3 minute read
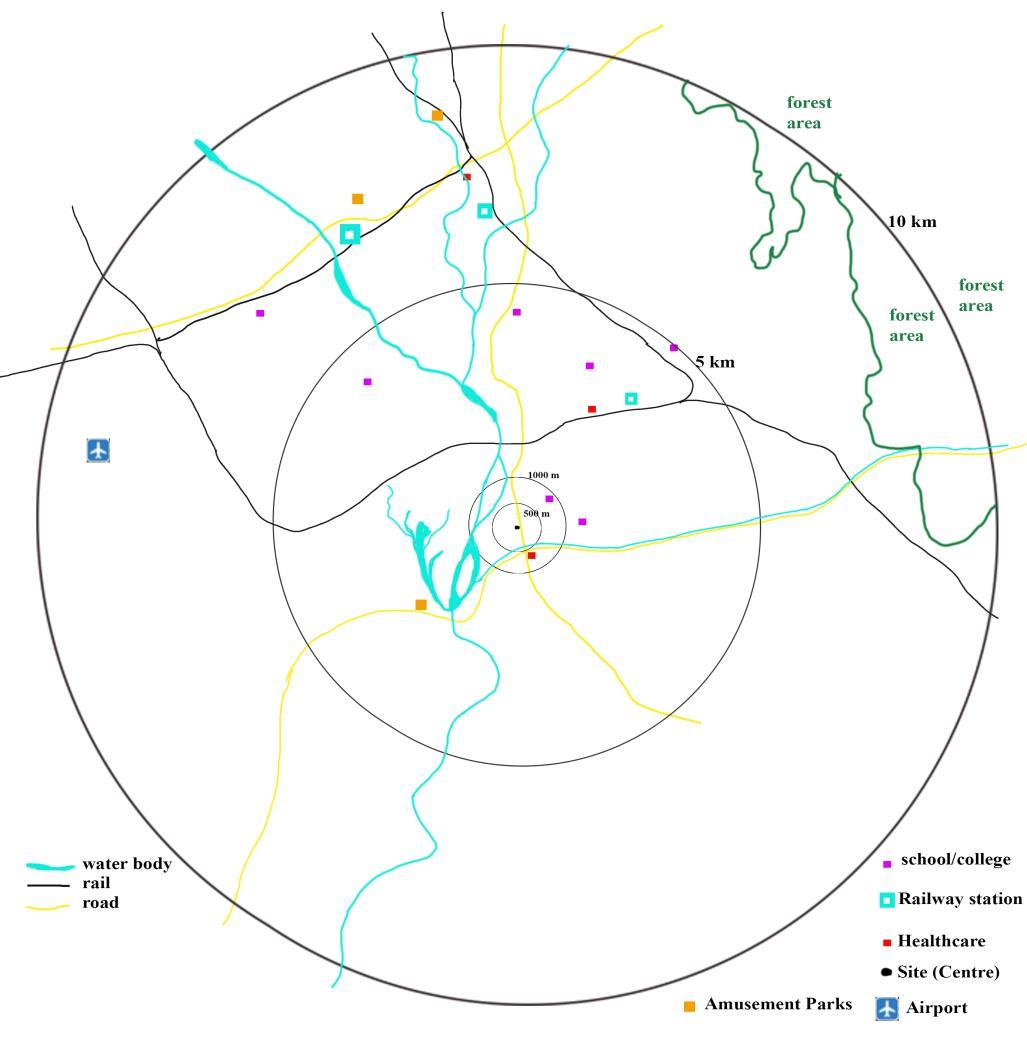
Figure 2-3Showing the proximity of civic services, view and vistas from site
2.2 Location and Connectivity
Site is located on Asian Highway 2. It has access from East on AH-2. New Jalpaiguri Station – 4.5 km (approx.). Bagdogra Airport – 18 km (approx.). Siliguri Railway Station – 7 km (approx.). Amberi Canal 600m. Mahananda River – 850 m (approx.) Electrical substation – 1.7 km. School (2 schools) within 800m. Hospital – 2 km (approx.). (Google, 2020)
Advertisement
Figure 2-3Showing the proximity of civic services, view and vistas from site. (Google, 2020)
2.3 City Profile 2.3.1 Introduction Siliguri is signified by four T’s – Tea, Timber, Transport and Tourism. It is of the most rapidly developing metropolises of state. World famous Darjeeling tea grows within 100 km radius around siliguri. Siliguri is popularly known as the gateway or chicken-neck of northeast India as its corridor establishes a connection between the rest of India and NE states. Situated 392 feet above MSL.
2.3.2 Location Siliguri is located in proximity of 3 international boarders Bangladesh, China and Nepal. Located at 26.710 N and 88.30 E in the foothills of Himalaya. (Siliguri - wikipedia, 2020)
2.3.3 Connectivity a) Road It is connected to Kolkata by NH-31 and to the other cities of WB, Assam and Bihar state by road; it lies on Asian Highway 2. The Royal Government of Bhutan also operates buses from its border town Phuentsholing to Siliguri. Air-conditioned sleeper coaches from Kolkata, Patna and Assam is also available. b) Rail Has 3 railway stations Siliguri Town, Siliguri Junction and New Jalpaiguri. Siiliguri town is oldest and opened in 1880 during British Raj. Siliguri Jn was opened in 1949 and is only junction in India with all three gauges (broad, meter and narrow) used in India. Bagdogra and Naxalbari are also in this agglomeration. c) Air Nearest airport is Bagdogra International Airport about 15 km away is the only airport in the region.
2.3.4 Topography and Geology The North part of WB is mostly made up of glacial and fluvio-glacial deposits of Quaternary period, while South consists of Pleistocene to flood plain deposits. Siliguri occupy an Urban area of 117.54 km2 and metropolitan area of 2222.59 km2 (SJDA) (Siliguri - wikipedia, 2020). It is located in Terai (foothills) of Himalaya. Teesta, Jaldhaka, Rangit and Mahananda together with their tributaries, drain Siliguri.
2.3.5 Climate Siliguri has humid subtropical climate i.e. it has hot, humid summers and generally mild winters. As it lies in foothills of Himalayas, it is cooler than the Southern WB. Average temperature in summer rarely increases more than 350 C. hottest months are from May to mid-June with average temp of 280 C. Cold months are December to February where temp varies between 30C to 150C. Form mid-December to mid-January temp drops to 8-100C. Winters are foggy with light rain which favours tea, timber and tourists. Rainfall – Monsoon starts from mid-June to September with large variations (ranging from 1800 mm to 4000 mm). Siliguri’s annual railfall is higher than WB average. Intense Rains upto 200 mm/day in July and August has been recorded. Humidity – maximum RH in Siliguri ranges from 47-53% and minimum RH 29-31%. It is higher in May to mid-June. Wind – The city experiences winds predominantly from the east and the NE directions. (Siliguri - wikipedia, 2020)
2.3.6 Water A) Surface water Siliguri is situated on the banks of River Mahananda and River Balason. Their confluence is located at SW border of city. Mahananda river is main source of water. To the East, 25 km away stands the Gajol Doba reservoir, which was formed by the first Teesta Barrage. B) Ground Water It is the second major source of water for the city. With a spurt in the city’s population, this resource is exploited. But there is arsenic contamination in ground water and is


