
Multiple Choice Questions
1. The predicate term of the conclusion in a standard form categorical syllogism is called the
A. major premise.
B. minor term.
C. middle premise.
D. major term.
Subject area: 6.1 Standard Form, Mood, and Figure
2. Which of the following is not required in order for a categorical syllogism to be in standard form?
A. The premises and the conclusion are true.
B. The first premise contains the major term.
C. The second premise contains the minor term.
D. The conclusion is stated last.
Subject area: 6.1 Standard Form, Mood, and Figure
3. The mood of a standard-form categorical syllogism whose major premise is universal affirmative, minor premise is particular affirmative, and conclusion is particular affirmative would be
A. IAI.
B. IIA.
C. AII.
D. III.
Subject area: 6.1 Standard Form, Mood, and Figure
4. The figure of a standard-form categorical syllogism whose middle term is the subject term of the major premise and subject term of the minor premise would be
A. 1.
B. 2.
C. 3.
D. 4.
Subject area: 6.1 Standard Form, Mood, and Figure
5. The form of a categorical syllogism is completely specified by
A. its mood.
B. its figure and mood.
C. its figure.
D. its mood, figure, and validity.
Subject area: 6.1 Standard Form, Mood, and Figure
6. Which of the following categorical syllogisms is in standard form?
A. All dogs are mammals.
Cats are not dogs.
So, no cats are mammals.
B. All dogs are mammals.
No fish are mammals.
So, no dogs are fish.
C. Some mammals are small. No whales are small.
So, no whales are mammals.
D. No whales are mammals.
Some whales are fish.
So, some fish are not mammals.
Subject area: 6.1 Standard Form, Mood, and Figure
Chapter 06 - Categorical Logic: Syllogisms
7. Identify the mood and figure of this standard-form categorical syllogism:
Some turncoats are not confederate soldiers.
No confederate soldiers are abolitionists.
So, some turncoats are abolitionists.
A. OEI-4
B. OEI-1
C. IEO-1
D. IAO-4
Subject area: 6.1 Standard Form, Mood, and Figure
8. Identify the mood and figure of this standard-form categorical syllogism:
All excellent teachers are people who care about students.
All University 101 instructors are people who care about students.
So, all University 101 instructors are excellent teachers.
A. AAA-3
B. AAA-2
C. EEE-2
D. EEE-3
Subject area: 6.1 Standard Form, Mood, and Figure
Chapter 06 - Categorical Logic: Syllogisms
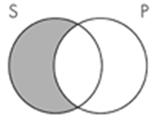
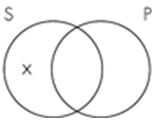
9. The Venn diagram representation of "All sailors are pirates" is which of the following?
A.

B.
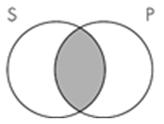
C.

D.
Subject area: 6.2 Venn Diagrams and Categorical Statements
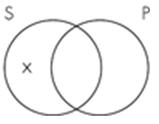
10. The Venn diagram representation of "No sailors are pirates" is which of the following? A. B.
C.

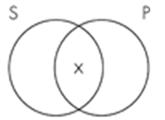
D.
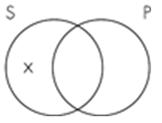
Subject area: 6.2 Venn Diagrams and Categorical Statements
Chapter 06 - Categorical Logic: Syllogisms
11. The Venn diagram representation of "Some sailors are pirates" is which of the following?
A.

B.
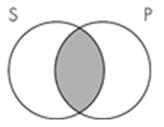
C.

D.
Subject area: 6.2 Venn Diagrams and Categorical Statements
12. The Venn diagram representation of "Some sailors are not pirates" is which of the following?
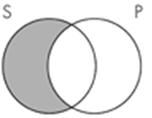
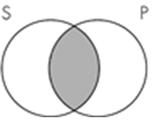
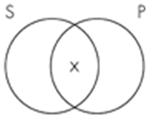

Subject area: 6.2 Venn Diagrams and Categorical Statements
Chapter 06 - Categorical Logic: Syllogisms
13. Identify the Venn diagram representation of the following syllogism:
All minerals are rocks.
All diamonds are rocks.
So, all minerals are diamonds.
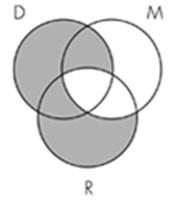
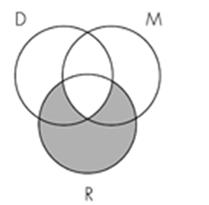
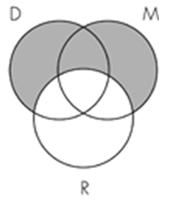
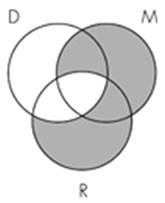
Subject area: 6.3 Venn Diagrams and Categorical Syllogisms
14. Identify the Venn diagram representation of the following syllogism:
Some ultraviolet radiation is not harmful to humans.
All ultraviolet radiation is a carcinogen.
So, some carcinogens are not harmful to humans.
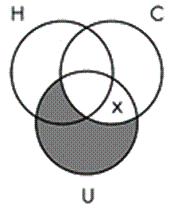
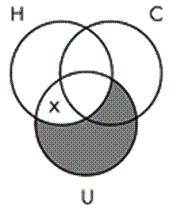
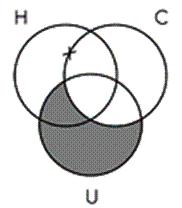
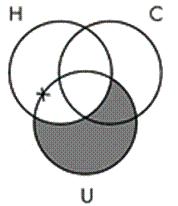
Chapter 06 - Categorical Logic: Syllogisms
15. Identify the Venn diagram representation of the following syllogism:
Some violinists are percussionists.
Some trombonists are percussionists.
So, some trombonists are violinists. A. B. C.
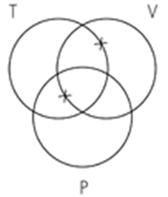
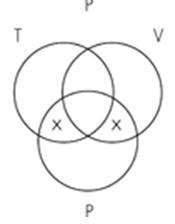
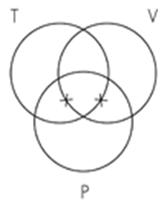
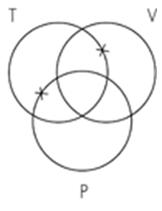
Subject area: 6.3 Venn Diagrams and Categorical Syllogisms
16. A categorical statement has existential import if and only if
A. it is a particular statement.
B. it implies that one of its terms denotes a nonempty class.
C. it implies that its subject term denotes a nonempty class.
D. it has importance for the nature of human existence.
Subject area: 6.4 The Modern Square of Opposition
Chapter 06 - Categorical Logic: Syllogisms
17. Which of the following relations on the Square of Opposition is valid, according to modern categorical logic?
A. contradictories
B. subcontraries
C. subalterns/subalternation
D. contraries
Subject area: 6.4 The Modern Square of Opposition
18. Which of the following immediate inferences is invalid according to modern categorical logic?
A. conversion
B. obversion
C. contraposition
D. contraposition by limitation
Subject area: The Modern Square of Opposition
19. An enthymeme is an argument that
A. is found to be valid when tested with a Venn diagram.
B. has missing or unstated steps.
C. is a standard form categorical syllogism.
D. has the mood and figure AAA-1.
Subject area: 6.5 Enthymemes
20. When supplying unstated steps, the principles of fairness and charity require that we
A. make the invalidity of the argument more apparent.
B. add only true (or at least plausible) steps.
C. supply premises that would improve the argument.
D. not make any critical remarks.
Subject area: 6.5 Enthymemes
Chapter 06 - Categorical Logic: Syllogisms
21. Which of the following is not a feature of standard-form sorites?
A. Each statement in the argument is a standard-form categorical statement.
B. Each premise (except the first) has a term in common with the immediately preceding premise.
C. The predicate term of the conclusion occurs in the last premise.
D. Each term appears twice once in each of two different statements.
Subject area: 6.6 Sorites and Removing Term-Complements
22. A sorites is
A. a chain of syllogisms in which the final conclusion is stated but the subconclusions are unstated.
B. an argument with an unstated premise or an unstated conclusion.
C. an argument comprised entirely of categorical statements.
D. a chain of inferences moving from the particular to the general.
Subject area: 6.6 Sorites and Removing Term-Complements
23. When removing term-complements, which of the following is not a permissible change?
A. changing "No S are P" to "No P are S"
B. changing "All S are P" to "Some P are S"
C. changing "Some S are not P" to "Some non-P are not non-S"
D. changing "Some S are P" to "Some S are not non-P"
Subject area: 6.6 Sorites and Removing Term-Complements
24. When removing term-complements, which of the following is a permissible change?
A. changing "Some S are P" to "Some non-P are non-S"
B. changing "All S are P" to "Some P are S"
C. changing "Some S are not P" to "Some non-P are not non-S"
D. changing "No S are P" to "Some S are not P"
Subject area: 6.6 Sorites and Removing Term-Complements
Chapter 06 - Categorical Logic: Syllogisms
25. A term is distributed in a statement when
A. it occurs in the subject position.
B. it occurs in the predicate position.
C. the statement says something about every member of its class.
D. the statement denies something about its class.
Subject area: 6.7 Rules for Evaluating Syllogisms
26. A fallacy of the undistributed middle is a violation of which of the following rules for evaluating categorical syllogisms? In a valid standard-form categorical syllogism¼
A. there are exactly three terms, and each term must be used with the same meaning throughout the argument.
B. the middle term is distributed in at least one premise.
C. a term must be distributed in the premises if it is distributed in the conclusion.
D. if the conclusion is particular, then at least one of the premises must be particular.
Subject area: 6.7 Rules for Evaluating Syllogisms
27. A fallacy of illicit minor is a violation of which of the following rules for evaluating categorical syllogisms? In a valid standard-form categorical syllogism¼
A. there are exactly three terms, and each term must be used with the same meaning throughout the argument.
B. the middle term is distributed in at least one premise.
C. a term must be distributed in the premises if it is distributed in the conclusion.
D. if the conclusion is particular, then at least one of the premises must be particular.
Subject area: 6.7 Rules for Evaluating Syllogisms
Chapter 06 - Categorical Logic: Syllogisms
28. Which fallacy is committed by the following categorical syllogism?
All cats are soft and furry animals.
Some amphibians are not soft and furry animals.
So, no cats are amphibians.
A. fallacy of the undistributed middle
B. fallacy of the illicit middle
C. fallacy of the illicit major
D. fallacy of the illicit minor
Subject area: 6.7 Rules for Evaluating Syllogisms
True / False Questions
29. The predicate term of the conclusion is the major term of a standard form categorical syllogism.
TRUE
Subject area: 6.1 Standard Form, Mood, and Figure
30. The term that occurs once in each premise is called the bridge term.
FALSE
Subject area: 6.1 Standard Form, Mood, and Figure
31. The minor term is the subject term of the conclusion.
TRUE
Subject area: 6.1 Standard Form, Mood, and Figure
Chapter 06 - Categorical Logic: Syllogisms
32. In a standard-form categorical syllogism, the minor premise always comes first.
FALSE
Subject area: 6.1 Standard Form, Mood, and Figure
33. In a standard-form categorical syllogism, the conclusion always comes last.
TRUE
34. The figure of a standard-form categorical syllogism indicates the position of the middle term.
TRUE
Subject area: 6.1 Standard Form, Mood, and Figure
35. The mood of a standard-form categorical syllogism is an indicator of the position of the middle term in the premises.
FALSE
Subject area: 6.1 Standard Form, Mood, and Figure
36. Two different categorical syllogisms cannot have the same mood and figure.
FALSE
Subject area: 6.1 Standard Form, Mood, and Figure
37. The form of a categorical syllogism is completely specified by its mood and figure.
TRUE
Subject area: 6.1 Standard Form, Mood, and Figure
Chapter 06 - Categorical Logic: Syllogisms
38. To show that an area of a Venn diagram is empty, we use an "x" in that area.
FALSE
Subject area: 6.2 Venn Diagrams and Categorical Statements
39. When an area of a Venn diagram is shaded, it indicates that there is at least one thing in that area.
FALSE
Subject area: 6.2 Venn Diagrams and Categorical Statements
40. When a syllogism contains both a universal and a particular premise, you should always diagram the universal first.
TRUE
Subject area: 6.3 Venn Diagrams and Categorical Syllogisms
41. A categorical statement has existential import when (and only when) it implies that its subject terms only denote classes that have at least one member (i.e., are nonempty).
TRUE
Subject area: 6.4 The Modern Square of Opposition
42. Aristotelian and modern logicians agree that universal categorical statements have existential import.
FALSE
Subject area: 6.4 The Modern Square of Opposition
