1 minute read
Porter's Five Forces
• Developed by Harvard Business School Professor Michael Porter, Porter's Five Forces is a framework that determines how profitable an industry could be for its players and where and how within it a company might have room to compete. Note that Porter's Five Forces is only a starting point for analysis - consultants would need to evaluate the company itself to make substantiated claims about its competitiveness.
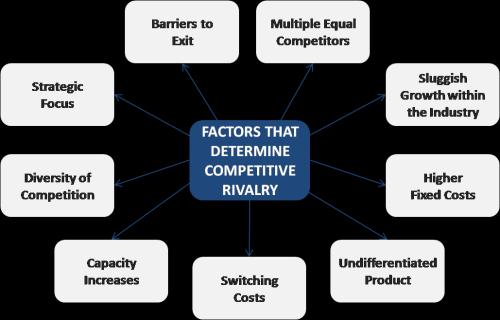
• At the centre of Porter's Five Forces is rivalry between companies. The other forces help to determine the intensity of the competition. These are divided into two "vertical forces" from other levels of the business worldthe bargaining power of suppliers and the bargaining power of buyers -and two horizontal forces from the same level of the business world - the threat of new entrants and the threat of substitute offerings. An industry where the five forces drive down overall profitability would be deemed "unattractive".
Advertisement
• Porter also added a long list of factors that affect the strength of each force to be considered when applying the model. For example, when evaluating the likelihood of new entrants consultants should consider, among other factors, economics of scale, government policy, capital requirements and importance of brand identity.
Porter's Five Forces is a framework for analyzing a company's competitive environment. The number and power of a company's competitive rivals, potential new market entrants, suppliers, customers, and substitute products influence a company's profitability.
What is Porters Five Forces?
The framework draws from industrial organization economics to derive five forces that determine the competitive intensity and, therefore, the attractiveness (or lack of it) of an industry in terms of its profitability. An "unattractive" industry is one in which the effect of these five forces reduces overall profitability.