abundant renewable energy resources, such as solar and wind, but these sources are intermittent. Energy storage enables the efficient storage of excess energy generated during peak production times and its release during
periods of low production, ensuring a continuous and reliable power supply.
Energy Access in Remote Areas: In many parts of Africa, particularly rural and remote areas, access to a reliable power grid is limited. Energy storage solutions, such as off-grid solar with battery storage, can provide a decentralized and sustainable energy source for communities that are off the traditional grid.
Mitigating power outages: Energy storage systems act as a backup during power outages, providing critical electricity supply for essential services, healthcare facilities, and businesses. This can enhance resilience and reduce economic losses associated with frequent power interruptions.
Reducing Transmission and Distribution Losses: By strategically deploying energy storage systems at various points in the grid, it is possible to reduce transmission and distribution losses, making the energy supply chain more efficient.
Supporting Industrial Growth: A reliable and stable energy supply is essential for industrial growth. Energy storage can play a key role in ensuring a constant power supply, supporting industrial development and economic growth.
Climate Change Mitigation: The deployment of energy storage technologies facilitates the integration of renewable energy sources, contributing to a reduction in greenhouse gas emissions and helping African countries meet their climate change mitigation goals.
Incentivizing Investments: The adoption of energy storage technologies can attract investments in the energy sector. It enhances the business case for renewable energy projects, making

them more financially viable and appealing to investors.
Job Creation: The development, deployment, and maintenance of energy storage infrastructure create job opportunities, contributing to economic development and poverty reduction.
Overall, energy storage technologies are essential for creating a more sustainable, resilient, and inclusive energy landscape in Africa, addressing both immediate energy needs and longterm development goals.
What challenges and opportunities do you anticipate in the adoption and implementation of sustainable energy solutions, including solar power and energy storage, in Ghana and other African nations?
The adoption and implementation of sustainable energy solutions, including solar power and energy storage, in Ghana and other African nations present both challenges and opportunities. Here are some key considerations:
Challenges:
Initial Costs and Financing: The upfront costs of installing solar power systems and energy storage solutions can be high. Access to affordable financing and investment is crucial for widespread adoption, especially in countries with limited financial resources.
Infrastructure and Grid Limitations: Some regions may lack the necessary infrastructure for effective energy distribution and storage. Developing or upgrading the grid to accommodate renewable energy sources poses a challenge, and intermittent power supply can be an issue.
Technical Skills and Training: Adequate technical skills for the installation, operation, and maintenance of solar and energy storage systems are essential. There may be a need for training programs to build a skilled workforce capable of managing and servicing these technologies.
Policy and Regulatory Frameworks: Clear and supportive policies are vital to incentivize investment and create a conducive environment for the growth of sustainable energy. Delays or uncertainties in regulatory frameworks can hinder progress.
18 SOLARQUARTER ANNUAL EDITION 2024 | SOLAR & STORAGE AFRICA LIVE EXPO SPECIAL ISSUE
InConversation
Public Awareness and Acceptance: There might be a lack of awareness and understanding among the general public about the benefits of sustainable energy solutions. Effective communication and awareness campaigns are necessary to promote acceptance and adoption.
Opportunities:
Abundant Renewable Resources: Many African nations, including Ghana, have abundant solar resources. Leveraging these resources can lead to a reliable and sustainable energy supply.
Energy Access and Rural Electrification: Sustainable energy solutions can play a crucial role in extending electricity access to rural and remote areas. Off-grid solar solutions can provide decentralized power sources, reducing reliance on centralized grids.
Job Creation: The renewable energy sector has the potential to create jobs, from manufacturing and installation to maintenance and support services. This can contribute to economic development and poverty reduction.
Climate Resilience: Adopting sustainable energy solutions helps reduce dependence on fossil fuels, contributing to climate change mitigation. It also enhances resilience to climaterelated challenges by diversifying the energy mix.
International Cooperation and Funding: Global initiatives and funding support for sustainable energy projects can provide African nations with opportunities to accelerate their transition to clean energy. Collaboration with international organizations and donors can facilitate access to financing and technology.
Technological Advancements: Ongoing advancements in solar and energy storage technologies may lead to cost
The deployment of energy storage technologies facilitates the integration of renewable energy sources, contributing to a reduction in greenhouse gas emissions and helping African countries meet their climate change mitigation goals.

reductions and increasEd efficiency, making these solutions more attractive and competitive.
In summary, while there are challenges to overcome, the adoption of sustainable energy solutions in Ghana and other African nations presents significant opportunities for economic development, job creation, and environmental sustainability. Success will depend on effective policies, international cooperation, and investment in both infrastructure and human capital.
What are your aspirations and goals for advancing renewable energy and sustainable practices in Ghana, and how do you plan to collaborate with other stakeholders to achieve these objectives?
To promote renewable energy and sustainability in Ghana, collaboration among various stakeholders is essential. Here are some potential goals and strategies:
Raise Awareness: Increase public awareness about the benefits of renewable energy and sustainable practices through education campaigns, workshops, and community outreach programs.
Policy Advocacy: Work with policymakers to advocate for supportive policies and regulations that encourage the growth of renewable energy infrastructure. This may include feed-in tariffs, tax incentives, and regulatory frameworks that prioritize sustainability.
Capacity Building: Collaborate with educational institutions and vocational training centers to develop programs that enhance the skills and knowledge of individuals in the renewable energy sector. This can help create a skilled
workforce to drive the industry forward.
Research and Development: Foster collaboration with research institutions to promote innovation in renewable energy technologies. This may involve supporting research projects, creating partnerships with technology companies, and facilitating knowledge exchange.
Public-Private Partnerships: Encourage partnerships between the government, private sector, and nonprofit organizations to jointly fund and implement renewable energy projects. Public-private collaborations can leverage resources, expertise, and networks to scale up sustainable initiatives.
Infrastructure Development: Collaborate with energy companies and investors to develop and invest in renewable energy infrastructure projects, such as solar and wind farms. These partnerships can accelerate the transition to clean energy sources.
Community Engagement: Involve local communities in the planning and implementation of renewable energy projects. This ensures that projects are culturally sensitive, address local needs, and have community support.
International Cooperation: Seek support from international organizations, governments, and NGOs that specialize in renewable energy and sustainable development. Collaborating with global partners can bring additional resources, expertise, and best practices to the local context.
By adopting a comprehensive and collaborative approach, stakeholders can work together to advance renewable energy and sustainable practices in Ghana, contributing to the country’s long-term environmental and economic well-being.
19 SOLARQUARTER ANNUAL EDITION 2024 | SOLAR & STORAGE AFRICA LIVE EXPO SPECIAL ISSUE
Renewvia Prioritizes Safety And Sustainability In Its Engineering Processes And Designs For Solar Energy Systems

Could you provide an overview of the current state of the solar energy landscape in the regions where Renewvia Energy operates, and how has Renewvia contributed to its advancement through its portfolio of projects?
In both Kenya and Nigeria, the solar energy sector is experiencing rapid growth, driven by several factors. These include high solar irradiance, increasing awareness about renewable energy, and a strong need for reliable and sustainable electricity, especially in rural and off-grid areas.
Kenya’s Solar Energy Landscape is characterized by a strong need for rural electrification. A significant portion of Kenya’s population still lacks access to the national grid, making solar minigrids and off-grid solutions crucial for electrification. Simultaneously, rising energy prices have driven many businesses to become more interested in solar energy solutions.
Nigeria’s Solar Energy Landscape is characterized by huge market potential, a large energy deficit, and exciting government initiatives. Nigeria, with its large population and high solar potential, presents a significant market for solar energy. Despite being an oil-rich nation, Nigeria faces a substantial energy deficit, particularly in rural areas. The Nigerian government is increasingly focusing on renewable energy policies to diversify its energy mix.
Renewvia’s Contribution is best thought of along five key axes:
1. Innovative Solar Mini-Grids: Renewvia has been at the forefront of deploying
Nicholas Selby
Director of Engineering
Renewvia Solar Africa
KEY HIGHLIGHTS
• Renewvia’s approach to integrating renewable energy storage technologies into our solar energy systems is a key aspect of our state-of-the-art solutions.
• Renewvia Energy balances innovation with practical implementation in solar energy projects
• Renewvia’s risk management in engineering projects involves a multifaceted approach
solar mini-grids in remote areas. These grids are not only environmentally friendly but also economically viable, providing a stable power supply at a lower cost than traditional diesel generators.
2. Community Engagement: We prioritize community engagement in our projects, ensuring that our solutions meet the specific needs of the local population.
3. Sustainability and Scalability: Our projects are designed with sustainability in mind, using high-quality equipment and ensuring easy scalability to meet growing energy demands.
4. Empowering Local Economies: By providing reliable electricity, we’re empowering local businesses and communities, fostering economic growth and improving the quality of life.
5. Partnerships and Funding: We actively seek partnerships and funding opportunities to expand our reach and impact, collaborating with local governments, NGOs, and international organizations.
How does Renewvia Energy balance innovation with practical implementation when developing engineering solutions for solar energy projects?
Renewvia Energy balances innovation with practical implementation in solar energy projects by focusing on three key areas:
1. Customized Solutions: We tailor our engineering designs to suit specific

Despite being an oil-rich nation, Nigeria faces a substantial energy deficit, particularly in rural areas. The Nigerian government is increasingly focusing on renewable energy policies to diversify its energy mix.
local conditions, ensuring that our solutions are both innovative and practical for the communities we serve.
2. Scalable Technology: Our projects use scalable and adaptable technologies. This approach allows us to innovate while also ensuring that the technology can be practically implemented, easily maintained, and efficiently upgraded as the local economy expands.
InConversation
20 SOLARQUARTER ANNUAL EDITION 2024 | SOLAR & STORAGE AFRICA LIVE EXPO SPECIAL ISSUE
InConversation
3. Stakeholder Collaboration: We engage with local stakeholders, including communities and local governments, to ensure our solutions are practically applicable and meet real-world needs. This collaboration helps us stay grounded in practical realities while pursuing innovative approaches.
When it comes to engineering processes and designs for solar energy systems, how does Renewvia prioritize safety and sustainability?
Renewvia prioritizes safety and sustainability in its engineering processes and designs for solar energy systems through the following approaches:
1. Strict Safety Standards: We adhere to IEC international safety standards in design and installation, ensuring all systems are reliable and pose no hazards to users or the environment.
2. Regular Maintenance and Monitoring: Regular maintenance and monitoring are integral to our approach, ensuring systems operate safely and sustainably over time.
3. Community Training: We provide training to local communities on the safe and sustainable operation of the systems, promoting long-term stewardship and care.
In terms of risk management, particularly in engineering

1. ssessment: We conduct thorough risk assessments at the project planning stage, identifying potential technical, environmental, and operational risks.
2. Stakeholder Engagement: Engaging with local communities and stakeholders helps us understand and mitigate site-specific risks.
3. Quality Control: We implement strict quality control measures in sourcing materials and during construction to ensure safety and reliability.
4. Regular Monitoring: Continuous monitoring of projects helps us identify and address risks proactively.
5. Training and Capacity Building:
We incorporate lithiumion batteries in all our mini-grid systems. Our engineering team optimizes system battery capacity based on the specific energy usage patterns and needs of each community. This ensures that the storage system is neither underutilized nor over stressed.
ensuring swift and effective response to unforeseen events.
Can you discuss Renewvia’s approach to integrating renewable energy storage technologies, such as batteries, into solar energy systems, and what challenges are anticipated in this process?
Renewvia’s approach to integrating renewable energy storage technologies into our solar energy systems is a key aspect of our state-of-the-art solutions. Without energy storage, off-grid solar systems, including mini-grids, simply would not work. We incorporate lithiumion batteries in all our mini-grid systems. Our engineering team optimizes system battery capacity based on the specific energy usage patterns and needs of each community. This ensures that the storage system is neither underutilized nor over

21 SOLARQUARTER ANNUAL EDITION 2024 | SOLAR & STORAGE AFRICA LIVE EXPO SPECIAL ISSUE
We Believe There Are Significant Opportunities For Project Development Of Utility Scale Renewable Projects Within Southern Africa.

How would you assess the current market landscape for renewable energy, specifically focusing on solar and storage solutions, within Southern Africa?
The future of energy in Southern Africa is very clearly going to be built on Renewables, and in particular, electricity from solar photovoltaics, balanced by battery storage. These two technologies are already being deployed at all scales, whether Solar Home Systems for lowincome, off-the-grid households, to grid-tied residential, commercial and industrial off-takers on the distribution networks, to much larger utility-scale projects tying in to the transmission network. Solar and storage technologies continue to reduce in price, and as they do, the deployment of such on a mass distributed scale will continue to grow exponentially. In addition, government no longer has the capital for large projects, and other fossil fuel, gas and nuclear technologies have just become too expensive and take too long to build. This will create many new opportunities for existing companies and new entrants to play in the Renewables space.
As you look to establish and expand solar + storage projects in the Southern Africa region, what are the primary challenges you foresee, and how do you believe these projects will benefit local communities and businesses?
There are three major challenges.
The first is the regulatory environment. Although the needle continues to move
Frank Spencer
Regional Director - Southern Africa Cainmani
KEY HIGHLIGHTS
• It is our dream to see every person and business with access to affordable, clean electricity.
• Solar and storage technologies continue to reduce in price, and as they do, the deployment of such on a mass distributed scale will continue to grow exponentially.
• Governments need to continue to move quickly and wisely to open up energy markets to new players
towards enabling the private sector to build the infrastructure required, this is not yet fully enabled for a market to operate both in individual countries and between countries. Governments need to continue to move quickly and wisely to open up energy markets to new players.
Secondly, the lack of grid infrastructure at all scales is already constraining the rate at which renewables could be built. Innovative financing needs to be found for new transmission infrastructure, while smart grid technologies also need to be financed and deployed.
Finally, considering the scale of infrastructure that needs to built, both in renewables generation and grid infrastructure, there is likely to be a significant shortage of skills and local manufacturing to meet the demand. Significant investment into training and local beneficiation or local minerals is needed asap to support the tsunami of infrastructure build that is coming.
Could you elaborate on Cainmani’s strategic plans for market expansion within Southern Africa and discuss the significance of this region within the company’s broader growth strategy?
We believe there are significant opportunities for project development of utility scale renewables projects within Southern Africa. Considering the need, we believe there will be demand for large quality projects for at least two decades still, and we will continue to focus here.
How does Cainmani navigate regulatory and operational complexities unique to the Southern African market, and what strategies does the company employ to ensure the success and sustainability of its projects in the region?
It is our dream to see every person and business with access to affordable, clean electricity. To achieve such, we believe it is important to work together with Energy Industry Associations and our fellow market players to engage constructively with governments, their electricity regulators, departments of electricity, and national utilities. Only through building relationships, collaboration and joint learning will we be able to shift to a clean, renewables-centric world of electricity generation, and bring the scale required to revolutionize energy in Africa.
Considering the scale of infrastructure that needs to built, both in renewables generation and grid infrastructure, there is likely to be a significant shortage of skills and local manufacturing to meet the demand. Significant investment into training and local beneficiation or local minerals is needed to support the tsunami of infrastructure build that is coming.
InConversation
22 SOLARQUARTER ANNUAL EDITION 2024 | SOLAR & STORAGE AFRICA LIVE EXPO SPECIAL ISSUE
Rensource Is Arguably The Fastest-Growing C&I Focused Solar Energy Company In Africa.

Can you provide an overview of the current state of the solar energy landscape in Nigeria, and how has Rensource Energy contributed to its development, particularly with its extensive portfolio of projects?
The solar energy landscape in Nigeria has been experiencing steady growth in recent years. The recent AFSIA report 2024, puts the total installed Solar capacity in Nigeria in 2023 at 34.7 MWp, this is a circa 400% increment to the total capacity in 2022 at 8.1 MWp. Nigeria, as a country blessed with abundant sunlight, has significant potential for solar energy generation. However, the adoption of solar energy technologies has been relatively slow due to various challenges, including the high initial investment costs, inadequate infrastructure, limited access to financing and revenue assurance.
Rensource Energy has been at the forefront of addressing these challenges and driving the development of solar energy in Nigeria. The company has made significant contributions to the solar energy landscape through its extensive portfolio of projects, although Rensource Energy started by providing energy using micro, mini-grid, and SHS systems, it has since pivoted to providing energy solutions to C&I customers.
In 2017, Rensource Energy launched Power as a Service business model which was focused on the deployment of SHS to homes and SMEs. Rensource later diversified its business portfolio to include “Powered by Rensource” model, focused on energising underserved commercial markets. Rensource later expanded its
Michael Iwu
VP Commercial Rensource Energy
KEY HIGHLIGHTS
• Rensource Energy’s extensive portfolio of solar projects has been instrumental in advancing the adoption of solar energy in Nigeria.
• Rensource Energy plays a crucial role in the execution of solar projects by leveraging its expertise, experience, and comprehensive approach to project delivery.
• Rensource Energy stays adaptable and responsive to regulatory changes and policies affecting the solar energy sector by maintaining a proactive approach
Power as a Service model to include systems for customer segments with higher energy requirements and in 2018, Rensource secured a pipeline of 25,000 merchants in 12 additional markets from the Rural Electrification Agency (REA) through the Energizing Economies Initiative and was able to raise USD 20 million to power African markets with solar.
However, with the outbreak of the COVID-19 pandemic, the solar for market initiative was badly affected. This affected revenue collection as there were no commercial activities during the Pandemic. Rensource Energy pivoted to focusing on C&I customers because of the following reasons; greater savings on electricity, grid stability, and greater impact on Co2 off-setting and revenue assurance.
Overall, Rensource Energy’s extensive portfolio of solar projects has been instrumental in advancing the adoption of solar energy in Nigeria. By demonstrating the viability and benefits of solar power across different sectors, the company has contributed to building confidence in solar technologies and driving momentum for further solar energy development in the country.
What key milestones and success stories have contributed to Rensource’s prominence in the Nigerian solar energy sector?
Rensource is arguably the fastestgrowing C&I focused Solar Energy company in Africa. The rise to the limelight I would say came when we installed our first C&I solar farm; a 700 KWp solar farm for a poultry farm in
Abuja and shortly after that we signed a 5 MWp Solar PPA for Baze University.
What role does Rensource Energy play in the execution of solar projects, and how does the company ensure successful project delivery from inception to completion, considering the unique challenges in the Nigerian market?
Rensource Energy plays a crucial role in the execution of solar projects by leveraging its expertise, experience, and comprehensive approach to project delivery. The company’s involvement typically spans the entire project lifecycle, from inception to completion, and encompasses a range of activities to ensure successful implementation, taking into account the unique challenges present in the Nigerian market.
At the outset, Rensource Energy adopts a consultative approach to understanding its clients’ specific energy needs and requirements. This initial assessment phase allows the company to tailor its solutions to meet the unique demands of each project, considering factors such as energy consumption patterns, infrastructure availability, and financial constraints.
Following this, Rensource Energy engages in detailed project planning and design, drawing on its team of experienced engineers, solar energy experts, and project managers. During the planning phase, the company conducts rigorous feasibility studies, site assessments, and technical evaluations to ensure that the proposed solar solutions are well-suited to the project’s context and capable of delivering the expected performance.
InConversation
23 SOLARQUARTER ANNUAL EDITION 2024 | SOLAR & STORAGE AFRICA LIVE EXPO SPECIAL ISSUE
In Conversation

In the context of the Nigerian market, Rensource Energy navigates various challenges such as inadequate infrastructure, financing constraints, and regulatory complexities. The company addresses these challenges by working closely with local stakeholders, government agencies, financial institutions, and regulatory bodies to ensure compliance, secure necessary permits, and develop financing structures that align with the specific requirements of each project.
As part of its commitment to successful project delivery, Rensource Energy places a strong emphasis on the quality of its solar installations and the reliability of its systems. The company carefully selects high-quality solar components and partners with reputable suppliers to ensure that its solar projects are built to last and can withstand the environmental conditions prevalent in Nigeria, including factors such as heat, humidity, and dust.
Furthermore, Rensource Energy employs robust project management practices, including stringent construction and installation standards, rigorous quality control processes, and comprehensive testing and commissioning procedures. By adhering to these best practices, the company ensures that its solar projects are implemented to the highest standards, meeting performance expectations and delivering long-term value to its clients and end-users.
In addition to the technical aspects of project execution, Rensource Energy also prioritizes community engagement, capacity building, and sustainability considerations. The company actively involves local communities in its project activities, fosters skills development through training and employment opportunities, and integrates environmental and social impact assessments into its project planning to ensure that its solar projects contribute positively to local development and environmental stewardship.
Overall, Rensource Energy’s approach to project execution encompasses a comprehensive and holistic perspective, considering technical, financial, regulatory, and social dimensions to ensure successful project delivery. By addressing the unique challenges present in the Nigerian market and leveraging its expertise in solar energy development, the company is able to overcome barriers and drive the successful implementation of solar projects that contribute to sustainable energy access and economic development in Nigeria.
Could you elaborate on Rensource Energy’s approach to addressing the specific energy needs and challenges of diverse market segments, such as residential, commercial, and industrial customers, through its solar solutions?
Rensource Energy takes a customized approach to address the diverse energy needs and challenges of different market segments. However, Rensource Energy key market segment is commercial, and industrial (C&I) customers and SMEs.
When it comes to commercial and small business clients, Rensource Energy understands the importance of energy reliability and cost-efficiency for driving business operations. The company offers scalable solar solutions that can power a range of commercial activities, including small shops, clinics, schools, and offices. These solutions are tailored to the specific energy requirements of the commercial sector, providing reliable power for lighting, appliances, computers, and other essential equipment. Rensource Energy also offers financing options and flexible payment plans to make solar energy more accessible to small businesses, enabling them to reduce operating costs and enhance their sustainability.
For industrial customers, Rensource Energy leverages its expertise in solar project development to design and implement large-scale solar installations that can offset a significant portion of the energy consumption of industrial facilities. The company’s team of engineers works closely with industrial clients to conduct energy audits, assess specific power needs, and develop customized solar solutions that integrate seamlessly with existing energy infrastructure. By deploying solar energy systems for industrial clients, Rensource Energy helps reduce operational expenses, minimize reliance on grid power, and contribute to the sustainability goals of the industrial sector.
In all market segments, Rensource Energy prioritizes the use of highquality solar components, robust system designs, and reliable installation practices to ensure that its solar solutions meet the performance expectations of diverse customers. The company also considers factors such as local regulations, grid availability, and energy consumption patterns to tailor its solar offerings to the specific needs and circumstances of each market segment, ensuring that customers receive sustainable, cost-effective, and reliable energy solutions that align with their unique requirements.
By addressing the distinct energy needs and challenges of commercial & industrial and SMEs customers through its tailored solar solutions, Rensource Energy demonstrates its commitment to driving the adoption of clean energy across diverse market segments and contributing to the overall sustainability and resilience of Nigeria’s energy landscape.
How does Rensource Energy stay adaptable and responsive to regulatory changes and policies affecting the solar energy sector, and how does this influence your commercial strategies?
Rensource Energy stays adaptable and responsive to regulatory changes and policies affecting the solar energy sector by maintaining a proactive approach to monitoring and engaging with regulatory developments at local, national, and international levels. The company’s commercial strategies are influenced by these factors in several ways:
1. Regulatory Compliance: Rensource Energy prioritizes compliance with
24 SOLARQUARTER ANNUAL EDITION 2024 | SOLAR & STORAGE AFRICA LIVE EXPO SPECIAL ISSUE
InConversation
evolving regulations and policies governing the energy sector. The company stays abreast of changes in energy laws, incentives, and standards to ensure that its solar solutions adhere to the latest regulatory requirements. This approach enables Rensource Energy to maintain its market presence and reputation as a compliant and trustworthy energy provider.
2. Advocacy and Collaboration: Rensource Energy actively engages with policymakers, industry associations, and stakeholders to advocate for supportive policies and collaborate on shaping regulatory frameworks. The company’s commercial strategies are influenced by its advocacy efforts, as it seeks to contribute to policy discussions, share industry insights, and influence the direction of regulatory changes that can impact the growth and viability of the solar energy sector.
3. Risk Management and Opportunities: Regulatory changes introduce both risks and opportunities for solar energy companies. Rensource Energy assesses the potential impact of regulatory shifts on its operations, supply chain, and customer base. By factoring regulatory risk into its commercial strategies, the company can mitigate potential disruptions and capitalize on new opportunities arising from policy changes.
Overall, Rensource Energy’s adaptability and responsiveness to regulatory changes and policies are integral to its commercial strategies. By closely monitoring regulatory developments, aligning its offerings with evolving standards, and actively engaging with stakeholders, the company positions
What is your vision for Rensource Energy in the coming years, and how does the company plan to sustain its leadership position in Nigeria’s solar energy sector under your leadership as VP Commercial?
As the VP of Commercial at Rensource Energy, my vision for the company is centered around driving sustainable growth, fostering innovation, and expanding our impact in Nigeria’s solar energy sector and Africa as a whole.
To sustain Rensource Energy’s leadership position, I plan to focus on several key strategies:
1. Market Expansion: We will continue to identify and penetrate new markets within Sub-Saharan Africa, leveraging data-driven insights to target regions with high solar energy adoption potential. This will involve conducting thorough market assessments, understanding local regulations and incentives, and tailoring our offerings to meet the specific needs of each region.
2. Product Innovation: Innovation will be at the core of our commercial strategy, as we seek to develop new and improved solar energy solutions that address evolving customer demands and technological advancements. This may involve enhancing our existing product portfolio, introducing new financing models, and integrating smart energy management technologies to optimize energy production and consumption.
3. Regulatory Engagement: We will maintain a proactive approach to engaging with regulatory bodies and industry stakeholders, advocating for supportive policies and influencing regulatory frameworks to foster a conducive environment

for solar energy adoption. By actively participating in policy discussions and contributing industry expertise, we aim to shape regulations that benefit the company and the broader solar energy ecosystem.
4. Strategic Partnerships: Collaborating with strategic partners, including financial institutions, technology providers, EPC companies, and community organizations, will be crucial to expanding our reach and accelerating the deployment of solar energy solutions. These partnerships will enable us to access new customer segments, drive awareness, and create innovative business models that enhance our market position.
5. Customer-Centric Approach: We will prioritize a customer-centric approach in all our commercial initiatives, aiming to deliver an exceptional customer experience, educate consumers about the benefits of solar energy, and provide tailored solutions that meet their specific energy needs. This will involve investing in customer service capabilities, conducting outreach programs, and leveraging digital platforms to engage and support our customers.
6. Sustainability and Corporate Responsibility: Sustainability will remain a key pillar of our commercial strategy, as we continue to prioritize environmental responsibility and social impact. We will seek to integrate sustainable practices into our operations, support local communities, and contribute to the advancement of clean energy initiatives beyond our core business activities.
7. Talent Development and Empowerment: Investing in our team’s skills and capabilities will be essential to sustaining our leadership position. We will foster a culture of continuous learning, empowerment, and innovation, providing our employees with the tools and resources they need to drive commercial success and contribute to our long-term vision.
By executing these strategies, we aim to solidify Rensource Energy’s position as a leading player in Nigeria’s solar energy sector whilst expanding to new markets, driving positive change, and shaping the future of sustainable energy in Africa.
25 SOLARQUARTER ANNUAL EDITION 2024 | SOLAR & STORAGE AFRICA LIVE EXPO SPECIAL ISSUE
Empowering Marginalized Communities: A Vision for Mini-Grids in Zimbabwe’s Energy Future InConversation

As the Chief Executive Officer of the Zimbabwe Energy Regulatory Authority (ZERA), how do you perceive the current status of mini-grid adoption in Zimbabwe’s energy landscape, particularly in marginalized areas and how has ZERA contributed to these initiatives?
There is a growing interest of developing mini-grids to support the marginalised communities. The mini-grids are using renewable energy technology of solar PV, coming with economic activities making them viable and sustainable.
Can you discuss the challenges marginalized communities face in accessing reliable energy and how mini-grids address them and how does ZERA plan to address them?
marginalised communities are located far from the main grid making it expensive to extend the grid to them.
Edington Tapera Mazambani
Chief Executive Officer
Zimbabwe Energy Regulatory Authority (ZERA)
KEY HIGHLIGHTS
• Mini-Grid Adoption: Mini-grids utilizing solar PV technology are fostering economic activities in marginalized areas of Zimbabwe, enhancing viability and sustainability.
• Challenges and Solutions: Marginalized communities in Zimbabwe face energy access challenges due to their remote locations, but ZERA is facilitating mini-grid development through private sector investment, streamlined regulations, and operator training.
• Technological Advancements: Under Edington Tapera Mazambani’s leadership, ZERA leverages technology such as power quality meters and computerized billing systems to improve efficiency and affordability, advancing Zimbabwe’s mini-grid expansion and integration into the broader energy ecosystem for resilience and equity.
ZERA also assists in capacitation of the operators of mini-grids through training.
How is ZERA, under your leadership, using technology to enhance the efficiency and affordability of mini-grid systems, and what role do emerging technologies play in expanding mini-grid networks?
ZERA has assisted in ensuring the right power quality is generated from the mini grid through the use of Power quality meters.
The Authority also donated a computer for the billing system for one of the mini-grids.
Can you share examples of successful mini-grid projects supported by ZERA and their impact on local communities,
has successfully maintained irrigation of 3 irrigation schemes.
Finally, could you outline your vision for the role of mini-grids in Zimbabwe’s energy transition journey, and how ZERA plans to support the integration of minigrids into the broader energy ecosystem to enhance resilience, equity, and sustainability?
Mini-grids accelerate the country’s vision to become a middle-income economy through ensuring universal access to clean affordable and sustainable energy by 2030. We anticipate more mini-grids to be commissioned and paying the same tariff as grid connected customers.
ZERA will continue to capacitate minigrids through trainings on safety and mini grid tariff models.

Mini-grids accelerate the country’s vision to become a middle-income economy through ensuring universal access to clean affordable and sustainable energy by 2030. We anticipate more mini-grids to be commissioned and paying the same tariff as grid connected customers.
26 SOLARQUARTER ANNUAL EDITION 2024 | SOLAR & STORAGE AFRICA LIVE EXPO SPECIAL ISSUE
Innovation Unleashed: Insights from Industry Pioneers

What’s the status of South Africa’s renewable energy landscape, particularly solar, and what’s MESAMA Energy’s impact with over 100 projects since its inception?
The renewable energy landscape has drastically evolved since the first projects on different levels. Just to pay special attention to the legislative frameworks which now make it easier for foreign investors/players and local IPPs/developers to partner according to their respective strengths. The current load shedding continues to frustrate users of power from residential and industrial perspectives to point that they continuously seek for solutions that will provide them with reliable power. These are mostly hybrid solutions which include solar PV + BESS as the combination of the two has been well implemented across the country and is quicker to implement. In recent years, we have seen large scale projects that include solar PV + BESS, due to the need to store power so it can be dispatched when the solar resource is limited. Mesama Energy’s team has participated in various of the projects dating back 2013, and in more recent years, consulted over various operational assets and others close to reaching COD.
As MESAMA Energy’s Founder & CEO, what are the significant milestones and success stories that have shaped its standing in the renewable energy sector?
Mesama Energy has been in existence since 2017 and has since built up its own pipeline amounting to approximately 3GW. These projects are from different technologies, which include solar PV,
Melusi Tshabalala
CEO
Mesama Energy
KEY HIGHLIGHTS
• Visionary Strategies: Delving into groundbreaking approaches shaping the future.
• Revolutionary Technologies: Exploring cutting-edge innovations redefining industries worldwide.
• Inspirational Leadership: Unveiling the guiding principles driving transformative change and success.
wind, biomass, hydro power, gases for power and mobility – including H2, and e-mobility. These projects are at different stages of development and the most advanced is currently undergoing financial close. We do have significant installations in the C&I space. Our consulting division has raised approximately ZAR 8BN for other IPPs through DFIs, corporate banks, private equity firms etc. We have also helped develop in excess of 4GW of projects by other IPPs.
What role does MESAMA Energy play in executing renewable energy projects, and how does it ensure smooth project delivery from start to finish?
It depends on the project. Some of the projects we have been involved in have required funding, project development, policy updates/creation, manufacturing, technical, commercial and financial DDs etc. A lot of our time is spent on planning for our projects which ensures a smooth execution phase of those particular projects.
How does MESAMA Energy integrate sustainability practices into its projects, and what innovative strategies or technologies does it use?
We stay abreast of the industry trends, policy reforms – in some cases, we lobby for these reforms for the greater good of our economies, specifically for the African context. Our projects are often tailor made, based on the available resources and the needs of the client. Some projects tend to be more innovative and some
more for the tried and tested technologies or approaches. Our approach ensures that all stakeholders of the project benefit positively from the existence of the project.
What’s your vision for MESAMA Energy’s future, and what strategies will you use to maintain its leadership in South Africa’s renewable energy sector?
Over the next 5 years, we seek to have progressed significantly with the development of our projects, to have reached COD for 65% of projects. We are currently busy with other projects in the e-mobility & hydrogen for storage and mobility space. These projects should be concluded in 2024 and 2025 respectively. We remain active with all the relevant stakeholders in the sector, participating in the most important conversations, and to continuously learn about all the different and new technologies that are available to us
Our projects are often tailor made, based on the available resources and the needs of the client. Some projects tend to be more innovative and some more for the tried and tested technologies or approaches. Our approach ensures that all stakeholders of the project benefit positively from the existence of the project.
InConversation
27 SOLARQUARTER ANNUAL EDITION 2024 | SOLAR & STORAGE AFRICA LIVE EXPO SPECIAL ISSUE
Africa’s Solar Surge: Racing to Achieve 16 GW of PV Capacity by 2023’s End

Across the vast expanse of Africa, a remarkable energy transformation is underway, driving the continent towards a future powered by renewable sources. At the heart of this evolution lies a collective ambition: to accelerate towards 16 GW of installed solar photovoltaic (PV) capacity by the end of 2023. This ambitious target represents a monumental leap forward in Africa’s renewable energy journey, marking a significant milestone in the continent’s quest for sustainability, resilience, and energy independence.
In the year 2023 alone, Africa witnessed the installation of an impressive 3.5 GW of solar PV capacity, underscoring the region’s growing momentum in embracing solar energy solutions. This substantial increase in solar installations reflects a concerted effort by governments, businesses, and communities across the continent to harness Africa’s abundant solar resources and transition towards cleaner, more sustainable sources of power.
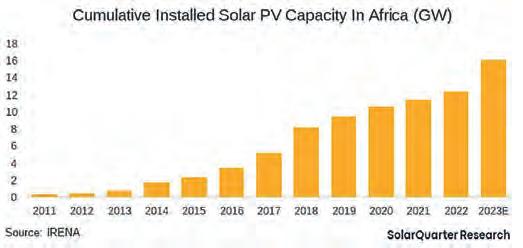
Among the top solar PV countries in Africa, South Africa, Egypt, Kenya, and Nigeria have emerged as leaders in the continent’s solar energy revolution. These countries have made significant strides in expanding their solar PV capacity, leveraging their unique geographical advantages, supportive policies, and innovative approaches to drive solar energy deployment.
Africa’s solar landscape.
Similarly, Egypt has made remarkable progress in expanding its solar PV capacity, propelled by its strategic location in the sunbelt region and ambitious renewable energy targets. The Benban Solar Park, located in Aswan Governorate, stands as a testament to Egypt’s commitment to solar energy development. With a total capacity of 1.8 GW, Benban is one of the largest solar parks in the world, comprising numerous solar PV projects developed under the country’s feed-in tariff program.
Kenya, renowned for its innovative approaches to renewable energy deployment, has also emerged as a key player in Africa’s solar revolution. The Lake Turkana Wind Power project, coupled with the Garissa Solar Power Plant, exemplifies Kenya’s commitment to diversifying its energy mix and harnessing the power of renewable sources. With favorable solar irradiation levels and supportive policy frameworks, Kenya is poised to continue its upward trajectory in solar PV deployment.
Nigeria, Africa’s most populous country and largest economy, is also making significant strides in expanding its solar PV capacity. The Nigerian government has launched several initiatives to promote solar energy adoption, including the Solar Power Naija program aimed at deploying solar home systems to rural and underserved communities. With a growing off-grid solar market and a conducive investment climate, Nigeria is poised to emerge as a major player in Africa’s solar energy landscape.
As Africa accelerates towards 16 GW of installed solar PV capacity by the end of 2023, the continent stands on the cusp of a historic transformation. The increasing adoption of solar energy not only promises to expand electricity access, drive economic growth, and create jobs but also to mitigate the impacts of climate change and build a more sustainable future for generations to come. With visionary leadership, innovative technologies, and collective action, Africa is poised to emerge as a global leader in renewable energy, inspiring the world with its commitment to a

Research | Insights
28 SOLARQUARTER ANNUAL EDITION 2024 | SOLAR & STORAGE AFRICA LIVE EXPO SPECIAL ISSUE
Empowering Africa: A Policy Perspective On Accelerating Solar And Storage Deployment
Africa stands at a critical juncture in its development trajectory. With a burgeoning population, rapid urbanization, and increasing energy demand, the continent faces significant challenges in meeting its energy needs while also addressing issues of sustainability, affordability, and accessibility. In this context, the adoption and deployment of solar and energy storage technologies emerge as pivotal components of Africa’s energy transition and development agenda.
The imperative to accelerate the deployment of solar and storage solutions in Africa stems from multiple factors. Firstly, the continent boasts abundant solar resources, with many regions receiving high levels of solar irradiation throughout the year. This presents a tremendous opportunity to harness solar energy as a clean, renewable, and virtually inexhaustible resource to power homes, businesses, and industries across Africa.
Moreover, the declining costs of solar photovoltaic (PV) technology, coupled with advancements in energy storage systems, have rendered solar energy increasingly competitive and economically viable compared to conventional fossil fuelbased power generation. This cost-effectiveness makes solar and storage solutions particularly attractive for Africa, where many regions grapple with limited access to reliable and affordable electricity.
In light of these dynamics, policymakers across Africa must adopt a holistic and forward-thinking approach to accelerate the deployment of solar and storage technologies. Such an approach should encompass a range of policy measures, regulatory frameworks, and institutional mechanisms aimed at fostering a conducive environment for investment, innovation, and widespread adoption of solar and storage solutions.
One key policy priority is the formulation and implementation of supportive regulatory frameworks that incentivize investment in solar and storage projects while ensuring transparency, predictability, and regulatory certainty for investors and stakeholders. This entails streamlining permitting processes, establishing clear guidelines for grid interconnection and net metering, and introducing favorable financial incentives


such as feed-in tariffs, tax credits, and concessional financing mechanisms.
Furthermore, policymakers must prioritize the development of robust energy infrastructure and grid modernization initiatives to accommodate the integration of solar and storage technologies into the existing energy landscape. This includes investments in smart grid technologies, energy storage systems, and decentralized energy solutions to enhance grid reliability, resilience, and flexibility while optimizing the utilization of renewable energy resources.
In addition to regulatory and infrastructure measures, governments should actively promote research, development, and innovation in solar and storage technologies through targeted funding, capacity-building initiatives, and collaboration with academic institutions, research centers, and private sector stakeholders. By fostering a culture of innovation and entrepreneurship, African countries can unlock new opportunities for local technological innovation, job creation, and economic development in the renewable energy sector.
Moreover, addressing barriers to financing and investment is essential to scale up solar and storage deployment across Africa. Governments should work in partnership with multilateral development banks, international financial institutions, and private sector investors to mobilize capital, de-risk investments, and facilitate access to affordable financing options for solar and storage projects, particularly in underserved and remote areas.
Crucially, efforts to accelerate solar and storage deployment must be aligned with broader sustainable development objectives, including poverty alleviation, gender equality, and environmental conservation. By prioritizing the deployment of solar and storage solutions in off-grid and rural communities, governments can improve energy access, enhance livelihoods, and empower marginalized populations, particularly women and youth, to participate in economic activities and community development initiatives.
In conclusion, the acceleration of solar and storage deployment holds immense potential to catalyze Africa’s sustainable development and energy transition aspirations. By embracing innovative policies, fostering strategic partnerships, and prioritizing inclusive and equitable access to clean energy resources, African countries can unlock new pathways towards a prosperous, resilient, and sustainable future for all.
Research | Insights
29 SOLARQUARTER ANNUAL EDITION 2024 | SOLAR & STORAGE AFRICA LIVE EXPO SPECIAL ISSUE
Empowering Sustainable Urbanization In Africa: The Integration Of Solar, Storage, And Smart Infrastructure
Africa’s urban landscape is rapidly evolving, with cities emerging as hubs of economic growth, innovation, and opportunity. As urbanization accelerates across the continent, African cities face formidable challenges in meeting the diverse needs of their growing populations while also addressing pressing issues of sustainability, resilience, and environmental stewardship. In this context, the integration of solar energy, energy storage, and smart infrastructure emerges as a transformative strategy to empower sustainable urbanization in Africa.
At the heart of this paradigm shift lies the recognition of renewable energy, particularly solar power, as a linchpin of Africa’s urban development agenda. With abundant sunlight and vast untapped solar resources, African cities are ideally positioned to harness solar energy as a clean, reliable, and affordable alternative to conventional fossil fuel-based electricity generation. By embracing solar photovoltaic (PV) technology, cities can not only reduce their carbon footprint but also enhance energy security, mitigate the risks of climate change, and foster economic resilience in the face of volatile energy markets.
The integration of energy storage systems further enhances the viability and effectiveness of solar energy deployment in urban settings. Energy storage technologies, such as batteries and gridscale storage solutions, enable cities to capture and store excess solar power during periods of peak sunlight and deploy it during periods of high energy demand or grid instability. This facilitates the seamless integration of solar energy into the urban power grid, enhances grid stability, and reduces reliance on centralized fossil fuel-based power generation, thereby mitigating the risk of blackouts and enhancing energy security for urban residents and businesses.
Moreover, the advent of smart infrastructure technologies holds immense promise for optimizing the efficiency, reliability, and sustainability of urban energy systems in Africa. Smart grids, intelligent sensors, and advanced metering infrastructure enable real-time monitoring, management, and optimization of energy consumption, distribution, and grid operations, empowering cities to optimize resource allocation, minimize wastage, and enhance energy efficiency across diverse urban sectors.
The benefits of integrating solar, storage, and smart infrastructure extend far beyond the realm of energy alone. By embracing

renewable energy and smart technologies, African cities can unlock new opportunities for economic growth, job creation, and technological innovation. The development of local renewable energy industries, including solar panel manufacturing, installation, and maintenance services, can spur economic development, create skilled employment opportunities, and catalyze entrepreneurship and industrialization across urban value chains.
Furthermore, the integration of solar and smart infrastructure can enhance the quality of life and well-being of urban residents by fostering healthier, more sustainable, and livable urban environments. Solar-powered street lighting, electric vehicle charging stations, and decentralized energy solutions can improve public safety, reduce air pollution, and enhance mobility and accessibility for residents, while smart urban planning and design initiatives can promote inclusive, equitable, and resilient cities for all.
However, unlocking the full potential of solar, storage, and smart infrastructure in African cities requires a concerted effort from policymakers, urban planners, businesses, and civil society stakeholders. Governments must enact supportive policies, regulatory frameworks, and incentive mechanisms to facilitate the adoption and deployment of renewable energy and smart infrastructure solutions, while also promoting public-private partnerships and investment in critical infrastructure projects.

In conclusion, the integration of solar energy, energy storage, and smart infrastructure represents a transformative pathway towards empowering sustainable urbanization in Africa. By leveraging the power of renewable energy and smart technologies, African cities can unlock new pathways towards prosperity, resilience, and inclusive development, while also charting a course towards a cleaner, greener, and more
Research | Insights
30 SOLARQUARTER ANNUAL EDITION 2024 | SOLAR & STORAGE AFRICA LIVE EXPO SPECIAL ISSUE

future of energy storage in Africa.
The evolution of battery storage technology represents a transformative force in the energy landscape, offering unprecedented opportunities to unlock the full potential of renewable energy resources and reshape the way energy is generated, stored, and distributed across the continent. From lithium-ion batteries to flow batteries, and beyond, a diverse array of battery technologies is emerging as game-changers in Africa’s quest for energy independence and sustainability.
One of the most promising innovations in battery technology is the rapid advancement of lithium-ion batteries, which have revolutionized the energy storage market with their high energy density, long cycle life, and rapid charging capabilities. In recent years, the cost of lithium-ion batteries has plummeted, making them increasingly affordable and accessible for a wide range of applications, from grid-scale energy storage projects to off-grid solar systems for rural electrification.
Moreover, the scalability and versatility of lithium-ion batteries make them ideal for addressing the diverse energy needs of African communities, from powering remote health clinics and schools to stabilizing the grid and integrating renewable energy sources into the energy mix. By harnessing the power of lithium-ion batteries, African countries can enhance energy access, improve grid reliability, and reduce dependency on fossil fuels, paving the way for a cleaner, greener, and more resilient energy future.
Beyond lithium-ion batteries, other innovative energy storage technologies are also gaining traction in Africa, offering unique advantages and applications in diverse contexts. Flow batteries, for example, utilize liquid electrolytes to store and release energy, providing enhanced flexibility, scalability, and safety compared to traditional battery chemistries. Flow batteries are particularly well-suited for grid-scale energy storage projects, microgrids, and decentralized energy systems, offering a cost-effective solution for managing fluctuating renewable energy output and optimizing grid stability.
Furthermore, advancements in battery management systems, smart controls, and predictive analytics are enabling greater efficiency, reliability, and performance optimization across the entire battery storage ecosystem. These technologies empower operators to monitor battery health, optimize charging and discharging cycles, and maximize energy yield, thereby
overall economic viability.
The integration of battery storage systems with renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind power, holds immense promise for accelerating Africa’s transition to a sustainable energy future. By coupling solar photovoltaic (PV) panels with battery storage solutions, African communities can overcome the inherent intermittency and variability of renewable energy generation, ensuring reliable power supply even during periods of low sunlight or inclement weather.
Moreover, the deployment of battery storage systems can unlock new opportunities for energy access, economic development, and social empowerment in underserved and marginalized communities across Africa. By providing reliable electricity for lighting, cooking, communication, and productive activities, battery storage solutions can improve living standards, enhance educational and economic opportunities, and catalyze sustainable development outcomes for millions of people.
However, realizing the full potential of battery technology in Africa requires a concerted effort from policymakers, regulators, investors, and stakeholders across the public and private sectors. Governments must enact supportive policies, regulatory frameworks, and incentive mechanisms to facilitate investment in battery storage infrastructure, incentivize innovation, and foster collaboration between industry stakeholders.
Moreover, capacity-building initiatives, technology transfer programs, and knowledge-sharing platforms can empower local communities, businesses, and entrepreneurs to leverage battery technology for economic growth, job creation, and social development. By fostering a culture of innovation, entrepreneurship, and collaboration, Africa can harness the power of battery technology to drive sustainable energy transformation and unlock new pathways towards prosperity,

31 SOLARQUARTER ANNUAL EDITION 2024 | SOLAR & STORAGE AFRICA LIVE EXPO SPECIAL ISSUE

a compelling solution for addressing the continent’s energy challenges, from rural electrification and off-grid communities to grid-scale power generation projects. Innovations in solar PV modules, inverters, and mounting systems have significantly improved efficiency, reliability, and performance, making solar energy an increasingly viable alternative to conventional fossil fuel-based power generation.
Moreover, the integration of energy storage technologies is revolutionizing the way solar energy is harnessed, stored, and utilized in Africa. Energy storage systems, including lithium-ion batteries, flow batteries, and pumped hydro storage, enable the capture and storage of excess solar power during periods of peak sunlight, allowing for reliable electricity supply even after sunset or during periods of low solar irradiation. By coupling solar PV with energy storage solutions, African communities can overcome the intermittency and variability of renewable energy generation, ensuring uninterrupted power supply and enhancing energy resilience in the face of fluctuating demand and grid instability.

decentralized energy systems are gaining traction as a means of extending electricity access to remote and underserved communities in Africa. Off-grid solar home systems, mini-grids, and microgrids leverage standalone solar PV arrays and battery storage to provide clean, reliable, and affordable electricity to households, schools, health clinics, and businesses in off-grid areas. These decentralized energy solutions offer a lifeline for millions of people living in rural and remote areas, empowering communities with access to modern energy services, education, healthcare, and economic opportunities.
Furthermore, innovations in financing mechanisms, business models, and policy frameworks are driving the widespread adoption of solar and storage technologies across Africa. From pay-as-you-go financing and leasing arrangements to resultsbased financing and risk-sharing partnerships, a diverse array of financing options is making solar energy accessible and affordable for consumers, businesses, and governments alike. Moreover, supportive policies, regulatory incentives, and market reforms are creating an enabling environment for investment, innovation, and entrepreneurship in the renewable energy sector, catalyzing private sector engagement and driving market growth.
Looking ahead, the continued advancement and adoption of solar and storage technologies hold immense promise for Africa’s energy future. By leveraging the power of the sun and harnessing the potential of energy storage, African countries can accelerate their transition to a sustainable, resilient, and inclusive energy system, unlocking new pathways towards economic prosperity, social development, and environmental stewardship for generations to come. As Africa harnesses the power of the sun and storage, the continent is poised to lead the global renewable energy revolution, demonstrating the transformative potential of clean, renewable energy to power a brighter and more sustainable future for all.
32 SOLARQUARTER ANNUAL EDITION 2024 | SOLAR & STORAGE AFRICA LIVE EXPO SPECIAL ISSUE
Solar Gold Rush: Navigating The Financial Landscape Of Investing In Renewable Energy Projects In Africa
The continent of Africa is experiencing a solar gold rush, as investors and developers flock to harness its abundant sunlight and vast renewable energy potential. With an increasing focus on sustainability, energy independence, and climate resilience, renewable energy projects, particularly solar, have become highly attractive investment opportunities across the continent. However, navigating the financial landscape of investing in renewable energy projects in Africa presents unique challenges and considerations for stakeholders.
One of the primary drivers behind the solar gold rush in Africa is the continent’s immense solar resource potential. With many regions receiving high levels of solar irradiation throughout the year, solar energy presents a clean, renewable, and virtually inexhaustible resource for powering homes, businesses, and industries across Africa. Moreover, the declining costs of solar photovoltaic (PV) technology have made solar energy increasingly competitive and economically viable compared to conventional fossil fuel-based power generation, further fueling investor interest in solar projects.
However, investing in renewable energy projects in Africa requires a nuanced understanding of the financial landscape and market dynamics. One of the key challenges facing investors is the lack of mature and well-established financial markets and regulatory frameworks in many African countries. Uncertainty surrounding political stability, regulatory risks, and policy inconsistencies can pose significant barriers to investment and deter potential investors from entering the market.
Moreover, financing renewable energy projects in Africa often entails navigating complex and fragmented financial ecosystems characterized by limited access to capital, high borrowing costs, and currency exchange risks. Traditional sources of financing, such as commercial banks and development finance institutions,

leveraging concessional finance, grants, guarantees, and risksharing mechanisms, blended finance instruments can de-risk investments and attract a broader range of investors to the renewable energy sector.
In addition to blended finance, innovative business models, such as power purchase agreements (PPAs), build-own-operatetransfer (BOOT) arrangements, and leasing options, are gaining traction as means of financing and monetizing renewable energy projects in Africa. PPAs, for instance, enable developers to secure long-term contracts with off-takers, such as utilities, corporations, and government entities, guaranteeing a stable revenue stream over the project’s lifecycle. Similarly, BOOT arrangements allow developers to build and operate renewable energy projects before transferring ownership to the off-taker or investor, providing an exit strategy and potential returns on investment.
Furthermore, the emergence of renewable energy investment platforms, crowdfunding platforms, and impact investment funds is democratizing access to renewable energy investments and empowering individual investors and communities to participate in Africa’s energy transition. These platforms provide retail investors with opportunities to invest in renewable energy projects through equity crowdfunding, peer-to-peer lending, and community investment schemes, thereby democratizing access to clean energy and fostering grassroots participation in the renewable energy revolution.

Despite the challenges and complexities of navigating the financial landscape of investing in renewable energy projects in Africa, the potential rewards are immense. Beyond financial returns, investing in renewable energy projects in Africa offers the opportunity to drive sustainable development, promote energy access, create jobs, and mitigate climate change impacts. As the solar gold rush continues to unfold, stakeholders must collaborate, innovate, and mobilize capital to unlock the full potential of Africa’s renewable energy resources and accelerate the continent’s transition to a
Research | Insights
33 SOLARQUARTER ANNUAL EDITION 2024 | SOLAR & STORAGE AFRICA LIVE EXPO SPECIAL ISSUE































20 24 NICHOLAS SELBY Director of Engineering Renewvia Solar Africa Sebastian Noethlichs CEO Equator Energy DAVID THUO Head of Service and Product Development W. Giertsen Energy Solutions PAM ONYANYO CEO/Founder SkyEnergy Africa MARK HANKINS CEO African Solar Designs Ltd. KELLIE MURUNGI Chief Investment Officer East African Power BRIAN OMEGA Regional Managing Director (East Africa) Soventix East Africa Limited BRIAN WAMBANI Investment Director Camco CATHERINE IRURA Managing Director SOWITEC Kenya SAMSON ONDIEK Deputy Director, Utility Management Consultancy Kenya Power and Lighting Company RYAN DUNN Chief Executive Officer GridX Africa
Co-Founder and CEO Ariya
Jenny Fletcher
Finergy
Director Finergreen
Founder and CEO Starsight Premier Energy Group
Sabula Chief Executive Officer AECF
Alemayehu Division Manager, Power Systems Operations African Development Bank 04 APRIL 2024 GOLD PARTNER SESSION PARTNERS JOIN US FOR THE MOST POWERFUL SOLAR EVENT OF EAST AFRICA Jonathan Mbutu Manager, Alternative Energy Rural Electrification & Renewable Energy Corporation FEATURED SPEAKERS EXPLORE OUR THRILLING LINEUP OF SPEAKERS | MORE TO BE ANNOUNCED SOON! 3rd Edition EMARA HOTEL OLE SERENI, NAIROBI, KENYA Get in touch: Smriti Charan | smriti@firstviewgroup.com | +91 9833011250 Andrew James Ferreira | andrew@firstviewgroup.com | +91 9630911134 SUPPORTING PARTNER MEET OUR CONFIRMED PARTNERS PREMIUM INVERTER PARTNER
Florian Cammas
Rupesh Hindocha
Victoria Chelangat
Wubeshet
Zegeye
































































































