
1 minute read
Environmental Strategy
35% of the energy used in Indian buildings are used on heating and cooling the internal environment. Hence it is vital that the environmental design considers the passive elements which can be harnessed to allow for a more sustainable and economically viable design.
ENVIRONMENTAL DESIGN CONSIDERATIONS:
Advertisement
• Wind exposure maximised by large openings on eastern to western walls to capture west prevailing winds •Internal airflow is maximised using the polycarbonate stack chimneys. Small vents on the top of the connectors create a pressure difference which allows for air movement. •Concrete barge on water creates a heatsink affect which cools the internal air by encouraging hot air to move towards the colder liquid •1m overhangs were provided on land and water interventions to ensure sufficient shading whilst allowing for light to enter. • Lightweight metal structure ensures thermal mass is kept relatively low •PV panels, hydro wheel and bio fuel used to generate electricity for buildings
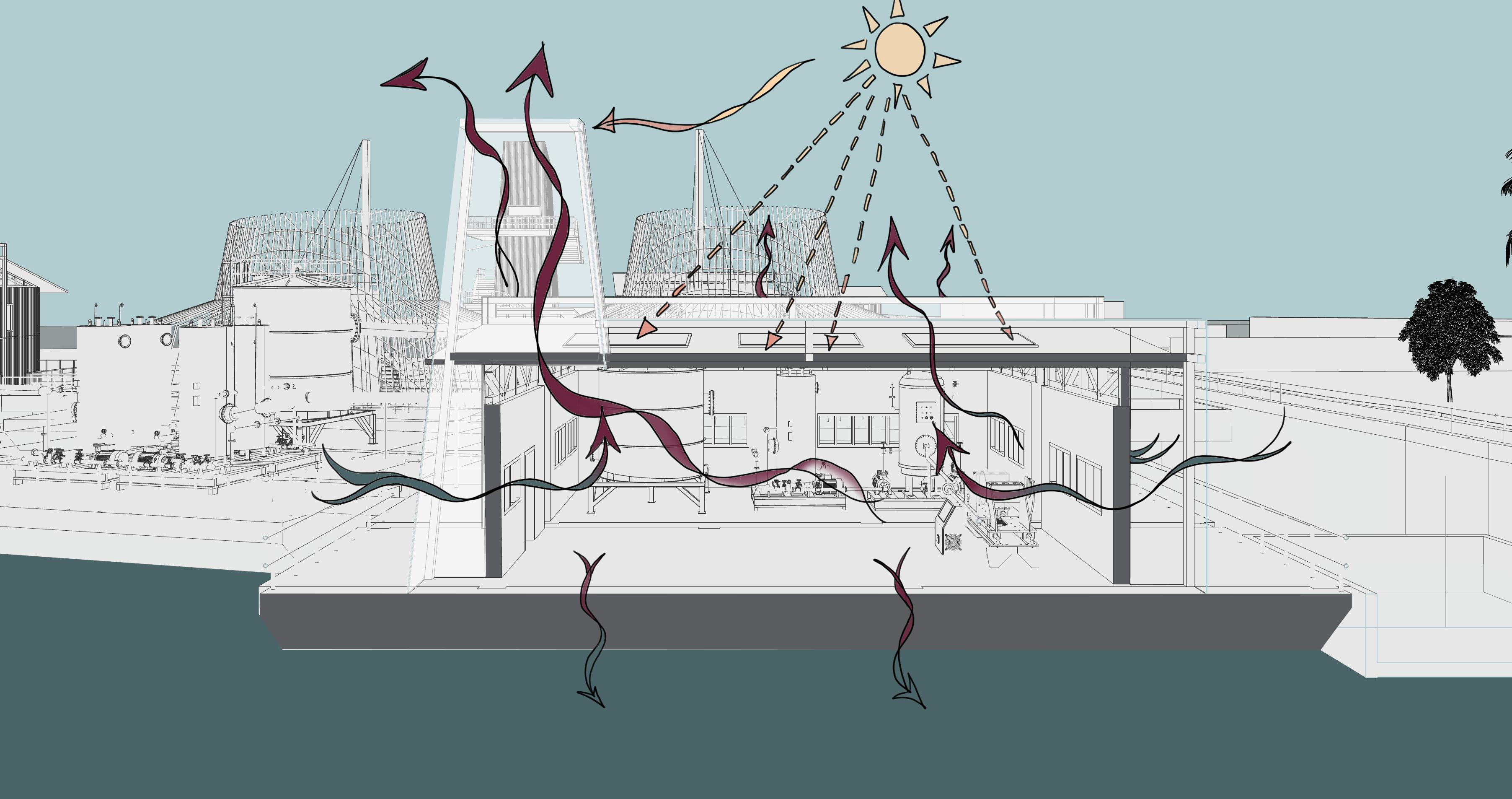
SUN-PATH THROUGHOUT THE DAY A basic sun path with shadows and lighting is highlighted bellow to show the cooling and shading elements of the design which were considered to allow for a comfortable thermal environment
















